-
CENTRES
Progammes & Centres
Location

WEEK IN REVIEW
Ø ENERGY: Indian Agriculture: From Source to Sink of Energy?
Ø ENERGY: India & Pakistan: Energy Cooperation with Love!
DATA INSIGHT
Ø Natural Gas Scenario in India: Who Consumes How much
NEWS HEADLINES AT A GLANCE
INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENTS
· Sesa Sterlite puts capex focus on oil, gas
· RIL to seek injunction against KG-D6 auction
· Cairn India Q4 net up 18 pc on Rajasthan output
· MRPL plans $1.4 bn expansion as margins set to rise
· RIL raises $550 mn from Japanese banks
· RIL, ONGC lock horns over gas transport from KG-D6 block
· SJVNL signs pact with Bhutanese company for 600 MW hydel plant
· OPGC urges state to move Centre for coal block clearance
· General Electric, Westinghouse keen to develop 12 GW of nuclear power in India
· DVC plans to opt out of retail distribution to cut losses
· CERC issues power trading license to Parshavnath Power
· Kashagan oil restart not expected this year
· Premier makes oil, gas finds in Indonesia, Pakistan
· ExxonMobil starts up LNG production at PNG project
· Signs of new natural gas field found off Israel coast
· Suncor uses rail, new pipelines to drive profit to record
· Slovakia signs deal to deliver gas to Ukraine
· Kuwait signs LNG import deal with Qatargas
· Spain's Acciona wins contract to build power plant in Mexico
POLICY & PRICE
· RIL asks Oil Ministry to announce new gas price on May 13
· Gas price revision will help augment availability: EY
· Govt's ethanol fuel blending plan falls short of target
· India to see a big rise in power demand this year
· CIL invites bids for 3rd phase of drilling mines in Mozambique
· PNGRB again extends date for CGD bidding
· No power tariff hike in Odisha for 2014-15
· No coal supply to projects failings to meet commercial output deadline: Power Ministry
· Kazakhstan offers India opportunity to explore Caspian Abai oil block
· Mexico parties enter final phase of oil bill discussions
· Ukraine crisis played 'elevated' role in recent LNG approval: US
· Japan starts releasing monthly spot LNG prices
· US crude inventories climb to highest level in 83 yrs
· China-Bangladesh MoU to set up 1.3 GW power plant
· ADB funds Pakistan power policy
· IDB provides $20 mn loan for rural electrification program in Panama
· India’s indecision keeps Bhutan’s 540 MW Amochu project under uncertainty
· Assess water diversion to thermal plants: Greenpeace to Maharashtra
· Gamesa Wind Turbines bags another 100 MW project from Greenko
· Suzlon bags 370 MW orders in first three months of 2014
· GE invests $24 mn in Welspun's MP solar plant
· French energy minister promises 100k green jobs
· SunPower and Google form $250 mn solar lease program
· China’s polysilicon makers double in 2013 as price increases
· Marubeni completes Japans’ largest solar-power station in Oita
· UK awards guaranteed power price contracts to Drax, Dong
· Yingli expects debt pressure to ease as solar shipments increase
WEEK IN REVIEW
ENERGY
Indian Agriculture: From Source to Sink of Energy?
Lydia Powell, Observer Research Foundation
|
I |
ndia began thinking about energy almost a decade before the oil crisis as it saw energy as the primary input for nation building. The Committee on Power & Energy in 1965 set up by the Prime Minister of India mapped energy resources of India and offered suggestions on how they may be utilized. The Fuel Policy Committee Report in 1975, the Report of the Working Group on Energy Policy set up by the Planning Commission in 1979, the Report of the Advisory Board on Energy set up in 1985 as well as Research Reports by the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) in 1985 provided data and recommendations broadly on the same lines. A striking feature in all the reports was that they offered elaborate projections for wood fuel / biomass demand in the future and predicted a supply-demand gap. A 1987 study found that 3-4 million people were ‘head-loading’ or collecting fuel-wood / biomass waste and carrying it on their head to the nearest market which made it the largest source of employment in the energy sector. Unfortunately the future did not turn out as an extrapolation of the past.
The anticipated demand-supply gap for wood fuel did not materialise and an important but unexpected shift that did materialise went unnoticed. The agriculture sector which was the primary source of energy accounting for roughly half of energy use in India was turning into a major sink for energy. However this was not a phenomenon that was ‘made in India’. Input heavy agriculture, more favourably referred to as the ‘green revolution’, was one of the major exports of western nations into poorer nations in the 1960s and 70s.
As per estimates quoted in a 1977 paper by the late energy veteran Amulya Reddy, an energy input of about 5-10 calories was required to obtain 1 calorie of food in the United States while an equivalent farmer in South Asia was able to obtain 50 calories of food with an input of just 1 calorie of external energy in the 1950s. Reddy estimated that if India’s 410 million acres of arable land consumed energy at the same rate, over 70% of India’s total energy consumption would have to be dedicated to agriculture. While the South Asian and Indian farmer derived most of the energy from human or animal sources, a farmer in the United States derived most of the energy from fossil fuels which meant that he had, under his command, almost 100 times the energy an equivalent farmer had in India.
Today the West is more likely to import the sustainability story of that poor Indian farmer highlighting his ‘organic farming’ techniques, but in those days he was seen to be ignorant of new knowledge and placed in the bottom rung of the competitive hierarchy. Knowledge of fertilisers derived from fossil fuels and information on irrigation practices using electrical energy was exported to him to make him more efficient and productive. In 1961-62 India was using about 2 Kg of nitrogen based fertiliser per hectare of arable land compared to 38 Kg for USA and 456 Kg for the Netherlands.[1] One additional tonne of fertiliser could generate roughly 12 tonnes of rice. In other words, $1 investment in fertiliser had the capacity to yield $ 3 worth of agricultural production which made increase in fertiliser use in India a very attractive proposition. The production and sale of fertilisers in India offered an even more attractive proposition. The price of one tonne of ammonium sulphate was $ 376 in India compared to $ 240 in Thailand and $ 278 in Japan. Understandably American oil and petrochemical companies such as Bechtel and American International (subsidiary of Standard Oil) lobbied hard to get into India. As a result, Madras Fertilisers was set up in 1966 with 49% American ownership but this was only after an acrimonious debate that closely resembled the current debate on FDI in retail. The rest as they is history.
Today India’s fertiliser consumption per hectare is about a 100 times what it was in the early 60s and most of it is nitrogenous (N) in composition. Commercial fertilizer production is a very energy-intense process. About 74% of total energy used to produce fertilizers comes from natural gas. During the last decades, N fertilizer prices have closely tracked energy prices, with 1 tonne of urea (46% N) costing about 40 times as much as 1 GJ of natural gas. During 2002–2007, India accounted for 73% of the production of nitrogen and 89% of phosphorous (P). Production in India alone of both N and P is three times the production in all Latin America and more than 100 times the production in all sub-Saharan Africa. India is today the second / third largest fertiliser consumer in the world after China and the USA accounting for roughly 12% of global fertiliser consumption.
The other energy intensive input going into Indian agriculture is pumped water. As the renowned water expert Tushar Shah has pointed out in many of his recent writings, rainfall and soil moisture management accounted for 70% of irrigation by Indian farmers until 1830. Between 1830-1970 water from tanks, canals and rivers accounted for most of the irrigation but from 1970 pumped ground water is the primary source of irrigation in India. Today India is the largest user of ground water in the world with a consumption of 250 cubic kilometres a year (cu km/year) with USA a distant second with about 100 cu km/year. According to Tushar Shah there are over 20 million tube wells in India and about 800,000 more are added every year. Farmers who do not have tube wells depend on ground water markets. In western and south western regions of India electricity is the primary energy source for pumping water while in other parts diesel accounts for most of the energy used for pumping. Even though the cost of pumping with electricity has been held steady, the cost of pumping with diesel has increased by a staggering 7-8 times between the early 1990s and late 2000s. In the same period, the farm-gate price of grain increased by less than 1.5-2 times.
Studies by Mukesh Anand, an economist at NIPFP show that the rupee input of fossil fuel per rupee of farming output 0.5% in 1998-1999 but has grown to 0.98% in 2007-2008. His study also showed that a 10% increase in price of fuel could increase average cost of cultivation by about 0.56%. What is more interesting is that the final consumption of energy in kilograms of oil equivalent per ` 1000 of GDP is declining for the aggregate economy but it is rising for the agriculture. It has reduced to 50% of its level in 1990-1991 for the economy but for the agriculture sector, it has doubled. As farm output prices are controlled, the price of energy inputs becomes very important. Agriculture as a sink for energy rather than a source of energy is not something that we have seriously thought about. If we keep converting our food and water problems into energy problems, Amulya Reddy’s nightmare may come true.
Views are those of the author
Author can be contacted at [email protected]
ENERGY
India & Pakistan: Energy Cooperation with Love!
Ashish Gupta, Observer Research Foundation
|
I |
n the height of the election wave in the country, most of the political parties were promoting their party stand on the basis of secularism. There is no certainty that these political parties have really understood the true concept of ‘secularism’. However one thing is certain. The concept of ‘secularism’ in terms of energy security in the context of geopolitics is surely not understood by the political leadership. That is why most of the issues are still unresolved with our neighbours, especially Pakistan. India must understand that keeping Pakistan in the loop is beneficial for us both in terms of economic as well as energy security. How can we strategise and plan that loop so that it encompasses the neighbourhood? Energy cooperation is the way forward!
The gigantic task for the new government taking oath in the month of June, 2014 will be on how to fix the problem with Pakistan. The notion of ‘self-reliance’ in terms of energy security is not going to work for India because imports of energy resources are becoming a necessity rather a choice. Self dependency must be complemented with harmonious relationship with the neighbours!
Given the increasing energy demand, India must try to resolve the issue in a tactful manner because a single wrong move can be devastating for India, while a positive move will take India one more step towards energy prosperity. There is another genuine concern that any good initiative between the national governments will be jeopardised by terrorist organisations. Indeed that is an issue! But in this context one just has to take leaf of the book of China – Japan relationship. The political relationship between China and Japan which is as acrimonious as that between India and Pakistan has been transformed due to economic trade activities which have risen to US $ 334 Billion. Now they dare not touch each other because of the financial stakes are high. They do not like each other but still they need each other! The same kind of approach is required while dealing with Pakistan.
As a new government takes office, a new approach is the need of the hour. Though many initiatives have been taken by the Indian government, they have failed in leading to a positive conclusion because of misunderstandings. A fresh look is required to understand why we have failed in our attempts. Starting from Independence, we have been trying to fix problems on paper by signing various treaties where the emphasis is more towards questionable security benefits rather than economic benefits. Take the case of Indus Water Treaty, 1960 which is an engineering solution attached to a security concern or the Iran-Pakistan-India (IPI) pipeline Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India (TAPI) Natural Gas Pipeline, which is again engineering solution with security concern. This is why these seemingly genuine steps do not take off. We have limited our approach to the engineering concept on account of great suspicion. Apart from that we have literally failed to bank on our strengths i.e. coal and small civil nuclear power reactor exports and our expertise in the power sector.
Having said that, IPI/TAPI Pipeline (dialogue started in 1990) which would have been concluded by now is simply continuing on paper and we are still not clear when the pipelines will come on-stream. In the midst of this extended drama, China gained as Central Asian gas is flowing into China! The Myanmar-Bangladesh-India pipeline has not materialised even after signing a deal with Myanmar in 2006. Here again China became the beneficiary. It is not that India has to win every time, but should it lose every time? This does not mean that India looks towards Pakistan in desperation but working with neighbours is surely in the interest of our broad vision of achieving energy security. By taking these pipelines to their logical conclusion, India can a play a part of being an importer as well as exporter of gas and Pakistan and Afghanistan would gain by getting substantial sum as transit fee. Indian companies too can benefit by exporting refined petroleum products to Pakistan as India has excess refining capacity to fulfil the entire demand of Pakistan.
Pakistan is currently struggling with power issues as most parts are facing huge power cuts. The recent incident of gas supply to Prime Minister Secretariat being cut off shows the vulnerability of Pakistan in terms of energy security. In this context India can make significant gains in energy diplomacy by exporting coal to their thermal power plants. The question which will be asked immediately is why we should export coal or for that matter even electricity when we have a shortage but few tonnes of coal or a few kilowatts of electricity is not a high price to pay for regional peace and security. There could be a co-benefit of a marginal reduction of current account deficit.
Delhi electricity privatisation models is already seen as a role model in Pakistan and therefore we are in a good position for providing consulting service to many of the electricity utilities in Pakistan who are looking towards privatisation. The Karachi Electricity Supply Company is a very interesting example in this context in which the ownership of the company changed many times but it is still unable to revive itself. India’s State and private distribution companies can be a role model to Pakistani distribution utilities. This will not only bring diplomatic benefits but also open an additional source of revenue for distressed utilities. Even in the construction of power plants, companies like Bharat Heavy Electrical Limited and L&T can take a major share of business which is currently going to Chinese companies. These activities will become a game changer for India. Apart from political will, a proper framework is required so that our companies do not suffer undue losses. There is no doubt in commercial relationships that depend on mutual good will and trust, mutual harm is unlikely. The economic stakes are too high!
Views are those of the author
Author can be contacted at [email protected]
DATA INSIGHT
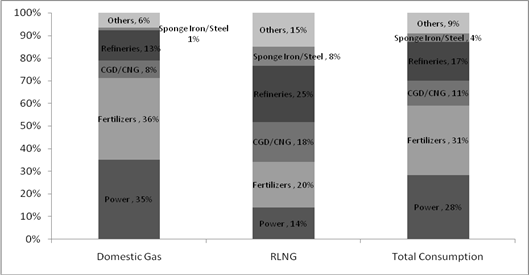
Natural Gas Scenario in India: Who Consumes How much
Akhilesh Sati, Observer Research Foundation
MMSCMD
|
Sectors |
Domestic Gas |
RLNG |
Total Consumption (upto January 2013) |
|
Power |
30.36 |
5.8 |
36.2 |
|
Fertilizers |
31.02 |
8.37 |
39.4 |
|
CGD/CNG |
6.69 |
7.28 |
14 |
|
Refineries* |
11.59 |
10.36 |
22 |
|
Sponge Iron/Steel |
1.11 |
3.49 |
4.6 |
|
Others |
5.56 |
6.19 |
11.8 |
|
Total Supply |
86.33 |
41.49 |
127.8 |
Sectors’ share in Domestic and Imported Gas Consumption
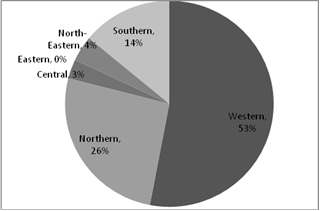
Regional Gas Markets and their Share
* includes sectors Petrochemicals and also Shrinkage for liquid extraction- LPG.
Source: Report “Vision 2030: Natural Gas Infrastructure in India” by Industry Group for PNGRB.
NEWS BRIEF
NATIONAL
OIL & GAS
Upstream
Sesa Sterlite puts capex focus on oil, gas
April 29, 2014. Vedanta Resources Plc.’s Indian unit Sesa Sterlite Ltd is set to spend more on its oil and gas business where it sees a potential for growth and less on metals and mining where most expansions are complete, the firm said. Sesa Sterlite said capital expenditure in oil and gas will be largely driven around field interventions in Rajasthan which are crucial for growth of the commodities and oil company. Sesa Sterlite has a 58.8% stake in oil company Cairn India Ltd and is investing $2.4 billion over three years to mainly go into enhanced oil recovery of the Mangala field and development of Barmer Hill north and South, a new field in Rajasthan. The erstwhile UK firm is eyeing a doubling of oil output from the current 200,000 barrels per day by 2017. The company achieved record productions of oil and gas in Rajasthan and mined and integrated metal at its zinc operations in Rajasthan. (www.livemint.com)
RIL to seek injunction against KG-D6 auction
April 26, 2014. Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) told the Supreme Court that it would seek an injunction from an arbitration panel against auction of five blocks in the KG D6 basin which it had relinquished under protest. Further, it said it would sue the government for damages and compensation for the delay if it won in arbitration proceedings. RIL counsel Harish Salve said RIL would not share its infrastructure if someone else gets those blocks in an auction. He said RIL has asked for a price of $6 per unit for gas from these blocks but the government turned down the request and instead asked it to relinquish the blocks. A three-judge bench, comprising Justices BS Chauhan, Jasti Chelameswar and Kurian Joseph, is hearing twin petitions by CPI leader Gurudas Dasgupta and NGO Common Cause seeking to have the Production Sharing Contract (PSC) scrapped on the ground that the contractor had failed to abide by its commitment under it. RIL has initiated arbitration proceedings after the government refused to allow it to recover some of its costs on the ground that it had failed to abide by commitments. While both RIL and the government has appointed arbitrators, both former chief justices of the Supreme Court, arbitration proceedings have not commenced as the two sides could not agree on a third arbitrator.
In a separate proceeding, the Supreme Court had appointed a third arbitrator but the court later called back its decision as the person was on a list of possible arbitrators listed by RIL. The court now has to find a replacement. In the court proceedings, Salve dared the top court to strike down the PSC on the ground that it was against public policy. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Cairn India Q4 net up 18 pc on Rajasthan output
April 23, 2014. Higher production from the Barmer oilfields in Rajasthan helped Cairn India report an 18 per cent jump in net profit to ₹ 3,035 crore in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2014 from ₹ 2,564 crore in the same quarter of the previous fiscal year. For the full year, the company posted a 3 per cent increase in net profit, at ₹12,432 crore, against ₹12,056 crore in the previous year. It paid a dividend of ₹6.50 a share for the fiscal year. The block has met its projected target of 200 million barrels since production started in August 29, 2009.
Cairn said that it is considering more potential in the Rajasthan asset. The company said that it would continue to focus on key development projects to enhance recovery, with a planned overall net capex of $3 billion by fiscal year 2017. Cairn aims to achieve a reserve replacement ratio of 150 per cent in the next three years, subject to the extension of the production sharing contract of the block till 2030. Cairn’s revenues for the fourth quarter of 2014, after profit sharing with the Government and the royalty expense in the Rajasthan block, were ₹5,049 crore, up 1 per cent quarter-on-quarter.
During the quarter, the Government earned profit petroleum of ₹ 1,201 crore and royalty of ₹ 1,097 crore from the Rajasthan block, and profit petroleum of ₹ 107 crore from other blocks. The average crude price realisation Cairn earned from the block during fiscal year 2014 was $95.2/barrel, at an 11.5 per cent discount to Brent. The average price at which Indian refiners sourced crude from the international market during the last fiscal year was $105.52 a barrel. (www.thehindubusinessline.com)
MRPL plans $1.4 bn expansion as margins set to rise
April 29, 2014. Mangalore Refinery & Petrochemicals Ltd. (MRPL) plans to spend $1.4 billion to expand crude processing at its facility in western India to meet growing fuel demand in Asia’s third-largest economy. Mangalore Refinery, a unit of India’s biggest state-run explorer Oil & Natural Gas Corp., will raise capacity by 40 percent to 420,000 barrels a day by end-March 2018. MRPL is planning the expansion after spending $300 million on a 60,000 barrel-a-day delayed coker that started earlier this month and $330 million for a 44,000 barrel-a-day fluidized catalytic cracker that will begin next month. The facilities allow the company to process cheaper, heavier crudes into high-value products like diesel, liquefied petroleum gas and propylene. Refiners including Indian Oil Corp., the nation’s biggest, are expanding capacity to meet rising domestic demand, which the oil ministry forecasts to grow by more than 21 percent in the four years to March 2017 to about 186 million tons a year. MRPL is seeking to revive earnings after reporting losses in four of the past five quarters as the Indian rupee’s plunge to a record against the dollar drove up import costs. The company earned $2.42 for every barrel of crude it processed during April to December last year, compared with $2.60 a barrel a year earlier, it said. Margins at Mumbai-based Reliance Industries Ltd., operator of the world’s biggest refining complex, were $7.80 a barrel in the same period due to its ability to process cheaper grades into high-quality fuels it can sell to Europe and the U.S. (www.bloomberg.com)
HPCL to shut crude unit at Mumbai refinery
April 25, 2014. Hindustan Petroleum Corp Ltd (HPCL) will shut more than half of its crude processing capacity at its 130,000 barrels per day (bpd) Mumbai refinery for maintenance. The state-run refiner's Mumbai plant, in western India, has two crude units of 70,000 barrels per day (bpd) and 60,000 bpd. The Mumbai refinery processes about 22,000 tonne (about 161,000 barrels) per day (of oil). So in the 45 days shut down, crude processing will decline by about 55%. The secondary units will operate at lower levels during the shutdown, which will complete on June 10. HPCL also operates a 166,000 bpd refinery at Vizag, in southern India, and has a stake in HPCL-Mittal Energy Ltd, which operates a 180,000 bpd Bathinda refinery in northern India. (www.business-standard.com)
RIL raises $550 mn from Japanese banks
April 23, 2014. Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) said it has raised USD 550 million loan for part-funding expansion of its petrochemical plant and new gasification unit from Japanese banks. The 12-year loan will part finance the proposed expansion of RIL's petrochemical plants and setting up of new gasification unit and refinery off-gas cracker over the next 2-3 years. This is the first time that Japan International Bank for Cooperation (JBIC) is extending credit to RIL. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Transportation / Trade
RIL, ONGC lock horns over gas transport from KG-D6 block
April 24, 2014. Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) wants to transport gas from a new field in the KG-D6 block with a pipeline through ONGC's adjoining block, but the state-run firm is reluctant to allow this, giving another twist to their relationship a year after they agreed to look at prospects of sharing infrastructure in the deep-sea region. ONGC had earlier said that using RIL's infrastructure would speed up the development of its own field and cut costs by up to 40%, signaling bright prospects of cooperation between India's top two exploration firms. But ONGC subsequently complained to the government last year that the two adjoining blocks may have a common reservoir, from which Reliance could potentially draw gas. The latest turn in the relationship came, when Reliance was countering allegations that it had overspent and under-produced in the block, which led to a hefty penalty and an arbitration case. The company told the Supreme Court that vested interests were targeting it although the company had done the maximum exploration and produced gas quickly. In contrast, RIL said, there was no scrutiny of ONGC, which found gas in the same basin, raised its cost many times and produced nothing in 18 years. ONGC said that if RIL lays a pipeline across it block, it would obstruct exploration activity. ONGC's discovered gas fields are bordering the Reliance-operated D6 block in the Krishna-Godavari basin. Officials in the oil ministry, which controls ONGC, said the two operators could resolve the issue. The Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH) said laying pipeline through neighbouring blocks is a common international practice and ONGC and RIL are in dialogue with each other over this matter. ONGC will evaluate the proposal and take a view. RIL already has a control and riser platform required to collect gas produced from its D1, D3 and MA fields in the neighbouring block held by GSPC. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Policy / Performance
RIL asks Oil Ministry to announce new gas price on May 13
April 29, 2014. Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) has asked Oil Ministry to announce a new natural gas price immediately after polling ends on May 12, saying this was necessary to avoid irreparable loss to all parties, including the government. While a new formula for pricing of all domestically produced natural gas was notified on January 10 and published in Gazettee on January 17, the Election Commission asked the government to defer its implementation till general elections are completed. The new pricing formula, that almost doubles the price of natural gas to about $ 8.34 per million British thermal unit, was to be implemented from April 1 but following the directive of the poll watchdog, was put in abeyance till model code of conduct for elections is in place. RIL said the $ 4.205 per mmBtu price for gas from its eastern offshore KG-D6 field was valid for the first five years of production, which ended on March 31. But since the poll watchdog deferred implementation of the new pricing, the company continues to sell gas at old rate on "provisional basis". RIL has asked fertiliser companies, its sole consumers, to provide payment guarantees at new rate. Fertiliser companies have, however, refused to do so saying no new rate has so far been intimated. RIL said whenever the government notifies the gas price effective from April 1, it would recover the differential price from its customers. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
KG basin dispute: SC appoints ex-Australian judge as arbitrator
April 29, 2014. The Supreme Court (SC) appointed Michael Hudson McHugh, former judge of the High Court of Australia, as the third arbitrator to resolve the dispute between the Centre and Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) on KG basin. Justice S S Nijjar had passed an order on the issue of appointment of independent arbitrator as the Chairman of the Arbitral Tribunal whose two other members are former Chief Justices of India -- S P Bharucha and V N Khare. While RIL has nominated former Justice Bharucha as its arbitrator, the Centre chose Justice Khare as its nominee. The SC decided to appoint an international arbitrator as the Chairman for adjudication of dispute between RIL and the government over recovery of cost for developing the country's key natural gas field in KG basin. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
LS Polls 2014: People who cast vote will get ` 1 discount on petrol in Ahmedabad
April 29, 2014. In a bid to motivate people to vote, a group of city-based petrol pumps has announced an incentive to provide petrol cheaper by ` 1 per litre after verifying the indelible ink finger mark of every consumer. The scheme will be implemented for a day when polling will be held for 26 Lok Sabha seats in Gujarat. The federation is a group of 15 petrol pumps of Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) located in different parts of the city which fall in three Lok Sabha constituencies, including Ahmedabad east and west alongwith Gandhinagar. The federation has taken the decision to make people aware about voting and it does not relate to promotion of any political party. However, the rates of diesel or any other fuel will not be reduced. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
PNGRB again extends date for CGD bidding
April 28, 2014. Oil regulator PNGRB has once again extended the last date of bidding for licences to retail CNG and piped cooking gas in 14 cities, including Bengaluru and Pune, by two months to July 10. The Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) had invited bids for development of city gas distribution (CGD) networks in Eranakulam in Kerala; Rangareddy/Medak, Nalgonda and Khammam in Andhra Pradesh; Bengaluru rural and urban districts in Karnataka; Raigarh, Pune and Thane in Maharashtra; Daman; Dadar & Nagar Haveli; Shahjahanpur in UP; Guna in MP; Panipat in Haryana and Amritsar in Punjab. Bids were due on February 11 but the regulator in January extended the deadline to May 12. PNGRB further extended the deadline to July 10. Bidders have been asked to quote the tariff they will charge for the pipeline network to be laid in the city and the compression charge for dispensing CNG (compressed natural gas) over the 25 years. They have also been asked to quote the inch-kilometre of steel pipelines they will lay during first five years and the number of domestic consumers proposed to be connected by piped natural gas, according to the regulator. The cities offered for bidding include those that PNGRB had offered in the fourth CGD round in September 2010. The regulator had, however, cancelled the round in November 2011. In the fourth round, licences for Ernakulam in Kerala; Rangareddy/Medak, Nalgonda and Khammam in Andhra Pradesh; Alibag/Pen and Lonavala/Khapoli in Maharashtra; Guna in MP and Shahjahanpur in UP were offered. The current round is being called 4th round of CGD bidding, PNGRB said. PNGRB had invited bids for licences in 2009 for 13 cities in first two rounds. GAIL Gas Ltd walked away with four of the six cities offered in the round one. It won Sonepat in Haryana, Dewas in Madhya Pradesh, Meerut in UP and Kota in Rajasthan, while Bhagyanagar Gas Ltd got Kakinada in Andhra Pradesh and DSM Infratech Mathura in Uttar Pradesh. In round two, Indian Oil Corp-Adani Group combine walked away with Allahabad and Chandigarh, while Reliance Gas got Rajahmundry, Shahdol and Yanam in Andhra Pradesh. Jhansi went to Central UP Gas Ltd. The third round of bidding was opened in July 2010 and concluded in February 2011 (after extension), but final awards of most cities are yet to be made because of certain litigation involving PNGRB and a few other parties. City-based Jay Madhok Energy won rights to Jalandhar city, according to PNGRB. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Gas price revision will help augment availability: EY
April 25, 2014. The new natural gas policy that almost doubles the price of the fuel will lead to an increase in domestic production as it improves the commercial viability of marginal and deep-water fields, EY said in a report. In the report titled 'Natural Gas Pricing in India: Current Policy and Potential Impact,' EY said the current gas-pricing mechanism is complex and heterogeneous and not conducive for upstream players to realise commercial gains. This, coupled with rising demand for gas, has increased India's dependence on imported liquefied natural gas, making the country the world's fourth-largest importer of LNG. Since LNG procured through both long-term contracts and from the spot market is highly expensive, India is keen to reduce its dependence on imports. Higher production will help ease the supply crunch and reduce reliance on high-priced LNG, EY said. The government approved a new market-based pricing regime based on recommendations made by the Rangarajan committee. The policy, which was due to come into effect from April and has been put on hold due to the ongoing general elections, is expected to increase certainty and transparency in natural gas pricing in India. The new policy aims to enhance the commercial viability of gas fields, which would encourage investments in the upstream segment and increase production. It is also likely to boost the revenue of indigenous gas producers, incentivising them to invest more in the segment. The price of natural gas in India may almost double to $8.3 per million British thermal units when the Rangarajan formula is implemented. The government needs to effectively address concerns related to the increased price burden for consumers for the overall success of the policy. The policy will also increase gas availability for key consuming industries, including power and fertilisers, which may account for about 68 per cent of total demand in FY17. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Moily for raising prices of natural gas effective April 1
April 25, 2014. Oil minister Veerappa Moily wants natural gas prices to rise with effect from April 1, reversing the decision to deny retrospective increase in rates, as the government is concerned about the legal fallout of not abiding by a decision taken by the Cabinet. The ministry wanted new gas prices to be implemented from July 1. The Cabinet had approved the Rangarajan formula, which would almost double prices. The government notified the new formula that would have come into effect in April, but the Election Commission vetoed it. The oil industry has strongly objected to the decision of the poll authority. The Association of Oil and Gas Operators (AOGO) wrote to the chief election commission saying the industry was "disappointed" because the government's decision to implement new prices was taken much before the elections were announced. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
BJP working on rejig plan for gas pricing, exploration policy
April 24, 2014.The BJP's Energy Cell has settled down to unclutter policy for oil hunters, confident that the party will form the next government at the Centre. The initial contours of the cell's manual for a BJP-led government's oil minister indicate pressing the pause button on the 10th round of exploration block auctions, cleaning up grey areas in policy and contracts with a simple, transparent and well-regulated cost-recovery model and reworking gas pricing. The thinking is to fix gas pricing issue and resolve disputes with explorers quickly so that decision-making does not become hostage to controversy like it has happened in the wake of Reliance Industries Ltd's continued skirmish with the oil ministry under S Jaipal Reddy and M Veerappa Moily. The cell is also toying with the idea of different pricing regimes for various types of blocks — onland, shallow water and deep water. The gas pricing formula is to be tweaked for a price that would satisfy the power and fertilizer units without eliciting allegations of extending windfall benefit to producers. Undoubtedly, these ideas would be debated and examined in the government and industry in detail before being accepted as policy - if the BJP forms the government. Narendra Taneja, the cell's national convenor, declined to comment on its working except saying India's E&P sector was in a "big mess". Oil minister M Veerappa Moily launched the primer for 10th round of block auctions by showcasing 46 concessions. This was done in spite of an air of uncertainty created by contradictory recommendations from two panels under C Rangarajan and Vijay Kelkar. Rangarajan recommended switching from the present production-sharing regime to royalty-sharing model that is seen leaving little room for dispute or controversy over recovery of costs by operators like in the case of RIL's KG-D6 block. Kelkar endorsed the present regime, reflecting the opinion that royalty-sharing is not an attractive model for a low-prospectivity country like India. Gas pricing and the ministry's dispute with Reliance has hogged the election campaign. Arvind Kejriwal's Aam Aadmi Party and Left leader Gurudas Dasgupta have been going to town against the government'' move to double gas prices from April in line with a pricing regime suggested by the Rangarajan panel. (timesofindia.indiatimes.com)
India’s gas demand to jump 55 pc to 378 mmscmd by 2016-17
April 24, 2014. India’s natural gas demand is likely to jump by over 55% to 378 million standard cubic meters a day (mmscmd) by 2016-17 but its availability will be way short of the requirement. Natural gas demand is projected to rise from 242.66 mmscmd in 2012-13 to 378.06 mmscmd in 2016-17 and more than double to 516.97 mmscmd in 2021-22, according to a study commissioned by the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB). However, gas availability in the country will lag the demand. Domestic production of 101.1 mmscmd in 2012-13 will rise to 182 mmscmd by 2021-22 while import of liquified natural gas (LNG) is projected to jump from 44.6 mmscmd to 188 in 10 years. The total availability of gas in 2016-17 at 299.7 mmscmd will be way short of the demand. In 2021-22, the study said cross border pipeline may start flowing 30 mmscmd of fuel raising the total availability to 400 mmscmd, still short of the requirement. It said the country’s gas output can more than double to 211 mmscmd by 2026-27 on the back of desired policy support and correct pricing signals. The natural gas sector, it said, is at the threshold of rapid growth in India supported by ever increasing demand, increased exploration efforts, commissioning of LNG import terminals and the development of a nationwide natural gas pipeline grid. (www.livemint.com)
Govt's ethanol fuel blending plan falls short of target
April 23, 2014. The government's ambitious plan to blend petrol with 5% ethanol has fallen far short of target, creating problems for sugarmills, which supply the alcohol, and the chemical industry, which is complaining that there is a big shortage in the market. Against the requirement of 105 crore litre of ethanol for mandatory 5% blending with petrol, oil companies have contracted just 62 crore litre, half of which is yet to be lifted from depots. Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP) was launched to promote green fuel and reduce the oil import bill. The sugar industry has estimated that oil companies could have easily saved ` 370 crore on their oil import bill if they had blended the 62 crore litre supplied by sugarmills in the past year. While oil companies cite 'procedural delays' in lifting the ethanol offered by the supplier sugarmills, the latter is unable to regularise its ethanol production and supply due to the same. The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs in November last year mandated 5% ethanol blending in petrol sold after June 30, 2013. It also allowed oil companies to negotiate the price with domestic and overseas suppliers of the bio fuel. Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) said that such a huge amount of ethanol procurement requires time and resources. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
POWER
Generation
SJVNL signs pact with Bhutanese company for 600 MW hydel plant
April 29, 2014. State-run SJVNL said it has signed a preliminary agreement with Druk Green Power Corporation of Bhutan for setting up a 600 MW hydro electric power plant in the neighbouring nation. The MoU was signed by SJVNL CMD R P Singh and DGPC MD Dashu Chhewang Rizin in the presence of P K Sinha, Secretary Power, Government of India and Dashu Sonam Tshering, Economic Affairs Secretary, Government of Royal Bhutan. SJVNL and DGPC have decided to form the Joint Venture (JV) Company within three months. It has also been agreed to set up a steering committee to initiate the tasks of getting statutory clearances and to acquire land required for the project. After finalising of the shareholders' agreement the Joint Venture will be formally registered. Financing for the project will be done on 70% loan and 30% equity. (www.business-standard.com)
OPGC urges state to move Centre for coal block clearance
April 28, 2014. Worried over the pending Stage-II forest clearance for Manoharpur coal block linked to its 1320 MW expansion at its Banharpalli plant near Jharsuguda, Odisha Power Generation Corporation (OPGC) has urged the state government to pursue the matter with the Centre. The Union ministry of environment & forests (MoEF) had granted Stage-I forest clearance for the block and the state government had submitted compliance to the ministry for grant of Stage-II forest clearance. (www.business-standard.com)
45-day power generation break at Moozhiyar from May 20
April 28, 2014. The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) will stop power generation at the Moozhiyar powerhouse of the Sabarigiri hydro-electric project for 45 days from May 20 to facilitate replacement of the butterfly valves in all the three penstock pipes. The storage position at the Sabarigiri reservoirs was 18.06 per cent of its total power-generation capacity of 916 million units (MU) which would be enough to generate 165.43 mu of power. Five generators at the Moozhiyar powerhouse had been running in full swing so as to bring down the storage position to mere five per cent before the start of the valve repair works which was scheduled to begin on May 20. The power generation at Moozhiyar was 6 MU. The valve replacement work on Penstock-I and Penstock-II leading to Generators III and IV would begin on a war-footing. The catchment areas of Sabarigiri had been receiving fairly good summer showers. (www.thehindu.com)
General Electric, Westinghouse keen to develop 12 GW of nuclear power in India
April 25, 2014. American majors General Electric and Westinghouse are looking to develop 12,000 MW of nuclear power in Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh, US Ambassador to India Nancy Powell said. The US is a key partner for energy and power development in India, Powell - who resigned from the post of US Ambassador to India - said at the American Chamber of Commerce annual general meeting. India's economy can't grow if it doesn't have sufficient power to develop and if 400 million people live without electricity, Powell said. She said that in 2013, US Department of Energy approved a second project to export liquefied natural gas (LNG) to India, which is likely to begin in 2017. The 5.6 million tons of LNG contracted have a value of over $ 1.5 billion per year and could increase India's gas supply by as much as 40 per cent, she said. The bilateral trade between India and the US stood at about $ 100 billion. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Bawana Power Plant ready to generate 1.5 GW
April 24, 2014. The Bawana Power Plant is in full technical readiness to service 1500 MW to the national capital, Delhi government said. The largest gas plant in Northen India, and second largest in the country, the Bawana power plant was able to produce only up to 350 MW for the city of Delhi, due to the non-availability of gas. According to the power department officials, full capacity of the plant has not been utilized due to non-availability of gas, which is a result of overall shortage of gas in the country. The principal secretary (Power), Arun Goyal visited the plant and reviewed its summer readiness. He was accompanied by the MD of Pragati Power Corporation Ltd (PPCL) and additional Secretary (Power) Ankur Garg and District Magistrate (North-West) Udit Prakash Rai. The team of senior officers from PPCL made a detailed presentation on the progress of on-going works and apprised the visiting dignitaries on various factors such as availability of gas and preparedness of the plant for meeting the power requirements of Delhi during the ensuing summer months. The functioning of both the modules of gas and steam turbines was inspected through detailed site visits. The plant consists of a total of six units - four gas units and two steam turbines. The work for this power project was awarded to M/s BHEL on turnkey basis. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Govt targets over 1k bn units of power generation in FY15
April 23, 2014. The government has set a target of generating over 1,000 billion units of electricity during the current financial year. The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) estimates generation of 1,023 billion units in 2013-14, an increase of about 5% from the previous financial year. The government hopes to achieve generation of 252 billion units in the April-June period, while the target for each of the subsequent quarters is 257 billion units. According to the CEA, over 393 billion units may be generated from central utilities and over 368 billion units from state utilities, while the remainder will come from private entities. About 5 billion units will be produced using power imported from neighbouring Bhutan. In 2013-14, power generation was 967 billion units, short of the target of 975 billion units. (www.business-standard.com)
Transmission / Distribution / Trade
Lok Sabha elections push power demand in UP
April 28, 2014. The Lok Sabha elections have pushed up power demand in Uttar Pradesh by almost 10 per cent above the normal demand-supply gap witnessed during summers. While state power utility, UP Power Corporation Limited (UPPCL), has the onerous task of balancing the demand-supply equation during summer, the elections have further widened the gap. The unrestricted power demand has been pegged at almost 13,500 MW on a daily basis, while UPPCL is able to provide under 11,500 MW through state and private sector power generation, hydropower, cogeneration, importing from central sector, buying power from energy exchange, etc. The constituencies going to polls are taken off the roster schedule and provided uninterrupted power supply. The uninterrupted supply to poll-bound districts starts from 6 am on the previous day of polling and remains in place till 10 pm of the polling day in rural areas. The non-polling areas have been witnessing long and erratic power cuts to meet the shortfall. Even the state capital of Lucknow, which is officially free from power cuts, has had its share of woes this season. Power outages and local breakdown of power due to transformer failure are common. The uninterrupted power supply is deemed imperative in view of polling activities, security of electronic voting machines (EVMs) and EVMs’ submission to strong rooms. Besides, election time means movement of security columns for poll duty and electioneering by top politicians, which have added to the rising power demand in UP. So far, three phases of polling (April 10, 17, 24) in UP had been completed and another three phases (April 30, May 7, 12) are still to come. This implies the precarious power situation would persist for at least another 15-20 days. The incremental electricity demand by consumers has already been putting pressure on the state power mandarins to cut burgeoning line losses, check rampant power theft, improve realisation and procure more power for industrial and domestic feeders. (www.business-standard.com)
DVC plans to opt out of retail distribution to cut losses
April 28, 2014. Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) has decided to opt out of retail distribution and move to bulk power sale to state utilities in West Bengal and Jharkhand, a move which has invited the ire of workers and officials. The company, which has loses amounting to ` 1,500 crore and outstanding dues of ` 7,500 crore, also intends to hand over water management services to the states which receive grants from the centre. A large section of officers and workers in the company have started opposing the management's decision. DVC would prefer to concentrate on power generation and pursue its goal of emerging as the second-largest power producer after NTPC. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
HC orders restoration of 300 MW supply to AP from Karnataka
April 24, 2014. The Andhra Pradesh High Court (HC) asked the Southern Regional Load Dispatch Center (SRLDC) to restore supply of 300 MW power to AP from Jindal Power plant in Karnataka. The supply was stopped from March 31, 2014, after the Karnataka government withdrew the No Objection Certificate (NOC) owing to the supply-demand mismatch being experienced within the state. AP Central Power Distribution Company Limited (APCPDCL) had entered into an agreement with JSWPTC last year for supply of 300 Mw to AP for a period from May 31, 2013, to May 29, 2014. (www.business-standard.com)
` 15 bn scheme to improve city power system approved
April 24, 2014. The state energy department has secured in-principle nod for its ambitious State Capital Region Improvement in Power System (SCRIPS) scheme planned at an investment of ` 1,500 crore. The scheme, aiming at ensuring stable and uninterrupted supply of power to the consumers in Bhubaneswar and Cuttack, involves massive overhaul of power transmission and distribution infrastructure. Under the scheme, the power transmission and distribution infrastructure has to be revamped. (www.business-standard.com)
CERC issues power trading license to Parshavnath Power
April 24, 2014. Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) has granted an inter-state power trading license to Parshavnath Power Projects Private Ltd. The balance sheet submitted by the company on September 30, 2013, showed its net worth was ` 2.66 crore. Parshavnath Power Projects stated in an affidavit that it will not apply for a power transmission license without surrendering the trading license. Parshavnath Power Projects is a wholly owned subsidiary of Parshavnath Power, which has a presence in power generation (thermal, hydro, solar and wind), transmission and distribution. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Power distribution cos write to Delhi govt about efforts for tariff relief
April 24, 2014. To help provide the people of Delhi get a tariff relief of upto 10 per cent, power distribution companies in the city are writing to the Delhi government about efforts to be taken in this direction. Since February 26, the Tata Powers Delhi Distribution Limited (TPDDL) is pushing with the Union Power Ministry seeking to reallocate its power purchase agreements with some of the gas and coal based power plants from where it is purchasing power at very expensive rates. The average power purchasing cost which is ` 5.66 per unit is expected to come down to ` 5.10 per unit if the Union Power Ministry accepts the company's proposal, the company said. This may result in 10 per cent of tariff reduction for the consumers. BSES proposed closing down of some plants like Rajghat Power House, Gas Turbine stations of IPGCL and three units of BTPS. Shifting of fuel linkages available to these plants to the new plants of APCPL (Aravali) and Pragati-III (Bawana) will benefit in increased generation from these plants resulting in saving in power purchase cost and can in turn bring about tariff reduction of upto 5-7 percent. The Reliance backed BRPL and BYPL also wrote to the chief secretary, Delhi government for the "urgent need for rationalisation" of generation cost of plants specific to Delhi which will end up saving ` 770 crore and will lead to the retail tariff reduction of upto 7 per cent. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Coal firms should take advance action to renew FSAs in time
April 23, 2014. An inter-ministerial panel has decided that coal companies, including Coal India Ltd (CIL), should take prior action to renew the fuel supply pacts in time to make sure that there are no interruptions in fuel supply to power plants. The decision was taken at the meeting of Standing Linkage Committee (SLC) under the Chairmanship of Additional Secretary, coal. Amid continuous delays, state-owned CIL has so far signed 160 fuel supply pacts with power units. The Cabinet Committee on Investment (CCI) had earlier stated that the timelines for signing of fuel supply pacts for power projects of 78,000 MW capacity should be met. Two deadlines set for the signing of Fuel Supply Agreements (FSAs) by CIL with the power producers could not be adhered to. The Coal Ministry had set the deadline of August 31, 2013 for signing of the FSAs, which could not be met. The second deadline had been set for September, last year. (www.business-standard.com)
India to see a big rise in power demand this year
April 29, 2014. Electricity demand in India may go up substantially this year as forecasters predict the possibility of an extended summer. Moderate weather in April, however, has kept power consumption almost flat in a month when demand usually starts picking up. Thunderstorms and showers in parts of the country this month brought relief for distribution companies that have limited paying capacity and face congestion in power transmission. However, the possibility of El Nino, a weather condition that usually affects monsoon rains in India, may trigger higher power demand for irrigation towards the fag end of summer. Delayed or scanty rains would reduce water levels in reservoirs, hurting operations of hydropower stations and possibly exacerbating the power situation.
In April, power demand was flat compared with the same month in the past couple of years. Rajasthan, Haryana and Punjab did not procure much power from the market to meet short-term requirements as moderate weather kept electricity demand in control. Despite this sluggish demand, electricity prices on trading exchanges increased to about ` 3.70 a unit from ` 3 in March. It will swell further as summer intensifies and consumers demand more power for cooling, said an electricity trader based in Ahmedabad. Tata Power Delhi Distribution, which distributes power in parts of the capital, is expecting demand to go over 6,100 MW in Delhi this year. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
CIL invites bids for 3rd phase of drilling mines in Mozambique
April 29, 2014. Taking forward its plans to develop mines in Mozambique, Coal India Ltd (CIL) has invited bids for the third phase of drilling in the African nation. CIL had earlier informed an inter-ministerial panel that the drilling of blocks in Mozambique had started in June, 2013. The selection of agency for the further drilling of 30,000 metre was completed in May, 2013. The panel reviews the performance of maharatna firms, including Coal India. The first stage of drilling of the mines had been completed in May last year. The contract for initial drilling was awarded in November 2012.
Coal India Africana Limitada (CIAL) had won 5-year licence for exploration and development of mines in Mozambique in August, 2009. Two coal blocks -A1 and A2- at Motaize, in Tete Province of Mozambique, are spread over 200 sq km.
CIL had registered its own subsidiary CIAL in mid-2009. Coal Minister Sriprakash Jaiswal had earlier said that the acquisition of coal mines overseas should be done in an aggressive manner to meet India's energy requirements. In order to tide over the shortages of the fossil fuel, the government is also proposing to import coal. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
No power tariff hike in Odisha for 2014-15
April 26, 2014. Odisha Electricity Regulatory Commission (OERC) has spared the hike in electricity tariff for 2014-15, after raising it for four successive years since 2010-11. Though OERC had decided on the new tariff order, it was not notified in view of the twin Lok Sabha and assembly polls in the state. After the two-phased polls and the re-polling for four assembly segments, the regulator notified the order.
Despite the distribution companies (discoms) projecting a distribution loss of 32.4 per cent, the commission considered an average distribution loss of 21.38 per cent for determination of retail supply tariff for consumers of the state. (www.business-standard.com)
No coal supply to projects failings to meet commercial output deadline: Power Ministry
April 25, 2014. The government plans to revoke the fuel supply assurances given to coal-based power projects that have failed to meet their commercial production deadline, according to the coal ministry. The power ministry is preparing a list of projects that were scheduled to begin power generation between 2009 and 2013 but have missed the deadline. Coal supply to these projects will be stopped and the fuel redirected to projects that are ready but have not tied up supplies. The move follows a recommendation made by a panel on coal supply in mid-April that commercial production be made the primary requirement for coal supplies by Coal India. Coal India had provisioned supplies to some 60,000 MW projects.
The new norm could affect some 10,000 MW projects. This rule, however, will not apply to projects that have faced delays due to reasons beyond the control of the promoters, if the panel is convinced. Earlier, the panel had decided to impose a penalty on projects that failed to adhere to the deadline, but later opted for scrapping fuel supply guarantees to enable coal supply to projects that are ready for generation but have not firmed up supplies. The coal ministry has already prepared a list of some 12,000 MW projects that are awaiting coal supplies to begin generation. These projects are now on the priority list and they will start receiving coal as soon as supply assurances from existing projects are revoked. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Lok Sabha polls 2014: Karnataka grabs power from mills to keep voters happy
April 25, 2014. While Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh have been reeling under extensive power-cuts in a harsh summer in the middle of Lok Sabha elections, Karnataka's Congress government escaped the voter wrath by forcing co-generating units in the state to sell all their electricity to the state grid. In fact, state energy minister DK Shivakumar declared that Karnataka's power availability is in excess of the demand. On March 26 — 20 days before Lok Sabha polls in the state — the Siddaramaiah government invoked Section 11 of the Indian Electricity Act 2003, directing sugar units that run power generation units to sell all their electricity to the state grid. Section 11 of the Electricity Act empowers a state government to issue appropriate directions to private generating firms under "extraordinary circumstances". With the help of this, the state has been buying 650 MW power at ` 5.50 per unit from co-generating units or sugar mills. In March, Karnataka faced a peak deficit of 837 MW, while Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh had peak deficits of 1,134 MW and 572 MW respectively, according to the Central Electricity Authority data.
Apparently, the 10-month old Congress regime in Karnataka did not want to rub voters on the wrong side ahead of the polls by imposing power-cuts. But the government action has left sugar mills seething in anger, and a couple of them have even approached the High Court, urging it to set aside the government direction. The mill owners are unhappy because summer is the peak season for them to get high price for their power from states such as Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Shut five power units in Delhi: BSES to govt
April 25, 2014. BSES, power distribution company of the Anil Dhirubhai Ambani group (ADAG), has suggested the government close five of its five power generation units in Delhi, shifting their fuel allocation to two other state-owned and newer power plants. It says the move would bring down retail electricity costs by five to seven per cent. BSES said there would also be additional generation of 820 million units of power a year by shutting the old and relatively inefficient state-run units. This and the reduction in costs would mean savings of ` 770 crore. BSES owns two of the three power distribution companies in Delhi. The third is a subsidiary of Tata Power.
It suggested the government close the three units of NTPC at Badarpur, the Rajghat Power House and gas turbine stations of Indraprastha Generation. All these units are more than 25 years old. BSES suggests a shift in the old plants’ fuel allocations to the newer ones at Aravali/Bawana, also in the city and government-owned. BSES suggests the city government ask the Union power ministry to close the old units and shift their fuel linkages to Aravali/Bawana. Some months earlier, when the Delhi government was briefly run by Arvind Kejriwal’s Aam Aadmi party, it had threatened to cancel the licence of BSES if the company did not improve its services, and sought an audit into their financial books over allegations of profiteering. (www.business-standard.com)
SC panel raps Uttarakhand hydropower projects
April 24, 2014. A Supreme Court (SC)-appointed panel has blamed hydro projects in Uttarakhand as being responsible for intensifying the magnitude of the catastrophic floods that hit the state last year leaving death and destruction in its wake. But that conclusion has been bitterly contested by government agencies and utilities that say that it unfairly puts at risk the country's hydropower sector, which is seen as a solution to India's power shortage as nuclear plants face public protests and thermal units are starved of fuel. The committee has faced flak from the Central Water Commission and the Central Electricity Authority, representatives of which resigned from it alleging bias. The two authorities have submitted a parallel report stating the hydroelectric projects have only contributed to the development of the host state. Industry experts said the report raises questions on the government's process of awarding and clearing projects based on which companies invest money. It also casts doubt on the country's aim of achieving energy security at a time when its per capita compares poorly with the world average and other developing countries such as China. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
INTERNATIONAL
OIL & GAS
Upstream
Kashagan oil restart not expected this year
April 28, 2014. Output at Kazakhstan's huge Kashagan oilfield is not expected to restart this year after an investigation revealed that long stretches of oil and gas pipelines may need to be fully replaced, the project consortium said. The Central Asian nation of 17 million relies heavily on oil exports, and the setback in development at its flagship field could be a drag on state coffers. Production at the offshore deposit, the world's biggest oil find in 35 years, started in September but then halted in early October after the discovery of gas leaks in the $50 billion project's pipeline network. (uk.reuters.com)
Premier makes oil, gas finds in Indonesia, Pakistan
April 28, 2014. UK independent Premier Oil reported that it has made oil and gas discoveries offshore Indonesia and onshore Pakistan. Premier said that its Kuda Laut-1 well in the Tuna production sharing contract (PSC), where the firm is the operator with a 65-percent stake, found 183 feet of net oil-bearing reservoir and 327 feet of net gas-bearing reservoir. The well is to be side-tracked to drill the Singa Laut prospects in the adjacent fault block, with results expected in late May. Elsewhere in Indonesia, drilling is continuing at the Ratu Gajah-1 exploration well in the Natuna Sea Block A PSC, where Premier is also the operator with a 28.67-percent holding. Results here are expected in May. In Pakistan, the K-36 well on the Kadanwari block encountered a total net gas pay of 65 feet and flowed at 50 million standard cubic feet per day through a 64/64-inch choke on test. The well is now tied into the Kadanwari facilities and has been on production since April 16. Operations continue on the K-34 well with results expected in May. (www.rigzone.com)
ExxonMobil starts up LNG production at PNG project
April 28, 2014. Exxon Mobil Corporation announced the $19 billion PNG LNG project has started producing liquefied natural gas (LNG) in Papua New Guinea ahead of schedule. Production from the first LNG train will increase over the coming weeks and the first cargo is expected to be shipped to Asia markets before midyear. Work on the second train is progressing and LNG production from this unit is expected to start in the next several weeks. The project, which is operated by ExxonMobil affiliate ExxonMobil PNG Limited, is expected to produce more than 9 trillion cubic feet of gas over an estimated 30 years of operations. (www.rigzone.com)
Signs of new natural gas field found off Israel coast
April 27, 2014. An oil and gas group exploring offshore Israel said it may have discovered a field that contains an estimated 2.5 trillion cubic feet (tcf) of gas and 255 million barrels of oil. About 30 tcf of gas have been discovered off Israel's Mediterranean coast in recent years, turning the country once dependent on energy imports into a potential exporter. A report by Texas-based consultants Netherland, Sewell & Associates estimated a 23-27 percent chance of success for finding the 2.5 tcf of gas and a 16-18 percent chance for finding 255 million barrels of oil. (www.rigzone.com)
Baker Hughes plans to disclose all fracking Chemicals
April 25, 2014. Baker Hughes Inc. plans to disclose all of the chemicals used in the rock-cracking technique used to unlock oil and natural gas from underground. The world’s third-largest oilfield services provider hasn’t disclosed all of the ingredients used in fracking fluids in the past, citing competitive reasons, the Houston-based company, said. Hydraulic fracturing pumps water, sand and chemicals underground to fracture rock and allow trapped oil and gas to flow to the wellbore. The technique, coupled with horizontal drilling, has led the U.S. on the path to energy independence. In response to public concern about fracking, the website FracFocus was created for oil companies to voluntarily disclose their ingredients. Environmental groups complained that companies could still keep confidential too many of their chemicals. Baker Hughes has been working to change its policy “for some time,” including holding private discussions with its engineers and suppliers to make sure it could disclose all of the chemicals. (www.bloomberg.com)
Tethys finds gas at AKK19 exploration well in Kazakhstan
April 25, 2014. Tethys Petroleum Ltd, the oil and gas exploration and production company focused on Central Asia and the Caspian Region, reported the success of Well AKK19, the third shallow gas exploration well of its 2014 program at the Kyzyloi and Akkulka development in Kazakhstan. Analysis of data from the well indicates it has a pay zone twice as thick as the AKK15 well which tested gas at a stable rate of approximately 7 million cubic feet, or 195,000 cubic meters or 1,167 barrels oil equivalent per day, and the AKK19 well is anticipated to test at significantly more than that rate. The current shallow gas program includes the drilling of up to 10 new exploration wells, based on the latest seismic data, as well as workovers and tie-ins, and is targeting a threefold increase in gas production by the beginning of 2015. (www.rigzone.com)
Downstream
Polish refiner PKN eyes upstream deals to boost profit
April 24, 2014. Poland's largest oil refiner PKN Orlen may buy more oil producing assets in an attempt to increase profitability squeezed by low refining margins in Europe, it said. For the first time, PKN booked a profit from its own oil producing - or upstream - operations, while its Canadian unit TriOil Resources, which it bought last year, made core earnings of 37 million zlotys. While that was just 5 percent of the group's total first-quarter earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortisation (EBITDA) of 776 million zlotys, PKN said more upstream purchases were on the cards. TriOil produced 330,000 barrels of oil equivalent in the first quarter. Some analysts have expressed doubts about PKN's strategy of building an integrated oil company, which runs counter to the prevailing trends in the United States. PKN has been trying to build its upstream potential in shale gas in Poland, for example, but its efforts - despite being costly - have so far not resulted in commercial gas production. PKN's shares have fallen 8 percent over the last 12 months as it struggles with refining overcapacity in Europe and weak margins, compared with a 20 percent rise in Warsaw's main stock index.
The firm, which imports most of the oil it refines from Russia, said the Ukrainian crisis has not impacted its business as it does not rely on exports either to Russia or Ukraine. PKN said it was assessing the future of its loss-making Lithuanian unit Orlen Lietuva, which owns the Mazeikiai refinery. (www.downstreamtoday.com)
Transportation / Trade
Russia sanctions focused on individuals seen bearish for crude
April 29, 2014. U.S. sanctions on Russia that were announced are probably bearish for oil because they focused on individuals rather than the nation’s largest companies, according to energy analysts. Brent crude’s premium to West Texas International narrowed the most in four months. The U.S. sanctions target seven Russian executives and officials and 17 companies controlled by President Vladimir Putin’s allies, including OAO Rosneft head Igor Sechin. The nation’s largest companies were not included and the sanctions were perceived as “weak” by some traders. (www.bloomberg.com)
Suncor uses rail, new pipelines to drive profit to record
April 29, 2014. It’s a long way to send oil from Canada’s landlocked province of Alberta to refineries on the coasts. For Suncor Energy Inc., that can have its advantages: record profit. Canada’s largest oil producer by market value moved more crude by rail and on new pipelines like TransCanada Corp.’s Gulf Coast system to earn higher prices and reduce its refining feedstock costs in the first quarter. Like other companies producing bitumen from Canada’s oil sands, Suncor is slowly expanding its shipments to coastal markets while it waits for pipelines like TransCanada’s Keystone XL and Enbridge Inc.’s Northern Gateway to be built. In the meantime, the company is cobbling together a system of rail transport and space on new and existing lines to help booming North American output reach markets. Suncor shipped as much as 70,000 barrels per day of crude, or about 13 percent of its output, on the Gulf Coast system in the first quarter. At the same time, it used rail cars to supply its refinery in Montreal with 20,000 barrels a day of cheaper Canadian oil, replacing more expensive imported feedstock. The company saved C$20 million at the Montreal refinery by using cheaper North American crude in the quarter. By next year, Suncor will be able to supply the refinery entirely with oil from Canada and the U.S. (www.bloomberg.com)
Slovakia signs deal to deliver gas to Ukraine
April 28, 2014. Slovakia signed a deal to deliver natural gas to Ukraine, which is facing the threat of a cut-off in supplies from Russia because of a massive debt. Under the agreement, Slovakia will send gas through a pipeline that was meant for transporting gas from Ukraine but is currently unused. To be able to send the gas, some technical changes are needed that might take several months. The signing of a memorandum of understanding between the Slovak pipeline operator Eustream and Ukraine's Ukrtransgaz is another step in Ukraine's efforts to reduce its dependence on Russia. It has already agreed on gas supplies also from Germany, through Poland, as well as from Hungary. The German supplies, from utility RWE, already started. (www.downstreamtoday.com)
Kuwait signs LNG import deal with Qatargas
April 28, 2014. Kuwait has signed a contract to import liquefied natural gas (LNG) from fellow Gulf state Qatar to help meet its energy needs to the end of 2014. The first shipment of LNG will arrive in Kuwait under the contract between Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC) and state-owned Qatargas. (www.arabianbusiness.com)
How Obama shocked Harper as Keystone's frustrator-in-chief
April 26, 2014. On Thursday, Nov. 10, 2011, Canadian Prime Minister Stephen Harper, seated in his Ottawa office across from Parliament Hill, took an urgent call from U.S. President Barack Obama. Harper’s advisers were listening intently around a muted speakerphone in an adjoining room. The State Department, Obama said, would be making an announcement later that day putting the Keystone XL pipeline project on hold. There was no choice, according to the president. Nebraska wanted the route changed to protect a key aquifer under millions of acres of prime farmland. This would necessitate a new environmental assessment. He assured Harper the call wasn’t a game changer; neither a yes nor a no, just a delay. Harper was far from assured -- he was irritated. The project had already undergone three years of study and was, so the Canadians believed, on the cusp of approval. Delay, he told Obama, served no one’s interest. (www.bloomberg.com)
Williams plans $300 mn natgas pipe expansion for US LNG export
April 25, 2014. Williams Partners LP said it plans to expand part of its Transco pipeline to deliver natural gas to Cheniere Energy Partners LP's Sabine liquefied natural gas export facility under construction in Louisiana. Williams Partners, which is majority owned by Williams Cos Inc, said the project will cost about $300 million with a planned in service date in early 2017, subject to government approvals. Sabine is the only LNG export facility under construction in the United States and is expected to enter service in late 2015. There are however more than a dozen other companies seeking federal approvals to build LNG export facilities in the United States. (www.downstreamtoday.com)
Maliki looks to Iraq’s oil gusher for election edge amid strife
April 24, 2014. Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki is banking on sales from the highest crude oil output in 35 years to earn him a third term even as he struggles against an emboldened al-Qaeda and a surge in political violence. Under Maliki’s leadership, Iraq, with the world’s fifth-largest oil reserves, overtook Iran as the second-biggest producer in the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries, helped by foreign investors including Royal Dutch Shell Plc and Exxon Mobil Corp. It pumped 3.4 million barrels a day in March, 86 percent more than in December 2006 when he first became prime minister. (www.bloomberg.com)
Azeri shipyard, BP sign $378 mn contract on vessel construction
April 23, 2014. Azeri state energy company SOCAR's shipyard and British oil major BP have signed a $378 million deal to design and build a subsea construction vessel for the Shah Deniz II gas project, BP said. Azerbaijan's biggest gas field, Shah Deniz is being developed by consortium partners BP, Statoil, SOCAR and others. Shah Deniz I has been pumping gas since 2006 and has an annual production capacity of about 10 billion cubic metres (bcm) of natural gas. (www.rigzone.com)
Policy / Performance
Kazakhstan offers India opportunity to explore Caspian Abai oil block
April 28, 2014. Kazakhstan has offered India an opportunity to explore Caspian Abai oil block. The offer was made at the 11th Kazakhstan-India Inter-Governmental Commission (IGC) meeting that took place on April 24 and 25 in Kazakh capital Astana. The Kazakh delegation was led by the country's Vice-Minister of Oil and Gas, Mr. Magzum Mirzagaliev, while the Indian side was led by Petroleum Secretary Saurabh Chandra. Both sides inked a protocol during the of IGC meeting under which they agreed to consider broadening bilateral cooperation in the production and development of oil and gas fields in Kazakhstan. The Indian side expressed its readiness to participate in projects, both as a sole developer and as a consortium partner. Both sides agreed to make every effort to consider Kazakhstan's offer to explore the Caspian Abai oil block. The two sides also agreed to consider possibilities of expanding cooperation in the exploration and production of hydrocarbons in Kazakhstan. (www.newkerala.com)
Mexico parties enter final phase of oil bill discussions
April 26, 2014. Mexico’s two biggest parties reached agreement on key points of legislation needed to implement an energy overhaul that will end a more than seven-decade state oil monopoly. While the ruling Institutional Revolutionary Party, or PRI, and the National Action Party, or PAN, are working out details, such as how much autonomy regulators will be granted, negotiations are in the “final phase”. The oil proposal the federal government sends to Congress will be welcomed by the opposition as “a very good initiative,” declining to elaborate on contents of the bill. It will be presented before April 30, the last day of Congress’ spring session. (www.bloomberg.com)
Japan starts releasing monthly spot LNG prices
April 25, 2014. Japan started releasing average prices for spot liquefied natural gas (LNG) to add transparency to an opaque market and amid concern about rising fuel costs in the wake of the shutdown of nuclear plants after the Fukushima crisis. The move by Japan's trade ministry is most likely the first time that an average spot price has been publicly released based on actual transactions, Takashi Ishizaki, the trade ministry official in charge of the initiative. Japan takes in about a third of world LNG shipments, importing a record 87.73 million tonnes in the year through March. The average spot price is based on about 10 percent of the super-chilled fuel bought by Japan, according to Ishizaki. Japan has been importing record volumes of LNG to run power stations following the meltdowns at the Fukushima Daiichi plant north of Tokyo after the March 2011 earthquake and the ensuing shutdown of all 48 reactors in the country. That has helped to push prices for LNG to above $20 per million British thermal units (mmBtu) across Asia in early March, as North Asian buyers stockpiled fuel after a cold winter amid supply disruptions, notably in Angola. (www.downstreamtoday.com)
Ukraine crisis played 'elevated' role in recent LNG approval: US
April 25, 2014. The crisis in Ukraine and Russia played an "elevated" role in the most recent approval of a U.S. liquefied natural gas export project, and geopolitics will continue to influence decisions on how much LNG to export, U.S. Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz said. The energy secretary said the escalating crisis was a key factor behind the Energy Department's approval last month of exports of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from a plant to be built in Oregon, the second such authorization this year. (www.downstreamtoday.com)
UK shale could spark $55 bn in investment, E&Y says
April 24, 2014. U.K. shale-gas production has the potential to boost local demand for supplies from rigs to steel casings and waste-water management, according to an Ernst & Young (E&Y) LLP report commissioned by an industry lobby. About 33 billion pounds ($55 billion) would have to be spent to bring 4,000 wells into production by 2032, according to the report, commissioned by the U.K. Onshore Operators Group, or UKOOG. That would create 64,500 jobs, it said. The bulk of the expenditure, or 62 percent, would be for hydraulic fracturing, the controversial technique that pumps water, sand and chemicals at high pressure to release the trapped gas from rock underground. The U.K. government has promised tax breaks to drillers as it seeks to cut reliance on imports and stimulate the economy amid declining North Sea reserves. The industry is offering incentives to local communities affected by works as campaigners say the extraction process can contaminate ground water, pollute the air and cause disturbances. The Bowland basin, extending across an area of northern England that includes Manchester, Liverpool and Sheffield, may hold 1,300 trillion cubic feet of gas, according to the British Geological Survey. That’s enough to meet demand for about half a century at extraction rates similar to U.S. fields. (www.bloomberg.com)
Myanmar to sign PSCs for onshore blocks awarded in 2013 in mid-May
April 24, 2014. Myanmar expects to sign production sharing contracts (PSCs) awarded under Myanmar's Onshore Blocks Second Bidding Round 2013 in mid-May, later that an earlier timeline planned for January, the ministry of energy said. The Ministry of Energy awarded 16 of the 18 onshore blocks offered in the tender in mid-October 2013. Italy's Eni, India’s ONGC Videsh Ltd., Malaysia’s Petronas Carigali, Canada’s Pacific Energy Hunt Corp., Pakistan’s Petroleum Exploration (Pvt) Ltd. and British Virgin Islands-registered MRPL E&P Pte Ltd. were each awarded 2 blocks. (www.rigzone.com)
Canada to decide in June on proposed Enbridge oil pipeline: Minister
April 24, 2014. Canada will meet a mid-June deadline for its final decision on whether to authorize the construction of Enbridge Inc's proposed Northern Gateway crude oil pipeline, Minister of Employment and Social Development Jason Kenney said. A federal review panel recommended in December that the pipeline be approved if Enbridge meets 209 technical, environmental and social conditions. That set up a 180-day review period for the government to make its final decision on the project. Northern Gateway would carry some 525,000 barrels-of-oil per day from the Alberta oil sands hub of Edmonton to a deepwater port in Kitimat, British Columbia, where it would be loaded onto supertankers and shipped to international markets. The project is supported by Canada's energy industry, which currently sells most of its oil to U.S. buyers at a steep discount to benchmark prices. It is fiercely opposed by environmental groups and aboriginals concerned about a potential oil spill. (www.rigzone.com)
US crude inventories climb to highest level in 83 yrs
April 23, 2014. US crude stockpiles grew to the highest level since 1931 as production climbed to the most in 26 years, data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) showed. Inventories rose 3.52 million barrels to 397.7 million barrels, according to the EIA, the energy department’s statistical arm. Weekly government statistics go back to 1982 and monthly figures to 1920. Crude output climbed 59,000 barrels a day to 8.36 million, the most since January 1988. US production has surged as the combination of horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, unlocked supplies trapped in shale formations in the central US, including the Bakken in North Dakota and the Eagle Ford in Texas. Output dropped to 3.81 million barrels a day in September 2005, when hurricanes Katrina and Rita hit the Gulf Coast and accelerated a long-term decline. Output declined in 17 of the 20 years through 2008 before rebounding, EIA data show. (www.livemint.com)
POWER
Spain's Acciona wins contract to build power plant in Mexico
April 28, 2014. Spain's Acciona said it won a $107 million contract from the Federal Electricity Commission, to design, build and oversee the start of operations of the Baja California Sur V thermal power plant in Mexico. The power plant in La Paz, the capital of Baja California Sur state, will have a net generating capacity of 46.8 MW and is expected to be completed in June 2016, Acciona said. The contract calls for the expansion of an existing power plant whose first four phases are already in operation. The power plant provides electricity to La Paz and nearby tourist areas, meeting the energy needs of some 200,000 residents. The energy facility generates electricity by burning petroleum residues, thus "optimizing the crude oil cycle," Acciona said. Acciona is the largest producer of energy from renewable sources in Mexico with 556.5 MW of installed wind generating capacity, or 28 percent of the country's total. (latino.foxnews.com)
Nigeria's power generation hits 4 GW
April 23, 2014. Power generation in Nigeria had risen to more than 4,000 MW, Minister of Power Chinedu Nebo said. Nigeria's power generation capacity has picked up, reaching 4, 105.90 MW. Lagos, Nigeria's commercial center, had the highest with 985 MW while Abuja had 410.80 MW, said the minister said. Nebo maintained that the average power generation stood at 3, 800 MW contrary to insinuations that power had dropped below 2,000 MW, and many households now enjoyed enhanced power supply. The minister reaffirmed the government's resolve to consolidate efforts at removing all bottlenecks to sufficiency in power supply. (www.shanghaidaily.com)
Transmission / Distribution / Trade
Ovo Energy in bid to boost local power generation in challenge to big six
April 28, 2014. One of Britain's fastest growing independent energy suppliers is offering to act as a co-ordinator and technology partner to local communities in a move it believes could bring up to 500 new power providers onstream by 2020. Ovo Energy expects to encourage local authorities, community groups and other bodies to supply energy to people who have lost faith in the prices and practices of the much criticised big six firms. Ovo Energy said an open access technology model similar to the one Amazon uses in retail could also kickstart a revolution in power supply. Ovo has invested heavily in systems that can easily be scaled up to give community groups, local authorities and housing associations the tools they need to run a utility business, including customer service, billing and power generation. The company, through a new Ovo Communities division, will also offer smart metering, power purchasing and energy efficiency installations as part of its new platform. (www.theguardian.com)
New South Wales considers selling electricity network
April 27, 2014. New South Wales will consider selling the state’s electricity network, a transaction analysts estimate might raise $32 billion, to help fund infrastructure projects. Australia’s most populous state has already sold ports and a desalination plant to finance road and rail projects. A full sale of the network carrying electricity to homes and businesses -- assets known as poles and wires -- could bring in A$34.5 billion ($32 billion), Infrastructure Partnerships Australia estimated in 2011. The model of selling state assets to fund projects needed by local communities is “very compelling”. There’s “a huge amount” of capital tied up in the electricity network. The government wouldn’t sell the poles and wires without a mandate at the next state election in 2015. Australia’s antitrust regulator blocked the New South Wales government’s planned A$1.51 billion sale of power plants to AGL Energy Ltd. (www.bloomberg.com)
World Cup power cut fears spur record Brazil LNG buying
April 25, 2014. The soccer governing body FIFA says that during games the essential areas will run on generators and have backup electricity supply to prevent interruptions. Brazil’s grid will be able to cope during the World Cup because the weather will cool and with it demand, Deputy Energy Minister Marcio Zimmermann said. The nation’s system has enough thermal capacity to complement hydroelectric generation, Brazil’s Energy Minister Edison Lobao said, after the last monthly meeting of its electricity sector monitoring committee. (www.bloomberg.com)
Coal glut foils price rally with miners tied to exports
April 24, 2014. Australian mining companies are prolonging a supply glut that’s driven coal prices to a four-year low because of freight contracts that make it cheaper to ship at a loss than to cut output. Shipments of thermal coal from the second-biggest exporting nation will expand the most of any country this year, according to Morgan Stanley. The bank cut its 2014 price forecast by 9 percent to $77 a metric ton earlier this month, estimating global supply will outstrip demand by 4 percent. Prices averaged $77.24 so far this year, according to globalCOAL data. (www.bloomberg.com)
China-Bangladesh MoU to set up 1.3 GW power plant
April 28, 2014. The government will sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with China for setting up a 1320 MW coal-fired power plant in joint venture (JV) at Maheshkhali, Chittangong. Bangladesh Power Development Board (PDB) and China Huadian Hong Kong Co. Ltd. will set up a joint-venture company on 50:50 equity basis like that of Indian NTPC for Rampal coal-fired power plant. Under the MoU, a new company will be formed that will arrange fund to install the power plant. (amarhealth.com)
Taiwan to halt construction of fourth nuclear power plant
April 27, 2014. The Taiwan government will halt construction at the island's fourth nuclear power plant. President Ma Ying-jeou met with lawmakers from his Kuomintang Party (KMT) and reached a decision to seal off the plant's first reactor after the completion of safety checks, KMT said. Construction of the second reactor will be halted immediately, KMT said. The move is the latest sign of pressure on Ma's administration from opposition parties and anti-nuclear activists, who are concerned about the safety of such facilities in earthquake-prone regions of Taiwan following the 2011 Fukushima disaster in Japan. Tens of thousands of protesters gathered in downtown Taipei over the weekend, urging the government to abandon nuclear energy. Ma refused opposition demands for an immediate referendum on the future of Taiwan's contentious fourth nuclear plant, but reiterated that the government would hold such a vote before the facility starts operations. Taiwan's three current nuclear power facilities would have to serve longer if the fourth one does not start operating as planned, the economics ministry has said. Taiwan's first nuclear plant is set to be decommissioned from 2018-19, while the second is set to close between 2021 and 2023. Some 40 percent of the island's electricity is generated by burning coal, 30 percent using natural gas and 18.4 percent by nuclear power plants, according to the economics ministry. (www.reuters.com)
ADB funds Pakistan power policy
April 26, 2014. The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has approved a US$ 400 million loan to support the government of Pakistan's National Power Policy, which was approved in July 2013. The National Power Policy aims to increase the country's electricity generation to 26,800 MW, encourage public and private investment, and import electricity from India, Iran and Central Asian states. (www.khl.com)
Poland pushes coal on Europe as Putin wields gas weapon
April 24, 2014. Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk says the country’s giant coal fields should become a cornerstone in Europe’s defense against a newly aggressive Russia. Because the fossil fuel supplies 90 percent of Poland’s power it has less need of Russian natural gas than other Eastern European nations, burning half as much per capita as the neighboring Czech Republic, for example. As politicians wrestle with how to respond to the crisis in Ukraine, Tusk argues Europe needs to “rehabilitate” coal’s dirty image and use it to break Russia’s grip on energy supply. Poland burns over 50 million tons of coal a year, more than any European nation other than Germany, while having the lowest reliance on natural gas among the EU’s 10 largest economies, according to International Energy Agency data. That’s a popular position in a nation where Soviet troops were stationed for four decades until the early 1990s. That doesn’t mean Poland is completely independent of Russia. While less vulnerable than some of its neighbors, it remains a gas importer and any disruption in supply would raise energy costs by forcing it to seek more expensive imports from elsewhere. (www.bloomberg.com)
IDB provides $20 mn loan for rural electrification program in Panama
April 23, 2014. The Inter-American Development (IDB) has approved a $20 mn loan to finance a rural electrification program in Panama. The program will promote public and private investment to provide service for over 10,000 rural households, located mostly in remote areas, which would increase Panama's electricity coverage rate to approximately 81% of Panama's rural households by 2018. The program will offer incentives for grid-extension and off-grid systems, as well as improving the Panamanian government's institutional capacity for the formulation, execution, oversight and evaluation of rural electrification projects. (utilitiesretail.energy-business-review.com)
India’s indecision keeps Bhutan’s 540 MW Amochu project under uncertainty
April 23, 2014. Bhutan's 540 MW Amochu Hydroelectricity project, an important one in Indo-Bhutan power planning, is under deep uncertainty over security as well as environmental issues. Despite being one of the most financially viable and technically feasible one, the project's upcoming is under uncertainty. Though it was supposed to enter into construction phase in 2013, it is, in actual, still at planning stage now. According to the office of Bhutan Prime Minister Mr. T. Tobgey, India had not decided on the financing of Amochu. But the project was included in the 10,000 MW power augmentation target of Bhutan to take place by 2020. As learnt, government of India is concern on the exact location of Amochu project that falls at India's tri-junction, the point where boundaries of three nations meet. And it posed security issues. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
RENEWABLE ENERGY / CLIMATE CHANGE TRENDS
National
Assess water diversion to thermal plants: Greenpeace to Maharashtra
April 29, 2014. Asking Maharashtra government to take the weak monsoon forecast and low reservoir levels in the state seriously, NGO Greenpeace demanded urgent assessment of water diversion to thermal power plants. Two new pieces of information were released -- one by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and another by the state Water Resources Department (WRD) -- which are of great consequence to Maharashtra. While the IMD (and private meteorological depts) predicted below average rainfall in the state (and country-over), the WRD disclosed figures showing that water is already dismally low in many reservoirs (especially in Marathwada), the NGO, working on environment-related issues, said. The state government should not take these two indicators lightly and undertake an urgent assessment of diverted water in order to stabilise water mismanagement and defend the state from a repeat of the 2012 crisis, it said. The Water Resources Department's weekly report on the current water availability in the state's reservoirs shows the reservoirs of Marathwada were already dismally low at 31 per cent -- Jayakwadi dam (Aurangabad) had only 13 per cent water available, Majalgaon (Beed) only 23 per cent and Manjra (Beed), Lower Terna and Sina Kolegaon (Osmanabad) ran dry, it said. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Gamesa Wind Turbines bags another 100 MW project from Greenko
April 28, 2014. Technology provider and wind farm developer Gamesa Wind Turbines has bagged another 100 MW project, out of the total 300 MW agreement signed with owner and operator of clean energy projects Greenko, for an undisclosed sum. With the latest project, Gamesa has secured 250 MW of projects which are currently under various stages of implementation, Chennai-based Gamesa said. In the 100 MW project, Gamesa would supply and commission 50 units of G97-2.0 MW Turbines at various sites in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Rajasthan. Gamesa would start delivering the turbines from May 2014 and commissioning has been planned in phases, beginning September. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
GE invests $24 mn in Welspun's MP solar plant
April 26, 2014. General Electric (GE) is entering India's clean energy sector with a $24 million investment in India's largest solar power plant, the 150 MW project of Welspun Renewable Energies in Madhya Pradesh (MP). India's vast potential for solar power had also prompted Goldman Sachs to invest about $320 million in Sumant Sinha-promoted ReNew Power last year in two phases, making it the largest investment so far in Indian renewable energy generation industry. Asian Development Bank (ADB) invested $30 million in NSL Renewable Power in May 2013. India's clean energy sector attracted investments of $7.8 billion in 2013, 80% of which was through domestic investors, though the amount of foreign funding is rising. (economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Suzlon bags 370 MW orders in first three months of 2014
April 25, 2014. The Suzlon Group bagged contracts for wind energy capacity of 370 MW in the first three months of this year, with projects spread across Europe and India. The wind power major will supply turbines for wind farms in Germany, the UK, India, Belgium and other European nations. In the fourth quarter of 2013-14, the company signed contracts for 370 MW, it said.Group firm Senvion SE's said it has suitable turbines for each individual site in the product portfolio. Suzlon has an order book worth about $7.7 billion. (www.business-standard.com)
Green bonds could cut India clean-energy cost 25 pc: report
April 24, 2014. Funding renewable projects with Indian government-backed green bonds could lower the cost of clean power by as much as 25 percent, according to a study. The government could sell bonds and lend the proceeds to wind and solar farm developers. India could offer funds a third cheaper than commercial bank loans and for double the tenor as the government has the highest domestic credit rating, according to a report by the Indian School of Business and Climate Policy Initiative, a San Francisco-based research firm. India, ranked Asia’s third-most attractive country for renewable investments by Ernst & Young LLP this year, plans to double its clean-energy capacity to 55 GW by 2017. Lack of affordable financing is an obstacle to reaching that target as the central bank is raising interest rates to combat inflation and commercial banks are wary about lending to new technologies. The state-run Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Ltd. raised about ` 7.2 billion ($117.8 million) selling 10-, 15- and 20-year tax-free bonds to help finance clean-energy projects. In addition to green bonds, the government could step in with other financing instruments such as infrastructure debt funds, partial credit guarantees for projects and a low-cost credit line to mitigate currency depreciation risk, the report said. Indian commercial banks offer 10-year loans with interest rates of about 12 percent to renewable plants. Such unfavorable terms add as much as 32 percent to the cost of renewable energy in India, Climate Policy and the Indian School of Business said in a separate report. (www.bloomberg.com)
Global
French energy minister promises 100k green jobs
April 28, 2014. Segolene Royal, appointed French energy and environment minister this month, said she planned to create 100,000 jobs in the next three years with a drive for green growth. She wanted to accelerate investment in renewable energies like wind, solar, biomass and marine energy, as well as in insulation of buildings. In coming days, Royal will make a joint proposal with the housing minister to provide low-income families financing options for insulation, aiming to renovate 500,000 homes by 2017. (uk.reuters.com)
Rooftops, empty lots offer Japan space for solar panels
April 25, 2014. Developers of solar projects in Japan are looking to rooftops, empty lots and industrial parks in response to constraints limiting connections to the grid and difficulties finding suitable land. Government approvals for smaller-sized projects of less than 1 megawatt have outnumbered larger projects every month since May 2013. The pattern of approvals reverses the trend set when Japan first began offering incentives for clean-energy in July 2012. Developers initially favored “mega” projects built on large patches of open land. From May 2013 through January -- the latest available figures provided by the government -- Japan approved 6,500 megawatts of solar projects in the 10-kilowatt to 1-megawatt category. That’s double the approvals for larger projects. A solar plant with 1 megawatt of capacity can generate enough electricity for about 316 typical Japanese homes. Projects of less than 1 megawatt are usually found on rooftops, unused land, or in industrial areas, the Institute for Sustainable Energy Policies said in a report. The segment accounted for about a half of Japan’s solar capacity added after the introduction of inducements designed to boost clean-energy development, according to the report. (www.bloomberg.com)
China takes on pollution with biggest changes in 25 yrs
April 25, 2014. China passed the biggest changes to its environmental protection laws in 25 years, outlining plans to punish polluters more severely as leaders work to limit contaminated water, air and soil linked to economic growth. Now the world’s biggest carbon emitter, China has moved to address the environmental damage that has been a byproduct of its breakneck economic growth and become a leading cause of social unrest. Government reports and recent comments from top officials about pollution have revealed the extent of the damage and raised new concern about its health effects. The amendments become effective from Jan. 1, according to the revised law, which was passed by the Standing Committee of National People’s Congress, China’s top legislature. It allows for consecutive daily fines on polluters if they don’t get better and offers channels for whistle-blowers to make environment-related appeals. Non-government groups can also file lawsuits for environmental damage under certain conditions, it says. (www.bloomberg.com)
SunPower and Google form $250 mn solar lease program
April 24, 2014. SunPower Corp., the second-largest U.S. solar manufacturer, and Google Inc. are creating a $250 million program to finance residential solar systems. The solar producer is committing $150 million and Google will provide $100 million, San Jose, California-based SunPower said. The program will support solar leases for rooftop systems that use SunPower panels. Leasing, the fastest-growing part of the U.S. solar market, allows homeowners to pay little or nothing up front for systems in exchange for monthly payments. This is the second clean-power investment in two days for the Mountain View, California-based search-engine company. Google has invested more than $1 billion in renewable energy worldwide, including two prior deals in residential solar, the company said. (www.bloomberg.com)
China’s polysilicon makers double in 2013 as price increases
April 24, 2014. The number of polysilicon makers in China, the world’s biggest supplier of solar panels, more than doubled to 15 last year as prices climbed. The nation produced 84,000 metric tons of the raw material, used in most solar panels, in 2013, an 18.3 percent increase from a year earlier, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology said. At the beginning of last year, the country had seven manufacturers. Polysilicon output in China may reach 110,000 tons to 120,000 tons in 2014. Chinese panel output increased 13 percent to 26 GW in 2013, equivalent to more than 60 percent of global production, the ministry said. (www.bloomberg.com)
Marubeni completes Japans’ largest solar-power station in Oita
April 23, 2014. Marubeni Corp., a Japanese trading company, has completed an 82 MW solar-power station in the southwestern prefecture of Oita. The plant, the largest in Japan, began commercial operations, the Tokyo-based company said. Marubeni is also building a 28.3 MW solar-power station in Miyagi prefecture in northern Japan, the company said. (www.bloomberg.com)
UK awards guaranteed power price contracts to Drax, Dong
April 23, 2014. Drax Group Plc, Dong Energy A/S and SSE Plc will get guaranteed power prices for U.K. biomass and offshore wind plants, the first renewable energy projects to benefit from a new aid program. A project by Drax to convert a coal-fired unit at the U.K.’s biggest power plant to burn biomass was on a list of eight that the Department of Energy and Climate Change said had won the new contracts. A second unit, that had been shortlisted in December, was excluded. Five of the projects were for offshore wind, including three by Dong, one by SSE and a venture between Statoil ASA and Statkraft AS. The contracts are the first under a new assistance system for renewables that will guarantee the price generators will get for their power for 15 years. The government said that the eight projects will lead to as much as 12 billion pounds ($20 billion) of investment by 2020, supporting 8,500 jobs and adding as much as 4.5 GW of generating capacity. The government is trying to spur 110 billion pounds of spending on power plants and the grid by 2020, while meeting binding renewable energy and carbon emissions targets. (www.bloomberg.com)
Yingli expects debt pressure to ease as solar shipments increase
April 23, 2014. Yingli Green Energy Holding Co., the world’s largest maker of solar panels, expects its debt burden to ease as higher shipments edge the company closer to turning a profit after three consecutive annual losses. Yingli Energy (China) Co. is forecast to return to profit in the second quarter, while the listed company may do so in the third, Chief Financial Officer (CFO) Wang Yiyu said. China’s clean-energy industry faces record debt payments this quarter, heightening risks after panel maker Shanghai Chaori Solar Energy Science & Technology Co. became the country’s first onshore bond issuer to default. Yingli, whose American depositary receipts have dropped 11 percent since Jan. 1, had $1.11 billion in short-term debt at the end of 2013. China International Capital Corp., an investment bank, flagged Yingli Energy (China) Co. as one of 12 companies with outstanding onshore bonds in “great need” of more scrutiny. Yingli Energy must pay interest on May 3 on bonds due 2015 and 2017. (www.bloomberg.com)
Geothermal power installations grow most since 1997
April 23, 2014. Geothermal power producers added the most capacity since 1997 last year as developing nations in Asia and other regions seek alternative energy sources, while installation declined in the U.S., according to the Geothermal Energy Association. The industry added 530 MW of new power plants and total installed capacity now exceeds 12 GW worldwide, the Washington-based trade group said in its annual report. Geothermal power is growing at 4 percent to 5 percent annually. New U.S. capacity fell 43 percent from 2012 to 85 MW as low prices for natural gas and inadequate transmission infrastructure helped curb demand for geothermal power. With more than 3.4 GW in operation, the U.S. is the biggest market, and it’s bucking the global trend. Almost 700 geothermal power plants are under development in 76 countries, often in developing nations seeking to exploit clean sources of power to drive economic growth. (www.bloomberg.com)
[1] The data and historic information on the fertiliser segment is from the book ‘The Political Economy of International Oil and the Underdeveloped Countries,’ by Michael Tanzer, 1966, Beacon Press, Boston
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.