-
CENTRES
Progammes & Centres
Location

In a world grappling with the dual challenges of personal health and environmental sustainability, the concept of sustainable nutrition emerges as a beacon of hope and conscientious living. At its core, sustainable nutrition is a holistic approach that transcends the mere act of eating for sustenance. It is rooted in three fundamental pillars: environmental responsibility, social equity, and economic viability (figure below). This triad forms the basis for a dietary philosophy that goes beyond personal well-being to embrace the interconnectedness of human health with the health of the planet.
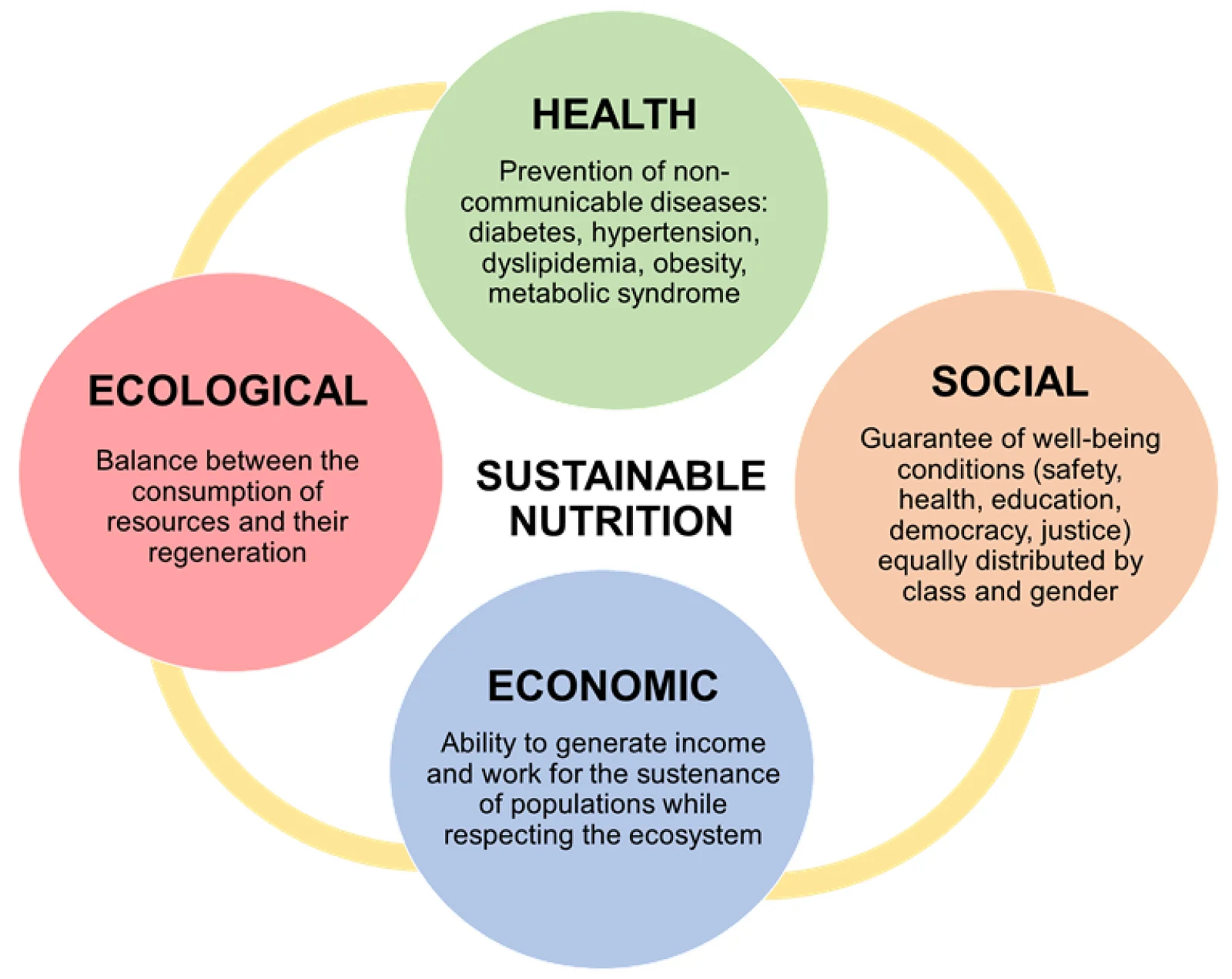
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353698829_Towards_a_More_Sustainable_Nutrition_Complementary_Feeding_and_Early_Taste_Experiences_as_a_Basis_for_Future_Food_Choices
The environmental aspect of sustainable nutrition examines the ecological footprint of our food choices. It challenges us to consider the impact of our dietary preferences on land use, water resources, and greenhouse gas emissions. From farm to fork, the lifecycle of our food contributes to the larger narrative of environmental sustainability. Social equity within the framework of sustainable nutrition calls for the inclusivity of our food systems. It prompts considerations about food access, labor conditions within the agricultural sector, and the equitable distribution of resources. Economic viability acknowledges that sustainable practices must be economically feasible in the long term. It challenges the misconception that eco-friendly and socially responsible choices are inherently more expensive or impractical. In fact, sustainable nutrition recognizes the value of investing in practices that ensure the resilience and longevity of our food systems.
From farm to fork, the lifecycle of our food contributes to the larger narrative of environmental sustainability.
A plant-centric approach often characterizes sustainable nutrition, recognizing the environmental benefits of reducing reliance on animal products. This doesn't necessarily mandate a strict vegetarian or vegan diet but advocates for a mindful balance that minimizes the environmental impact of our dietary choices. Mindful eating practices are another cornerstone of personal nourishment within the realm of sustainable nutrition. The crux of sustainable nutrition lies in its recognition that our dietary choices have far-reaching consequences on the health of the planet. This environmental imperative challenges us to adopt practices that not only sustain ourselves but also contribute positively to the ecosystems that support life on Earth.
By minimizing ecological footprints, sustainable nutrition seeks to reduce the environmental impact of food production and consumption. This involves choosing foods with lower carbon footprints, supporting sustainable agriculture practices, and minimizing the use of resources such as water and energy in the food supply chain. Also emphasizing the importance of biodiversity in ecosystems, sustainable nutrition supports agricultural practices that preserve and enhance biodiversity, like promoting diverse crop varieties, reducing monoculture, and preserving natural habitats. Diversity in our food choices, particularly embracing locally sourced and indigenous ingredients, becomes a celebration of culinary biodiversity that is environmentally sustainable and contributes to community identity. Central to this environmental narrative is an examination of food production methods. Sustainable agriculture, with its focus on regenerative practices, minimizes soil degradation, preserves biodiversity, and mitigates the use of synthetic inputs. The goal is to create a harmonious relationship between food production and the natural environment, recognizing that the health of one is intricately linked to the health of the other.
Sustainable nutrition advocates for fair and ethical treatment of workers within the food system. This includes supporting fair labor practices, ensuring equitable access to food resources, and addressing issues of social justice within the food supply chain. Promoting food security is a key aspect of social equity. Sustainable nutrition encourages policies and practices that ensure all individuals have access to nutritious and culturally appropriate food, addressing issues of food affordability and distribution.
Sustainable nutrition encourages and ensures responsible consumption by reducing waste at the consumer level and prioritizing recycling, resources invested in food production are utilized more efficiently.
Economic Viability by recognizing the importance of supporting local farmers and businesses. This principle encourages consumers to choose locally produced and sourced foods, fostering economic viability within communities and reducing the environmental impact associated with long-distance transportation. It promotes investments in practices that ensure the long-term resilience and viability of the food system by supporting agricultural methods that are economically viable, environmentally sustainable, and socially responsible. Reducing food waste emerges as a critical component of nourishing the planet sustainably. The staggering amount of food that goes uneaten contributes not only to economic losses but also to environmental degradation. Sustainable nutrition encourages and ensures responsible consumption by reducing waste at the consumer level and prioritizing recycling, resources invested in food production are utilized more efficiently.
The adoption of sustainable nutrition practices proves to be a pivotal solution to the challenges posed by climate change, deforestation, and resource depletion. By embracing plant-based diets, reducing food waste, and supporting local and regenerative agriculture, individuals can actively contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the mitigation of environmental degradation. Moreover, sustainable nutrition recognizes the importance of ethical treatment of animals, emphasizing humane practices and responsible sourcing. Thus achieving harmony on the plate involves a symbiotic relationship between the choices we make for our nourishment and the impact on the planet. By adopting sustainable eating habits, people are contributing to a healthier, more balanced world, creating a future where eating is seen as a conscious and meaningful part of our collective mission to create a more sustainable and more harmonious world.
This commentary originally appeared in Illuminem.
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.

Dr. Shoba Suri is a Senior Fellow with ORFs Health Initiative. Shoba is a nutritionist with experience in community and clinical research. She has worked on nutrition, ...
Read More +