-
CENTRES
Progammes & Centres
Location

The Electricity Act 2003 (EA 2003) established a framework for increasing the offtake of power generated from variable renewable energy (RE) sources by authorising state regulatory commissions (SERCs) to specify that a percentage of the total consumption of electricity in the area of a distribution licence should be RE based. In addition to the provision for grid connectivity from the source of generation to the consumer and open access for all generators enabled by EA 2003 provide the legal and regulatory framework for RE adoption along with competition between retail suppliers.
RE adoption by state distribution companies (discoms) is difficult to quantify accurately as power consumption (as opposed to generation) by fuel (coal, natural gas, nuclear, hydro, wind, solar, small hydropower, biomass and others) state-wise is not readily available. If RE-based power generation including large hydro is used as a proxy for RE adoption, “hydro-rich” states like Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland come out on top, as large hydropower accounted for 100 percent of power generation in each of these states in 2022-23. States that are not hydro-rich, such as Tripura had the lowest share of RE generation at 0.10 percent of total generation, followed by Bihar at 0.52 percent and Chhattisgarh at 0.52 percent in 2022-23.
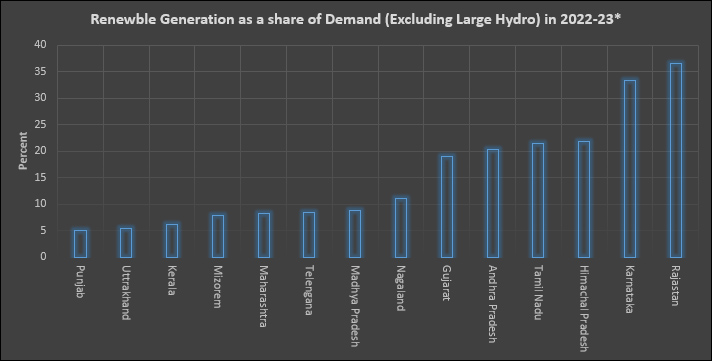
If generation from large hydro is excluded (as it depends on resource endowment rather than on policy or cost-based RE adoption), Rajasthan, Nagaland, Karnataka and Gujarat come out on top. In 2022-23, over 38 percent of power generation in Rajasthan and Nagaland was from RE sources (excluding large hydro), followed by Karnataka at 34 percent and Gujarat at 31 percent. Tripura and Sikkim, with 0.10 percent of RE generation (not including large hydro) have the lowest share of RE, followed by Bihar and Arunachal Pradesh at 0.52 percent and Jharkhand at 0.94 percent.
Regarding RE (including large hydro) as a percent of state electricity demand in 2022-23, Sikkim was far ahead of other states as it generated more than 10 times its electricity demand from RE, all of it derived from large hydropower. Arunachal Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh also generated 3-4 times their electricity demand from hydropower. Tripura had the lowest share of RE meeting demand at 0.31 percent, including large hydro. It was followed by Delhi at 0.56 percent and Bihar at 0.65 percent in 2022-23.
If large hydro is excluded, “RE rich” states come out on top. In 2022-23, Rajasthan generated over 36 percent of electricity demand from RE sources followed by Karnataka at 33 percent and Tamil Nadu at over 21 percent. As in the case of hydro power, the key driver of higher RE generation in these states is favourable wind speed and solar insolation. In addition to Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh and Kerala, these states are among the states classified as “RE rich”. On average, India’s RE-rich states have a higher share of RE generation than most countries internationally. The states with the lowest RE share in demand (not including large hydro) are the same as those in the case of RE including large hydro. Overall resource endowment (water, sun, wind) appears to be strongly correlated with RE generation and adoption.
As of 2022-23, the ownership and operating model of electricity distribution companies do not seem to influence RE adoption. Discoms of the three top-performing states in 2022-23 were state owned discoms, though some had enlisted the services of a distribution franchisee (DF). DFs are expected to source power from the distribution licensee which limits choice over source of power. The financial status of the discoms too does not seem to influence RE generation. The discoms of Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu are rated poorly on financial sustainability and economic efficiency in the annual integrated rating of power distribution utilities brought out by the Ministry of Power (MOP) for 2021-22. The three DFs under the discom of Rajasthan are ranked 19th, 29th and 39th out of 57 distribution companies with C and C- ratings while the discom of Tamil Nadu is ranked 49th with a C- rating and a cautionary “red card” indicating precarious financial status. The DFs under the discom of Gujarat however are ranked among the top 10 distribution companies with an A+ rating.
SERCs that were set up as mandated by EA 2003, imposed renewable purchase obligations (RPOs) on discoms to purchase a certain percentage of electricity from RE sources. With the amendment of tariff policy in January 2016, SERCs were required to reserve a minimum percentage for the purchase of solar energy to reach 8 percent of total consumption of energy, excluding hydropower, by March 2022 or as notified by the central government from time to time. In July 2018 the central government notified the long-term growth trajectory of RPOs for solar as well as non-solar RE, uniformly for all states and union territories, reaching 21 percent of RPO by 2022 with 10.5 percent for solar based electricity. RPO share beyond 2021-22 as per MOP order dated 22 July 2022 is expected to touch 43 percent of total energy consumption by 2030. For 2022-23 the total RPO target including hydro purchase obligation (HPO) is 24.61 percent.
On compliance of RPO targets, “hydro-rich” states score better than “RE rich” states. In 2022-23, Sikkim led the rankings with 88.4 percent RPO compliance followed by Himachal Pradesh at 78.2 percent and Uttarakhand at 60.4 percent. Among “RE-rich” states Karnataka had the highest compliance of 46.7 percent, followed by Kerala at 36.3 percent and Andhra Pradesh at 28.5 percent. RPOs are complimented by RE certificates (RECs), a tradable market-based instrument introduced in 2010-11. RECs facilitate compliance with RPO mandates and serve as a channel for alternative valuation for low-carbon electricity generation.
The “must-run” status accorded to solar and wind projects in line with EA 2003 by the Indian Electricity Grid Code 2010 (EGC 2010), a technical directive to maintain grid stability added to the attractiveness of investing in RE-based power generation in “RE-rich” states. The “must-run” status, accelerated depreciation, waiver of interstate transmission (ISTS) charges, RPOs that were enforced by SERCs and long-term power purchase agreements of up to 25 years added to the attractiveness of the market for RE based power with predictable, relatively stable and long-term returns. India’s ambitious targets for RE capacity addition also attracted low-cost finance from multilateral development banks that substantially improved the competitiveness of RE projects. These, along with a slew of upstream incentives such as the notification of competitive bidding guidelines for the procurement of solar and wind power under EA 2003; priority lending status for RE projects; green energy corridor (GEC) for installing transmission lines and sub-stations and procurement of electricity from 2500 megawatt (MW) ISTS grid-connected wind power projects with up to 20 percent blending with solar PV power through a transparent process of bidding makes RE generation, procurement, and consumption attractive for distribution companies.
Overall, the key drivers of RE adoption by discoms are resource endowment (“RE-rich” and “hydro-rich”) and government policy push. In other words “nature” and “nurture” (financial and non-financial subsidies and incentives) are key to RE adoption by discoms. This raises some questions over the progress of market-oriented reforms in the electricity distribution sector.
Source: Monthly Reports from Central Electricity Authority & Grid-India; *states with share > 5 percent
Demand Growth
According to International Energy Agency (IEA), India’s demand for electricity for running household air conditioners (ACs) is estimated to expand nine-fold by 2050 and will exceed total power consumption in the whole of Africa. As per the agency India will see the largest energy demand growth of any country or region in the world over the next three decades. It projected India’s energy supply to rise from 42 exajoules (EJ) in 2022 to 53.7 EJ in 2030 and 73 EJ in 2050 under stated policies scenarios and 47.6 EJ by 2030 and 60.3 EJ by 2050 as per announced pledges. Electricity consumption due to space cooling increased 21 percent between 2019 and 2022, and today nearly 10 percent of electricity demand comes from space cooling requirements. The growth in ownership and use of air conditioners and other cooling equipment is one of the key drivers of the increase in peak electricity demand in India.
India’s electricity consumption grew nearly 8 percent to about 847 billion units (BU) in the first half of this fiscal year from April to September, showing uptick in economic activities in the country. According to the data, electricity consumption rose to about 847 BU during April-September 2023 from 786 BU in the same period of the previous fiscal. The industry experts opined that the widespread unseasonal rain in April, May and June has affected the power consumption as it could have grown in double digits in the country.
Electricity Trade
NLC India Ltd (NLCIL) has emerged as the successful bidder for supply of power to Rajasthan at a tariff of INR2.64 per unit. The company had participated in a tender floated by Rajasthan Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Limited (RRVUNL) for procurement of power from 810 MW Grid Connected Solar photovoltaic power projects to be set up in 2,000 MW Pugal Solar Park in Bikaner, Rajasthan.
India has allowed Nepal to sell electricity generated through two hydropower projects in its real-time energy market starting, according to the Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA). It is for the first time that India granted project-wise approval ensuring that Nepal could sell hydroelectricity in India’s Real-Time Market (RTM). The Central Electricity Authority of India has allowed the trading of 44 MW of electricity generated from the 19.4 MW Lower Modi and 24.25 MW Kabeli B-1 hydropower projects in the real-time market in the first phase, according to NEA. Nepal is currently selling 13,000 MW of electricity to India on a daily basis. India has been allowing Nepal to sell its power in its day-ahead market since November 2021.
Transmission
The Union Cabinet approved INR207.73 bn (US$2.49 bn) to set up a transmission line for evacuating power from for 13 GW renewable energy project in Ladakh. Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced setting up a 7.5 GW Solar Park in Ladakh. After an extensive field survey, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) prepared a plan to set up a 13 GW Renewable Energy (RE) generation capacity along with a 12 gigawatt hour (GWh) Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) in Pang, Ladakh.
The Warora-Kurnool Transmission (WKTL), spanning 1,756 circuit kilometres (ckm) across Maharashtra, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh, was fully commissioned by Adani Energy Solutions Limited (AESL). The project will strengthen the national grid to ensure seamless power flow of 4500 megawatt (MW) between the western and southern regions, it said. The project will also enhance the southern region grid and support large-scale generation integration from renewable energy sources, it said. WKTL was incorporated in April, 2015 to establish an additional inter-regional alternate current link for import into southern region, i.e., Warora-Warangal and Chilakaluripeta-Hyderabad-Kurnool, along with the creation of a 765/400 kV (kilovolt) sub-station in Warangal.
Adani Energy Solutions Ltd’s shares were up by 0.12 percent after the company commissioned the Kharghar-Vikhroli Transmission Ltd (KVTL) project. The project addresses the need for additional power in Mumbai, given the city’s burgeoning electricity demand. In the wake of recent grid failures in Mumbai, the Kharghar-Vikhroli line will ensure an additional 1,000 MW of power supply. The project grants Mumbai a 400 kilovolt (kV) grid within its municipal boundaries. KVTL encompasses approximately 74 circuit km of 400 kV and 220 kV transmission lines, along with a pioneering 1,500 MVA (megavolt-ampere) 400 kV Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) at Vikhroli.
Sterlite Power has acquired Beawar Transmission Ltd for developing an electricity transmission project in Rajasthan. Beawar Transmission is a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) of REC Power Development and Consultancy Ltd. The SPV was awarded to Sterlite Power through tariff-based competitive bidding in August. Through the Beawar Transmission Ltd, the company will build the Green Energy Corridor project on Build, Own, Operate, Transfer (BOOT) basis, for a period of 35 years. This is Sterlite Power’s 19th power transmission project in India acquired through tariff-based competitive bidding. The Beawar Transmission will entail construction of three integral components. Initially, a 350 km 765 kV (kilovolt) transmission corridor connecting the renewable energy zone of Fatehgarh III to the substation at Beawar will be developed. Then, a 3,000 MVA (megavolt-ampere) 765/400 kV Substation at Beawar will be constructed and finally, there will be construction of two LILO lines, covering approximately 120 km. Sterlite Power is a leading private sector power transmission infrastructure developer and solutions provider with a robust portfolio of 32 completed, sold and under-construction projects covering about 15,350 circuit km of transmission lines across India and Brazil.
Discom Reform
Uttar Pradesh (UP) power ministry directed officials to ensure uninterrupted supply of electricity across the state for the next four weeks covering festivals like Navratri, Dussehra and Diwali. As per the ministry all discoms (distribution companies) are working to replace old power lines and poles with new ones. Transformer capacity is being increased to solve the problem of low voltage. Maintenance work is being done on a large scale in the entire state at the cost of INR220 million, which will ensure uninterrupted supply of electricity.
Recognizing the crucial role of electricity in agriculture, Karnataka Energy Minister affirmed that the government is committed to providing 5 hours of uninterrupted power supply to farmers. Earlier the Minister held a review meeting with the Managing Directors of Electricity Supply Companies (ESCOMs) and urged them to implement efficient measures to ensure uninterrupted power supply to farmers. To ensure seamless implementation of the same, Nodal Officers have been appointed district-wise among Chief Engineers, overseeing the provision of an uninterrupted 5-hour power supply, following the directives of the Chief Minister. Action will be taken to purchase short-term electricity deficit, taking the approval of the KERC (Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission). The minister explained that Section 11 of the Electricity Act has been invoked under national disaster management to procure electricity from power generators in the State and the power shortage would be overcome.
The Assam government approved a INR51.97 bn (US$ 23.65 mn) project to modernise the power distribution infrastructure across the state. The detailed project report for the implementation of the distribution infrastructure work in the power sector got a cabinet nod. The project for modernising the power distribution system of Assam will be implemented under the Union government’s Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme.
In a bid to meet the electricity requirements of Kerala, the state government decided to urge the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) to reinstate contracts in the power sector that it previously denied permission to. The state government would give this direction to the CERC under Section 108 of the Electricity Act. State Power Minister K Krishnankutty said that the key regulator is legally bound to follow the direction of the state government. The decision was taken considering public interest and to ensure that the state would not experience a power crisis. Meanwhile, the Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) Officers' Association welcomed the cabinet decision. The regulator’s decision to cancel the contract that provided 465 megawatt (MW) of electricity to Kerala would have caused a power crisis in the state and also put a huge financial burden on KSEB and the consumers. The association congratulated the state government for invoking its special powers through Section 108 to direct the commission to reinstate the contract.
The Meghalaya Cabinet approved a proposal to clear INR5.65 bn (US$67.84 mn) pending power dues of NTPC Ltd in 20 instalments, state Power Minister AT Mondal said. The proposal of the Meghalaya Power department was approved by the state cabinet chaired by Chief Minister Conrad K Sangma. Mondal said the department has moved the NTPC for negotiation after the power dues rose to INR6.65 bn. If allowed to continue the dues would soon cross INR10 bn and create a burden for the Meghalaya Power Distribution Corporation Ltd (MePDCL), Meghalaya Energy Corporation Ltd (MeECL) and also for the state government. The Meghalaya power minister said that earlier the state government had availed the Atmanirbhar loan and cleared 50 percent of the accumulated power dues of INR4.88 bn to NTPC.
Adani Group bagged two contracts worth INR138.88 billion (bn) ($1.67 bn) from a state-owned discom (distribution company) to install smart meters. A total of six tenders were awarded by the Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company Ltd (MSEDCL) to install smart meters, of which two have been bagged by the Adani Group. The diversified group, which has a sizeable presence in the power sector and had recently won a INR10 bn (US$ 120 million (mn)) contract to install smart meters in the area serviced by BEST Undertaking in Mumbai, will act as an advanced metering infrastructure service provider for smart prepaid metering in MSEDCL, it said. The two zones awarded to Adani include Bhandup, Kalyan and Konkan having 63.44 lakh meters, and Baramati and Pune having 52.45 lakh meters, it said. The group’s transmission arm Adani Energy Solutions, which was earlier known as Adani Transmission, is active in the smart meter segment. Adani Group will emerge as the largest smart meter supplier in the country, commanding a 30 percent share of the market. It has already won contracts to install such meters in four to five states.
Regulation and Governance
Tata Power Delhi Distribution Ltd (Tata Power-DDL) appealed to the residents of the capital to avoid burning effigies near electrical installations and overhead power lines during Dussehra celebrations. Tata Power-DDL has appealed to citizens to avoid burning effigies of Ravana, Kumbhakarna and Meghanada near electrical installations and overhead power lines during Dussehra celebrations as it may be dangerous and can interrupt power supply and other essential services resulting in inconvenience to all. The power distribution company (discom) is organising an extensive safety drive for its consumers and field staff to reduce the chances of electricity-related incidents.
Nearly 25 years after their homes plunged into darkness due to damage to infrastructure by Naxals, 342 families from seven remote villages of insurgency-hit Sukma district are back on the electricity supply grid. In the late 1990s, these villages had to bear the brunt of Left Wing Extremism after Naxalites ran amock in the area, destroying electricity poles and other infrastructure and depriving the locals of basic facilities.
Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) administration has been able to provide more electricity to the people compared to the previous years, but the losses have also increased, Lieutenant Governor (LG) Manoj Sinha said. According to LG, the recently approved 13 gigawatt (GW) renewable energy project in Ladakh would benefit J&K a lot as it would reduce dependence on hydroelectricity which diminishes during the winter.
Delhi Chief Minister (CM) Arvind Kejriwal approved a policy direction proposed by the power minister Atishi to enhance public safety and ensure timely assistance to electrocution victims. The policy aims to control accidents caused by electricity and provide financial assistance to the victims in Delhi. A policy will soon be introduced to control accidents caused by electricity and provide financial assistance to the victims in Delhi. The proposal from the Power Ministry was presented to Kejriwal by the Atishi. Keeping the welfare of Delhiites a top priority, the Chief Minister approved this proposal immediately. DERC is responsible for regulating all the discoms (distribution companies) located in Delhi. Section 108 of the Electricity Act empowers the government to issue directions to DERC for policy formulation. Delhi Chief Minister (CM) Arvind Kejriwal has said his government is providing free and round-the-clock electricity supply as he has the god’s blessings. Kejriwal said only two states, Delhi and Punjab, ruled by the AAP (Aam Aadmi Party) have provided free electricity, whereas in other states people are paying higher bills and yet faced hours-long power cut.
Global
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the world must add or revamp 80 million kilometres (km) of power grids by 2040 – equal to all grids globally – to meet national climate targets and support energy security. Annual investment in grids, which has remained broadly stagnant, needs to double to more than US$600 bn a year by 2030, the IEA said in its Electricity Grids and Secure Energy Transitions report. The report found that existing electricity grids had not been keeping pace with the rapid growth of key clean energy technologies such as solar, wind, electric cars and heat pumps.
Asia Pacific
Japan’s government is set to decide to extend gasoline, natural gas and power subsidies to the end of March that were set to expire at the end of 2023. The extension of the subsidies, which were previously extended to the end of 2023 in August, will be featured in an economic package Prime Minister Fumio Kishida’s cabinet plans to compile. The subsidies for gasoline, electricity and gas utilities were seen as urgent because the government wants to reduce the burden on Japanese firms to keep alive the momentum towards wage hikes at the annual labour talks in March.
Japan’s biggest power generator JERA will decommission three oil-fired power stations with a combined capacity of 2.6 GW at Hirono in eastern Japan. The move comes as the company is replacing old thermal power plants with new ones with less emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2). JERA, a joint venture between Tokyo Electric Power and Chubu Electric Power, will permanently close the 43-year-old 0.6-GW No.1 unit, the 34-year-old 1-GW No.3 unit and the 30-year-old 1-GW No.4 unit, all of which have been shutdown since 2016-2018. JERA is currently replacing 2.99 GW thermal power plants with new facilities. After the decommission, JERA’s capacity of thermal power plants would total 55.77 GW, excluding those under construction.
North & South America
The Biden administration announced US$3.5 bn for 58 projects across the country to strengthen electric grid resilience as extreme weather events such as the deadly Maui and California wildfires continue to strain the nation’s aging transmission systems. Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm said it was the largest federal investment ever in grid infrastructure, supporting projects that will harden electric systems and improve energy reliability and affordability. The federal spending, combined with money promised by private partners, could result in up to US$8 bn in investments nationally to upgrade the grid, Granholm said. Projects funded by the federal Grid Resilience and Innovation Partnerships program will increase the flexibility, efficiency and reliability of electric power systems, with a particular focus on spurring solar, wind and other renewable energy, Granholm said. The largest grant, US$464 mn, will go to improve five transmission projects across seven Midwestern states, from Iowa to North Dakota.
Rapid electrification poses risks to power grids across the US (United States) that are straddling the twin goals of decarbonizing the sector and maintaining reliable supply, grid operators told US lawmakers. Appearing before the Energy, Climate, and Grid Security Subcommittee of the US House of Representatives, officials from all seven of the country’s grid operators said multiplying electricity demand will strain the power supply as the sector shifts from burning fossil fuels towards renewable sources. While new technologies like battery storage develop to become commercially viable and scalable, electric grids will need to keep relying on conventional sources like coal and natural gas. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission recommended revising reliability standards for power grid and natural gas infrastructure to avoid issues during extreme weather.
Europe & Russia
Britain’s electricity and gas grid operators said they expect to have sufficient supplies this winter, with more power generation available than last year and brimming gas stores across Europe, but cautioned geopolitical risks remain. Last year, National Grid’s Electricity System Operator (ESO) warned Britain could face three-hour planned power cuts if the country was unable to import enough gas as Europe grappled with reduced supply from Russia and low gas storage levels. ESO said its base case for de-rated margin, which is a measure of the amount of excess capacity expected above peak electricity demand, is currently 4.4 GW for winter 2023/24, or 7.4 percent of capacity, up from 3.7 GW, or 6.3 percent last winter. ESO will again use its demand flexibility service (DFS) which pays people, usually via money off their bills, for turning off appliances such as ovens and dishwashers during a specific periods when electricity demand is high. Last winter, the scheme saved over 3,300 megawatt hours of electricity or enough to power 10 million homes, but Dyke said it expects to treble the amount of capacity available under the mechanism this year.
Europe’s electricity industry has warned that unprecedented investments are needed to upgrade ageing electricity grids, or the EU (European Union)’s will fail to meet its clean energy targets. The EU’s plans to curb climate change foresee millions more electric vehicles on European roads by 2030, as well as a massive expansion of renewable energy, and electric heat pumps starting to replace fossil fuel boilers in houses. Electricity industry association Eurelectric said that to support those goals, average annual investments in Europe’s electricity grids from now to 2050 need to be at least 84 percent higher than they were in 2021. The European Commission has said power grid investments of €584 bn (US$626.3 bn) per year are needed until 2030 to meet green goals. EU Energy Commissioner Kadri Simson said grid projects will be included in an upcoming list of cross-border infrastructure that will be offered faster permits and access to EU funding. Forty percent of Europe’s power distribution grids are over 40 years old. Most are designed around large centralised power plants, and will need upgrading to distribute power from the fleet of local solar panels and wind farms expected to plug in this decade. EU countries are negotiating power market reforms that could make it easier and faster for grid operators to invest in upgrading networks. However, governments have been struggling to approve the law since June because of a dispute over state aid for power plants.
31 October: India’s Russian oil imports eased in October after prices climbed although supply from Saudi Arabia rose, according to preliminary data from ship tracking agencies Kpler and Vortexa. India, the world’s third biggest importer and consumer of oil, has been binging on Russian oil sold at a discount after Russia was shunned by some western countries following its invasion of Ukraine last year. However, Indian refiners have slowed Russian oil imports in recent months from the nearly 2 million barrels per (bpd) peak seen earlier this year as discounts have narrowed. Data showed a 12 percent and 8 percent decline in India’s monthly intake of Russian oil in October from the previous month to 1.57 million bpd and 1.49 million bpd, respectively. Indian refiners buy Russian oil on a delivered basis and pay for the cargoes after their discharge depending on the terms of the contract and volatility in crude oil markets push up the landed prices.
31 October: India’s crude oil production in September 2023 recorded a steady growth, with a total output of 2.4 million metric tonnes (MMT), according to data released by the Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell (PPAC). The Oil ministry detailed that the lion’s share of the production came from the Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC), which produced 1.5 MMT. Oil India Limited (OIL) contributed 0.287 MMT, while private sector producers added another 0.60 MMT to the tally. The country also saw a 6.1 percent increase in crude oil imports for September 2023, in line with the April-September 2023 period that observed a 0.4 percent growth compared to the same duration the previous year.
26 October: Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) launched India’s first gasoline and diesel reference fuel, used by automobile manufacturers for testing vehicles. Launching the reference fuel, Union Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas Hardeep Singh Puri said, production of these specialised fuel by IOC not only reduces India’s dependence on imports but also catapults country’s energy industry to the select global players armed with exclusive competencies. Reference fuels are required by automobile manufacturers for developing engines and assessing vehicles’ performance to ensure operability in all the global climatic conditions. Currently, these reference fuels are being imported by India from select companies of Europe and the United States (US). The current demand in the country for gasoline or petrol reference fuel is around 120 kl (kilolitre) per annum and demand for diesel reference fuel is around 15 kl per annum. IOC said that at present the company can fully meet the domestic demand and also aims to export the fuel in future by ramping up the existing capacity. IOC has established facilities for production of gasoline reference fuels, with available grades of E0, E5, E10, E20 and E85, at its Paradip refinery and diesel reference fuel (B7 grade) at Panipat refinery. The fuels have been tested in NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories) accredited refinery laboratories, IOC R&D Centre and Intertek (UK and India) laboratories.
31 October: India’s largest gas distributor GAIL (India) Limited posted a bigger-than-expected rise in quarterly profit, buoyed by a boost in its gas transmission volume. Natural gas transmission volume stood at 120.31 million metric standard cubic metre per day, 3.4 percent higher than last quarter. The company’s revenue from natural gas transmission segment rose 56 percent year-on-year. Performance, however, was constrained due to lower realisation in polymers and liquefied natural gas (LNG) which are expected to improve going forward. Last year, GAIL had to cut gas sales to fertiliser and industrial clients after supplies under its long-term deal with the German unit of Russia’s Gazprom were hit when it was taken over by Berlin, which diverted volumes to its own market.
30 October: India’s top gas importer Petronet LNG is not seeking additional volumes when it renews its long-term LNG (liquefied natural gas) deal with Qatar. Petronet has a 7.5-million metric tonnes per year (tpy) long-term LNG import deal with Qatar and its promoters Indian Oil Corp, Bharat Petroleum Corp and GAIL (India) Ltd has a 1 million tpy deal. Petronet previously said that it would seek up to 1 million tonnes per annum of additional LNG when it renews its deal.
30 October: The country’s coal production has picked up momentum in the last 15 days after unprecedented rains in early October in coal producing states, the government said. Total production of coal from all sources during the last 15 days is over 26.40 lakh tonnes per day. The trend of coal stocks at coal-based power plant, which was showing a depletion earlier, is now during the last 10 days registering an accretion trend indicating that the supply and receipt of coal at thermal plants is more than the consumption.
29 October: South Eastern Coalfields Limited (SECL) announced that it had surpassed 100 million tonnes (MT) of coal dispatched for the current fiscal year, achieving a growth of 17.65 percent over the previous year when the Coal India Limited (CIL) subsidiary dispatched 85 MT of dry fuel. Of the total dispatch, more than 80 percent went to the power sector, with the company sending around 81 MT of coal to thermal power plants across the country, according to the company. SECL’s Gevra mine, currently the largest coal mine in the country, contributed 30.3 MT, while Dipka and Kusmunda contributed 19.1 MT and 25.1 MT of coal, respectively. SECL’s Korea Rewa coalfield, where most of the old and underground mines are located, also made a notable contribution of 11.75 MT, an increase of about 20 percent compared to last year when the figure was 9.75 MT. SECL is one of the largest coal-producing subsidiaries of Coal India. The company produced 167 MT of coal and accounted for about one-fourth of CIL's total coal production in FY'23. This year, the company has set a target of 197 MT of coal production.
26 October: The All India Power Engineers Federation (AIPEF) demanded withdrawal of the power ministry’s order extending coal imports till 30 June 2024, saying there is no shortage of the dry fuel in the country. In a 23 October notification, the government asked imported coal-based power plants to operate at full capacity until 30 June 2024, amid a surge in electricity demand and inadequate domestic coal supplies. Earlier, the directive was extended till 31 October 2023. The government in March this year issued the first directive under Section 11 of the Electricity Act to ISB (imported-coal based) plants. AIPEF Chairman Shailendra Dubey demanded that the power ministry’s directive be withdrawn and the more economic indigenous coal be utilized instead as there is no shortage of indigenous coal. The data and statistics released by the coal ministry indicate that coal import was not justified, and coal stock on 21 October 2023 was 71.35 million tonnes (MT) as against 60.44 MT last year. The power ministry issued an advisory to domestic coal based plants to increase ceiling of imported coal for blending from four percent to six percent.
25 October: India has extended by eight months the operation of power plants using imported coal, as high consumption and poor supply deplete domestic stocks of the fuel, according to a government order. The order invoked emergency powers in asking such plants, with a capacity of nearly 17 gigawatt (GW), to operate so as to meet high demand for electricity until next June. Indian power plants that use imported coal, such as those owned by Tata Power and Adani Power, stop operations when prices of fuel shipments rise. The extension came as worries mount over shrinking coal stocks at power plants, where inventories fell in the first half of October at their fastest in two years.
25 October: Coal India Ltd (CIL) will auction fuel linkages for non-regulated sectors in the month of July every year, according to a tentative auction calendar released by the PSU. Each round of auction is expected to be completed within nine months from the date of commencement of the sale of linkages. The sequence of sub-sectors under non-regulated sector (NRS) linkage auction includes sponge iron, cement, captive power plant and steel (coking), according to CIL’s tentative calendar notice on NRS linkage auction.
29 October: The central government has asked states that they have no power to impose any tax or duty on electricity generated from any source - coal, hydro, wind or solar and any such levy is illegal and unconstitutional. In a circular, the Union Ministry of Power, said it had come to the notice of the central government that some state governments had imposed additional charges on generation of electricity from various sources under the guise of development free/charges/fund.
26 October: Police have registered an offence against two brothers for allegedly stealing electricity worth more than INR16 lakh at Taloja in Navi Mumbai since 2017. The power theft came to light after a flying squad of the Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company Ltd (MSEDCL) conducted an inspection and found that the electricity meters at two premises owned by the duo were tampered with. During the operation, the MSEDCL squad detected power meters of the two premises owned by the duo in Taloja, including a gym, were tampered with to reduce the amount of energy consumption recorded, which resulted in the company suffering losses.
31 October: Driven by the government’s plan to phase out all fossil fuel-based energy generation by 2070, the NTPC Limited is set to make a shift to nuclear power, CK Asnani, chairman and managing director of the Uranium Corporation of India Limited CMD (chairman and managing director) CK Asnani said. Asnani underscored the vital role of nuclear energy in environmental sustainability, highlighting its dual significance in revenue generation and environmental preservation. He emphasised the multifaceted benefits that India’s nuclear prowess has brought to the nation, spanning crucial sectors such as electricity, healthcare, strategic defence, and environmental sustainability. He said that there are four critical imperatives that have guided India’s nuclear trajectory. First, the indispensable link between electricity and national progress. He highlighted India’s strategic imperative to develop nuclear capabilities, citing the end of World War II with the nuclear bombings at Hiroshima and Nagasaki, compelling Japan’s surrender to the USA. He emphasized that India’s pursuit of nuclear arms was essential for its security and stability. He noted the vital role of nuclear deterrence in averting a potential third world war. He discussed medical advancement, which included the role of nuclear medicine, and environmental sustainability as the third and fourth factors guiding the shift towards nuclear energy.
30 October: Waaree Energies has bagged a 200 megawatt (MW) module supply order from ENGIE India for a solar project in Surendra Nangar district of Gujarat. The company is developing the Sayla village project, designated as GUVNL 2, under a 25-year solar power purchase agreement (PPA) with Gujarat Urja Vikas Nigam (GUVNL), it informed. Waaree’s supply mandate with ENGIE is expected to commence from November this year and is likely to complete by February 2024, it stated.
28 October: Punjab Energy Development Agency (PEDA) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL) for setting up 10 compressed biogas (CBG) projects and other New & Renewable Energy projects across the state. HPCL will initially set up 10 Compressed Biogas (CBG) projects with an investment of about INR6 billion. It will also explore the possibilities to establish other New and Renewable Energy Projects in the State. These 10 CBG plants are expected to produce over 35000 ton of Biogas (CBG) and about 8700 ton of organic manure annually, besides generating revenue around INR3 billion annually from the CBG production. The projects will also generate direct employment opportunities for more than 600 persons and about 1500 indirect employment.
27 October: Renewable energy solutions provider Suzlon Group has bagged an order for a 50.4 megawatt (MW) wind power project from Juniper Green Energy. Suzlon will install 16 wind turbine generators with a hybrid lattice tubular (HLT) tower of its new product with a rated capacity of 3.15 MW each.
27 October: Adani Energy Solutions Limited (AESL) announced it has commissioned a new green evacuation transmission project in Tamil Nadu. The project will play a significant role in developing the national transmission infrastructure for the evacuation of wind energy in the Karur-Tiruppur region of Tamil Nadu. Industrial, commercial, and residential consumers will benefit from increased access to reliable and clean energy. The project will also help strengthen the Southern Regional grid and support the integration of renewable energy sources on a large scale. AESL secured this project through the Tariff-Based Competitive Bidding (TBCB) route in December 2021 for a period of 35 years, covering the build, own, operate, and maintain basis.
27 October: Tata Power Renewable Energy Ltd (TPREL) said it has inked a pact for building a 43.75 MW captive solar project for Mukand Ltd, a Bajaj Group firm. Located at Jamkhed in Maharashtra, the installation will generate 99.82 MUs (million units) annually and is expected to offset 54,687 tonne CO2 emissions per year. As per the Power Delivery Agreement (PDA), TPREL will undertake the construction, operation, and maintenance of the captive solar power plant, Tata Power said. The project is scheduled for commissioning by March 2024.
26 October: Replacing natural gas consumption with biogas and biomethane incrementally to 20 percent by 2030 can help India cut liquefied natural gas import bills by US$29 billion between financial years 2025 and 2030, according to a new report. The report from the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), underscores the environmental advantages of expanding biogas projects, including waste management, reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and enhanced renewable energy production. The report identifies several reasons for this, including the absence of a comprehensive market ecosystem, pricing challenges, complex approval processes, and fragmented government support.
31 October: The Sri Lankan government has renewed the petroleum products licence granted to Lanka IOC (LIOC), the local subsidiary of Indian Oil Corporation (IOC), for another 20 years. The licence originally issued in 2003 was to expire in January 2024. This will allow Lanka IOC to continue its retail operations on the debt-trapped island nation until 22 January 2044. The government has renewed the petroleum products licence granted to Lanka IOC, the local subsidiary of Indian Oil Corporation, for another 20 years. The LIOC holds around 20 percent of the market share in the auto fuel segment in Sri Lanka. When Sri Lanka plunged into an economic crisis with no forex to import petroleum products, the LIOC operation became crucial in the energy sector. It operates over 200 retail outlets throughout the island nation.
31 October: The World Bank said it expected global oil prices to average US$90 a barrel in the fourth quarter and fall to an average of US$81 in 2024 as slowing growth eases demand, but warned that an escalation of the latest Middle East conflict could spike prices significantly higher. The World Bank’s latest Commodity Markets Outlook report noted that oil prices have risen only about 6 percent since the start of the Israel-Hamas war, while prices of agricultural commodities, most metals and other commodities "have barely budged." The World Bank's "large disruption" scenario approximates the impact of the 1973 Arab oil embargo, shrinking the global oil supply by 6 million to 8 million bpd. This would initially drive up prices to US$140 to US$157 a barrel, a jump of up to 75 percent. The World Bank report said that China’s oil demand was surprisingly resilient given strains in the country’s real estate sector, rising 12 percent in the first nine months of 2023 over the same period of 2022. Oil production and exports from Russia have been relatively stable this year despite Western-imposed embargoes on Russian crude to punish Moscow over its invasion of Ukraine, the World Bank said.
31 October: United States (US) field production of crude oil rose to a new monthly record in August at 13.05 million barrels per day (bpd), the Energy Information Administration (EIA) said. Output rose 0.7 percent in August from the month prior, the data showed. The previous monthly high was in November 2019, when production reached 13.0 million bpd. The monthly high is still shy of a weekly record for US oil production at 13.2 million bpd, hit in the week to 6 October. Production in the world’s top oil producer recovered slowly over the last three years as companies used record profits to increase dividends and buybacks rather than spending to rapidly increase drilling and production. In Texas, the top US oil-producing state, output in August rose by 0.5 percent to a monthly record of 5.63 million bpd, the EIA data showed. In New Mexico and North Dakota, production rose to nearly 1.80 million bpd and 1.22 million bpd, respectively.
31 October: Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) oil output has risen for a third straight month in October, a survey found, led by increases in Nigeria and Angola and despite ongoing cuts by Saudi Arabia and other members of the wider OPEC+ alliance to support the market. The OPEC has pumped 27.90 million barrels per day (bpd), the survey found, up by 180,000 bpd from September. Production in August had risen for the first time since February. The steady rise in OPEC output is largely being driven by a small number of producers managing to overcome internal or external factors that have curbed supply, such as US (United States) sanctions or unrest. Despite the rise in output, oil prices are finding support from conflict in the Middle East. Nigeria boosted exports in October without any major disruption to shipments, according to shipping data and sources in the survey, increasing output by 50,000 bpd. The country is targeting a further recovery by next year. Angola also boosted exports in October, the survey found.
27 October: Russia’s offline primary oil refining capacity has been revised further up, by 7.7 percent to 4.915 million metric tonnes in October from the previous plan. This will be down by around only 1.9 percent from September. Idle primary oil refining capacity was also revised upwards for November, by 5.7 percent to 1.737 million tons, according to Reuters calculations. The rise in offline refining capacity usually leads to an increase in available crude oil volumes and, subsequently, higher exports. The offline capacity was increased from the initial plan due, in part, to further shutdown extension to 1 November from 12 October for the CDU-8 unit at Gazprom Neft-owned Omsk oil refinery in Western Siberia.
27 October: European Union (EU) discussed diversifying oil stocks and creating a buffer for diesel and gasoil during an emergency meeting of the bloc’s oil coordination group. This month’s conflict in Gaza has revived memories of the 1973 oil shock during the Yom Kippur War, when the Organization for Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) slapped an oil embargo on western supporters of Israel, triggering fuel shortages. The meeting of the EU’s oil coordination group concluded that the risks are much lower than 50 years ago as Europe only relies on oil for about 30 percent of its energy mix, although Saudi Arabia is one of its top three suppliers, the official said. According to an EU directive, member states must have emergency oil stocks equivalent to 90 days of net imports, or 61 days of consumption.
26 October: Brazilian oil company Petrobras said that its crude oil production during the third quarter rose 9.6 percent from the same period last year. Petrobras pumped 2.32 million barrels per day (bpd) in the July-to-September period, the firm said. Brazil is Latin America’s top oil and gas producer, ahead of other major regional petroleum suppliers Mexico, Colombia and Venezuela. Including natural gas output, the Brazilian oil giant produced a daily average of 2.877 million barrels of oil equivalent, up 8.8 percent from the same quarter last year. Around 81 percent of Petrobras output came from Brazil’s so-called pre-salt fields, an oil-rich offshore region off the country’s southeastern Atlantic coast. In the same quarter last year, 73 percent of the company’s oil production came from the same area.
31 October: Pakistan announced a sharp increase in the price of natural gas for most households and industry ahead of the cash-strapped country’s first review of a US$3 billion International Monetary Fund (IMF) bailout. A fixed tariff for 57 percent of household consumers has been raised to 400 rupees (US$1.42) a month, from 10 rupees, the energy minister of a caretaker government. Low- and middle-income households will be charged lower prices and high income households would be charged more, he said. Energy sector debt has been the main issue that the IMF has highlighted in tackling the fiscal deficit and it has been recommending measures to deal with it.
27 October: United States (US) liquefied natural gas (LNG) company Freeport LNG received approval from federal energy regulators to take more steps to return its export plant in Texas to full operation. A return to full operation would allow the plant, which shut for about eight months from June 2022 to February 2023 after a fire, to supply more LNG to global markets ahead of the winter heating season when demand for natural gas soars in the Northern Hemisphere. Global gas prices spiked to record highs in Europe and Asia over the summer of 2022 due in part to the Freeport LNG shutdown while Russia was reducing the amount of gas it supplied to Europe after Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine.
26 October: The United States (US) Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) agreed to a revised commissioning plan for Venture Global LNG’s Calcasieu Pass facility, allowing it to turn on three processing trains while work on faulty power equipment continues. The FERC decision supports Venture Global LNG’s argument that it cannot start full commercial operations because it has reliability issues, Rapidan Energy said. Venture Global LNG is involved in contract arbitration with customers Shell, BP, Edison and Repsol that separately seeks to force the company to supply them cargoes or pay financial penalties. Venture Global started gas processing at its Calcasieu Pass facility in March 2022 and has delivered at least 200 cargoes - which it says are "pre-commissioning cargoes" - through September. But the company has not provided cargoes to its contract customers, insisting the facility is not fully commissioned.
25 October: Turkmenistan revived the prospect of creating a pipeline linking its vast gas fields to Europe, as Western countries seek to fill the void left by Russian gas. The idea of building the Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline linking Turkmenistan to Europe has been discussed since the 1990s but never came to fruition amid logistical hurdles. Turkmen leader Serdar Berdymukhamedov said his country -- which has the fourth largest gas reserves in the world -- was again interested in launching new projects. The pipeline, which would run under the Caspian Sea to an existing terminal in Turkey, has faced opposition from competitor Russia as well as questions over its cost effectiveness. Turkmenistan sends most of its gas exports to China, but it is increasingly courting interest from European countries looking to end their dependence on Russia over the conflict in Ukraine.
30 October: China’s maximum power demand this winter may increase by 140 gigawatt (GW) or 12.1 percent from last year’s peak, as electricity usage surges in the second half of 2023. Last winter’s peak demand was 1,159 GW, according to the National Energy Administration (NEA) data. China’s power demand in September rose by 9.9 percent from a year earlier to 781,000 gigawatt hours (GWh), the NEA said. Hotter than normal temperatures have also contributed to higher electricity demand in the second half of the year, NEA said. By comparison, this summer’s record peak demand was about 50 GW higher than the previous summer, or a 3.6 percent increase from last year’s 1,390 GW. While winter power supply is generally guaranteed, shortages are expected in Yunnan province, and there could be power shortages in Inner Mongolia.
30 October: The European Union (EU) plans to invest €60 million (US$63 million) in upgrading one of the Uganda’s largest hydropower plants, helping partially plug a financing gap for the country’s ageing energy infrastructure. The Nalubaale and Kiira hydropower plant complex located at the source of River Nile at Jinja in Uganda’s east produces about 380 megawatt (MW) and is Uganda’s oldest power plant, commissioned in 1954. South African power giant Eskom ran the plant under a 20-year concession that ended early this year, after which the government retook control. Uganda has an installed capacity of about 1,400 MW of power, mostly from its hydro dams, and that will rise to 2000 MW when a Chinese-built plant, Karuma, also on River Nile is commissioned this year.
This is a weekly publication of the Observer Research Foundation (ORF). It covers current national and international information on energy categorised systematically to add value. The year 2023 is the twentieth continuous year of publication of the newsletter. The newsletter is registered with the Registrar of News Paper for India under No. DELENG / 2004 / 13485.
Disclaimer: Information in this newsletter is for educational purposes only and has been compiled, adapted and edited from reliable sources. ORF does not accept any liability for errors therein. News material belongs to respective owners and is provided here for wider dissemination only. Opinions are those of the authors (ORF Energy Team).
Publisher: Baljit Kapoor
Editorial Adviser: Lydia Powell
Editor: Akhilesh Sati
Content Development: Vinod Kumar
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.