-
CENTRES
Progammes & Centres
Location
Through a combination of digital transformation, financing, sustainable agriculture, healthcare strengthening, and education, the G20 nations show strong determination towards shaping a sustainable future

As India assumed the Group of Twenty (G20) Presidency on 1 December 2022 against the backdrop of the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic and Russia-Ukraine tensions, it had embraced an inclusive governance approach to foster multilateralism and address the sustainable development priorities of the Global South. Adopted in 2015, the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Agenda 2030 set out an ambitious blueprint for addressing global challenges and serves as a crucial framework for fostering a comprehensive and interconnected response to global challenges.
A two-way causality exists between domestic and international business environments and the SDGs, with the private sector and multilaterals playing essential roles in achieving these goals. Notably, the private sector is shifting away from short-term profit maximisation to embrace sustainability as a foundation for long-term business strategies. This shift is driven by the recognition that SDGs create favourable business conditions through several vital mechanisms.
Firstly, addressing SDGs reduces long-term environmental, political, and social risks. By proactively tackling these challenges, businesses safeguard their market competitiveness, even in the face of impending policy changes, and diminish long-term "transaction costs" for businesses. Secondly, the pursuit of SDGs promotes transparency in sustainability risks and impacts. This transparency is a positive externality, reducing information asymmetry and enhancing business governance processes.
Thirdly, aligning business solutions with the SDGs unlocks significant market expansion potential, revenue maximisation, and job creation opportunities. This occurs through forming partnerships at various levels, allowing businesses to tap into emerging markets driven by sustainable practices. And fourth, deepening partnerships for SDGs and integrating them into national and corporate budgets enhances business competitiveness, market resilience, and goodwill.
This contention is rooted in the recognition that the SDGs bolster the availability of four critical types of capital: Physical, natural, social, and human. These capitals—the economic linkages highlighted in the following figure—are essential for businesses to thrive and are integral to addressing the multifaceted challenges in the longer horizon.
Figure 1: SDGs and Capitals

Source: Bhowmick (2021), ORF Issue Brief No. 433
However, as the world approaches the halfway point to 2030, it has become evident that progress toward these goals is off-track. The following figure illustrates a blue line representing progress towards the SDGs without COVID19 impacts and a purple line depicting progress affected by those impacts. The grey dashed vertical line indicates the cumulative effects of shock loss and growth delay loss during the recovery phase. To be sure, the extent of progress loss is contingent on the resilience of the respective countries.
Figure 2: Conceptual Description of the Impacts on SDG Progress
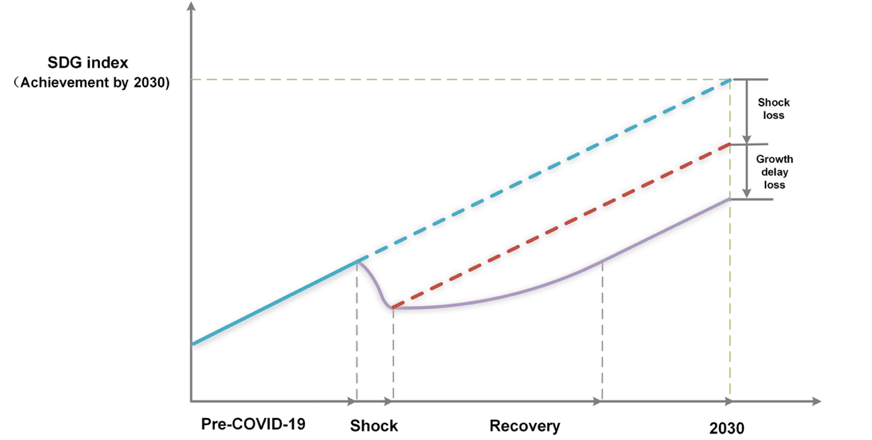
Source: Yuan et. al. (2023), Communications Earth & Environment, Vol. 4 No. 184
With only 12 percent of the targets on track, the G20 nations have reaffirmed their commitment to the SDGs and have outlined a comprehensive plan in the G20 New Delhi Leaders' Declaration, which was launched at the 18th meeting of the G2 hosted by India from 9-10 September 2023. Ten key elements of this commitment include:
Acknowledging the transformative role of digital technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and data advancements in advancing the SDGs, the G20 lends its support to the G20 Principles on Harnessing Data for Development (D4D).
The G20 emphasises the transformative role of culture in achieving the SDGs. The commitment to accelerating progress on the SDGs reflects a collective determination to address global challenges and improve the well-being of all people.
Furthermore, the G20 emphasises the transformative role of culture in achieving the SDGs. The commitment to accelerating progress on the SDGs reflects a collective determination to address global challenges and improve the well-being of all people. Through a combination of digital transformation, financing, sustainable agriculture, healthcare strengthening, and education, the G20 nations show strong determination towards shaping a sustainable future.
Soumya Bhowmick is an Associate Fellow at the Observer Research Foundation
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.

Soumya Bhowmick is a Fellow and Lead, World Economies and Sustainability at the Centre for New Economic Diplomacy (CNED) at Observer Research Foundation (ORF). He ...
Read More +