-
CENTRES
Progammes & Centres
Location

India seems to be cashing in on the availability of affordable natural gas in the form of LNG. India’s LNG imports in November were reported to have seen double-digit growth as relatively low prices attracted buyers. According to latest data published by PPAC, LNG imports in November were 2.01 BCM up 15.47 percent compared with the same month last year. For the April-November period, India’s LNG imports were 16.9 BCM up by 23.2 percent compared to the previous year.
FLNG re-gasification terminals are also attracting attention from Indian investors. Swan Energy which is leading the charge is reported to have got the approval for Rs56 billion from the Government of Gujarat. ONGC, IOC and BPCL have reportedly agreed to take 1 MTPA capacity each on the 5 MTPA floating LNG terminal. Swan Energy, which is building the project in joint venture with Exmar of Belgium, is said to be targeting 2019 for commissioning of the one jetty-moored FSRU at Jafrabad. Plans to expand the capacity to 10 MTPA through deployment of a second FSRU have also been reported in the media. ONGC and IOC own 12.5 percent stake each in Petronet LNG Ltd, which owns and operates a 10 MTPA LNG import terminal at Dahej in Gujarat. This terminal is being expanded to 15 MTPA by January 2017. Petronet also has a 5 MTPA LNG import facility at Kochi. GSPC is building its own L NG terminal in joint venture with Adani Group at Mundra in Gujarat by 2017. Also on the west coast is an under-utilised 5 MTPA Dabhol LNG import terminal, operated by state gas utility GAIL (India) Ltd. The charge of LNG into India’s market for imported gas raises doubts on the prospects for trans-border pipelines such as TAPI. However it was reported that Engineers India Ltd had signed an agreement with Gazprom to study the construction of a gas pipeline to India from Russia. According to Reuters Gazprom wanted to be ‘as big as RasGas in India’ given the country’s market size and its fast-growing economy. Though there is optimism over growth of gas consumption in India, speakers at the Petronet forum lamented that India the world’s third-biggest energy consumer lacks gas import and transport infrastructure that was stymieing faster adoption of natural gas. While India is the world’s fourth-biggest importer of LNG behind Japan, South Korea and China, and is seen as a market on the rise, growth in consumption of the fuel is still far outpaced by growth in consumption of oil and coal. Inadequate natural gas infrastructure has reportedly reduced the share of gas in India’s energy basket to about 6 percent from a high of 12 percent five years ago. India’s LNG imports from Qatar’s RasGas represented around 10 per cent of the Middle Eastern nation’s overall annual output. RasGas has a big presence in India through its 25-year contract with top importer of the fuel, Petronet LNG, and provides more than 50 per cent of the country’s LNG shipments. India renegotiated a long-term LNG supply deal with RasGas last year, nearly halving the price and avoiding a $1.5 billion penalty fee for lifting less gas than agreed as customers there preferred cheaper spot supplies. India’s oil ministry is reportedly planning to invest up to $15 billion in developing pipelines and setting up LNG terminals over the next five years.

Trans-border pipelines in Europe promoted by Russia continued to suffer set-backs. The latest was the refusal by the Swedish island of Gotland for a plan to lease a port to Russian gas pipeline project Nord Stream 2, after the Swedish government expressed disapproval. The Gazprom-led venture had planned to rent a port in the island as marshalling yards and shipment depots to save time and money.
Reacting to lower energy prices, Qatar which has the third largest natural gas reserves in the World after Russia and Iran was said to be merging state-owned LNG producers Qatargas and RasGas. With low prices continuing for more than two years, Gulf countries were reported to be reducing state spending and consolidating as a way to cut costs. The reasons for having two firms to deal with western and eastern markets and also to encourage some competition during the rollout phase of LNG facilities were said be less relevant. Qatargas is the largest LNG producing company in the world, with an annual output capacity of 42 MTPA followed by RasGas with a production capacity of about 37 MTPA.
ExxonMobil predicted that global LNG trade would grow more than 2.5 times from 2015 to 2040. Global gas demand is projected to grow by about 45 per cent during the same period. Demand is expected to grow in all major sectors with the majority coming from the power generation. Asia Pacific is expected to contribute to the majority of the 45 percent growth as its demand doubles by 2040. With the demand growth, LNG exports are expected to diversify. Europe and Asia Pacific are expected to account for about 90 percent of global imports as production decline in Europe is offset by the increase in LNG imports. Natural gas production in North America is expected to continue its growth and become the largest LNG exporter. Despite challenging market conditions, global Capex on FLNG facilities is forecast to increase significantly over the 2016-2022 period. Over 14 countries are expected to commission their first FLNG units in this period.
In terms of LNG supply, global LNG after reached around 250 MTPA in 2015 is expected to surge in 2016 this year due to incremental volumes brought to the market. Asia dominated LNG imports while Europe, the second market for LNG imports, increased LNG volume for the second year as domestic production declined and coal to gas switching took place in the region, driven by rising environmental awareness.
Asia is expected to account for more than 70 percent of the global LNG trade. Currently, low prices, growing environmental concerns and favourable energy policies are driving a robust gas and LNG demand mainly observed in China, India, Taiwan, and Pakistan. These four countries are set to contribute substantially to reach the balance in the global LNG market over the next five years. Many anticipate that China the third largest LNG importer in the world significantly increase its natural gas use as the Chinese government was determined to reduce pollution and increase natural gas share in its energy mix. Some even predict that China would overtake South Korea as the world’s second largest importer of LNG in the near future. India, currently the fourth largest LNG importer is also expected to more than double its gas import capacity. Natural gas production in 2016 is expected to average approximately 3.6 TCM slightly above the 2015 production levels.
However the increase in LNG prices following OPEC announcement that it would cut crude oil production in cooperation with Russia and by a tightening regional gas market raises questions over the continued affordability of LNG for developing Asia. Asian spot prices for LNG increased to around $7.40 per mmBtu their highest levels for 2016 after the OPEC announcement. With 80 percent of Asian LNG supply contracts linked to the price of crude, and oil playing a key role in shipping costs, the spot LNG market was also affected, pushing prices to their highest since November 2015.
However, according to experts, OPEC’s output cut could yield a growing price disparity between more expensive term supplies and cheaper spot cargoes as the gas price link with oil in supply contracts is said to be stronger than oil’s influence in spot markets for gas.
December 27, 2016. The Indian oil and gas (O&G) sector is set for a major fillip in the New Year with the government in advanced stages of awarding O&G blocks under the new Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP). The upcoming launch of the national sedimentary data repository will provide the new exploration policy an additional thrust and help ramp up output. A major highlight of the year gone by was the commissioning of India’s largest public sector refinery – Paradip in Odisha set up by state-run refiner Indian Oil Corp (IOC) – at a cost of Rs34,555 crore in January 2016. The mega refinery is currently operating at 65 percent capacity and is expected to work at an excess of 90 percent capacity utilization beginning 2017, according to IOC. In the New Year, the oil refining sector will also witness activity on the front of the planned 60 million tonnes per annum refinery being built by the three PSU oil firms – IOC, Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd (BPCL) and Hindustan Petroleum Corp Ltd (HPCL) — on the West coast. The companies signed an initial pact last month to construct the refinery at a cost of $30 billion. The project will be undertaken by a consortium of IOC, BPCL and HPCL with a 50, 25 and 25 percent stake, respectively. The detailed feasibility report of the project will be in works over the next year, according to IOC. Analysts said the biggest highlight of 2016 was the OPEC decision to cut output by 1.2 million barrels per day to rein in global glut and prop up prices. The rising oil price scenario will not translate into good news for the downstream refining and marketing companies, research agency India Ratings said.
Source: The Economic Times
December 26, 2016. Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd (BPCL) said cashless transactions at its outlets have jumped to 26 percent after November 8 when high value notes were banned, from 10 percent time before and expects at least half of all transactions to turn cashless by March. Retail sale of oil products — petrol, diesel, CNG/PNG and LPG — in volume terms account for around 7.3 trillion transactions per annum, according to BPCL. Towards achieving this target, BPCL tied up with SBI, HDFC Bank, and some other major banks to install PoS terminals apart from joining hands with Paytm, FreeCharge, Oxigen, Reliance Jio, SBI Buddy, and Fino for enabling mobile-wallet transactions at its retail outlets. BPCL said the three oil marketing companies (OMCs) together have 5,3000 pumps and over 78,000 LPG agencies. These outlets together clock daily transactions worth Rs500 crore (petrol), Rs450 crore (diesel & CNG) and Rs50 crore (LPG), which in volume terms work out to be 7.2-7.3 trillion transactions per day. Before the note ban, BPCL was doing only around 10 percent daily transactions cashless across the country, which was worth only Rs50 crore. Across the state, the cashless transaction for BPCL is around 32 percent of its total sales, BPCL said. BPCL has installed PoS machines at all its filling stations in Mumbai, Navi Mumbai, Thane and Raigad district, BPCL said. BPCL said since the pumps were allowed to dispense cash, over 3,000 pumps together have distributed around Rs155 crore to customers since the note ban announcement.
Source: Business Standard
December 24, 2016. The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) is likely to award around 31 oil and gas blocks to various bidders out of 46 contract areas (or 67 percent) which were put on offer. A final nod for awarding the contract areas to the selected bidders in discovered small and marginal field (DSF) auction will happen only by the third week of January. The oil ministry had indicated that the fields were likely to be allotted to the parties concerned by the end of December. The Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH), which was conducting the bidding, has already forwarded the list of selected bidders to the oil ministry. The ministry is likely to move the Cabinet for its final clearance by the third week of January. Forty-two companies took part in the current round of auction for the small and marginal fields, of which 37 were private companies. The 46 contract areas on offer got a total 134 e-bids and had an estimated reserves of 88 million tonnes of oil equivalent, which, if produced, can cut down India’s oil import bill by Rs3,500 crore annually. After the scrutiny of bids, at least 31 blocks are likely to be awarded to bidders for development.
Source: Business Standard
December 23, 2016. With assembly polls in Goa round the corner, the state government announced six percent reduction in the value added tax (VAT) on petrol, bringing down its price to Rs60 per litre. The BJP-led government had assured that the prices of petrol will not be allowed to cross Rs60 per litre in the state during its term. Former Goa Chief Minister Manohar Parrikar, after coming to power in 2012, had abolished the VAT on petrol bringing down the prices by Rs11 per litre. The state government had then imposed VAT on the petrol, but had assured that the prices would be kept within Rs60 per litre. The recent hike in the petroleum prices across country had forced the price to go beyond Rs60.
Source: NDTV
December 23, 2016. After declaring incentives to encourage cashless purchases of petrol, the government is now assuring users that it is safe to use mobile phones at petrol pumps, albeit within specific safety guidelines. The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP), through its Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organisation, has told the oil ministry that it is completely safe to use mobile phones at petrol stations at a certain height and distance from the pumps. Cashless payments at petrol pumps surged after it was announced that old Rs500 notes would no longer be accepted for transactions. The government had also allowed withdrawal of Rs2,000 at petrol pumps by swiping debit cards through point of sale machines. Various petroleum dealer associations had raised concerns over the use of mobile phones at fuelling stations. Apart from specifying zones where mobile phones can be used, petrol pumps are required to get point-of-sale machines approved by DIPP before using them. The department highlighted special precautions to be taken in case of two-wheelers because of their proximity to fuel pumps during payment transactions. Oil Minister Dharmendra Pradhan, who has been promoting cashless transactions at petrol pumps, had met Commerce and Industry Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently to discuss the safety issues.
Source: The Economic Times
December 22, 2016. Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC)’s declining output has been a cause of concern. While the company has been taking measures to correct the trend, the Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH) is reviewing the company’s production performance. The focus will be on assessing ONGC’s production profile of ageing fields with declining production and also the company’s largest projects under various stages of exploration and development. ONGC’s production performance has been consistently missing targets set by the company. According to the monthly Production Performance data released by Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell (PPAC) for the sector, during the month of November the country’s crude oil production fell 5.40 percent year-on-year. The output from ONGC’s western offshore fields declined 1.97 percent annually. According to the data, one of the reasons cited for ONGC’s output decline was the natural decline from matured and marginal fields of Mumbai High. The country’s domestic gas production also fell 1.71 percent year-on-year, with the output from offshore fields declining by 4.40 percent. ONGC’s performance in gas production too was tepid. But despite the subdued crude oil and gas production numbers, refineries showed a 1.98 percent increase in production over the last year. The cumulative production from April to November grew 8.01 percent with boosted demand for finished petroleum products. Consumption for petroleum products grew by 12.08 percent during November against the same month last year. PPAC data show that LPG consumption grew by 16 percent, petrol by 14 percent and diesel by 10 percent.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
December 21, 2016. India’s oil imports from Iran fell 19 percent in November from a record high the previous month after regional rivals Saudi Arabia and Iraq raised sales to the world’s third-biggest oil consumer, regaining their positions as the top two suppliers. Shipments from Tehran, Western sanctions against which were lifted earlier this year, were about 620,000 barrels per day (bpd) oil in November, according to ship tracking data. That was down from 765,500 bpd in October, but well above 138,100 bpd in November 2016. Supplies from Iran to India more than doubled in January-November to 468,900 bpd from 205,900 bpd in the same period last year, the data showed. Overall, India imported an average 4.28 million bpd of crude in the January-November period of 2016, up 7.6 percent from 3.98 million bpd a year ago. India’s average Iranian oil imports in April-November – the first eight months of India’s financial year – rose 126 percent to 532,100 bpd, the data showed. Tehran’s share in overall purchases jumped to 12.5 percent from 5.9 percent.
Source: Reuters
December 21, 2016. For the past month, 27-year-old Abhinav Sarin has been cooking meals on a mini 5 kg LPG cylinder that he bought from a market at Kondhwa rather than ordering takeout. According to those involved in the business, sale of mini 5 kg liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder has shot up post-demonetization. Many people, especially singles living alone or in groups, have started to cook simple meals at home to save money and avoid eating out. LPG agencies also pointed out that demand for small cylinders has increased since the past month. President of Pune LPG Dealers’ Association Usha Poonawala said that the sale of small cylinders had increased by around 10% post demonetization. LPG retailers agreed adding that documentation required to get the mini cylinders is not a tedious process. Those selling locally-made 5 kg LPG cylinders also said that more and more young professionals are opting for the cylinders. Due to high demand, the seller has increased the price slightly to Rs800 and is subject to bargain.
Source: The Times of India
December 21, 2016. Global investment bank HSBC forecast in its latest report on India’s Trade the position of petroleum products in the country’s imports are set to fall from the current second place to third place between 2015-2030. Data said that India’s import bill in the first six months of the current fiscal stood at $ 174.4 billion down 13.79 percent as compared to corresponding period last fiscal year. Of this, the share of total petroleum imports – including crude oil and petroleum products — stood at $37 billion, around 21 percent of India’s gross imports in value terms during the period. HSBC’s India Trade report further added that the composition of the country’s trading partners will largely reflect reliance on imported crude for domestic energy requirements. While the global investment bank forecasts a weakening of crude’s hold on the countries import bill, it goes on to say the contribution of petroleum products as part of the country’s export is also expected to fall slightly during the 2021-30 forecast period. India’s export bill in the first six months of the present fiscal year stood at $ 131.4 billion down by 1.72 percent as compared to the corresponding period last fiscal year, according to Petroleum Planning and Analysis Cell. Out of which the share of petroleum product export stood at $ 13.5 billion, around 10 percent of India’s gross exports in value terms in the first six months of the current fiscal.
Source: The Economic Times
December 23, 2016. Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) will buy Gujarat State Petroleum Corp (GSPC)’s entire 80% stake in the Deen Dayal West gas field in the Krishna Godawari (KG) basin off the Andhra coast for nearly $1 billion. ONGC will pay an additional $200 million to GSPC, the only oil company in the country owned by a state government, as an advance for six other discoveries in the block. ONGC said the company board approved payment of $995.26 million for GSPC’s 80% stake and operatorship of the field. GSPC has already built production infrastructure. The field, identified as Block KG-OSN-2001/3, was auctioned in the third round of bidding under now-discarded NELP regime. In 2005, the discovery was touted as the largest, with 20 trillion cubic feet of reserves. GSPC was originally scheduled to begin gas production from the field in 2013. But after spending $3.6 billion, it was found that gas reserves are one-tenth of the 20 trillion cubic feet claimed in 2005. Even this lower reserve was considered technically difficult to produce.
Source: The Times of India
December 22, 2016. The government’s plan to more than double the share of natural gas in India’s energy mix to 15 percent would necessitate investments of at least Rs65,000 crore ($10 billion) just to augment gas import and pipeline infrastructure, Crisil Research said. Crisil Research said if the share of gas in India’s energy mix has to rise to 10 percent by 2020, it would mean a doubling of gas consumption to over 100 billion cubic meter from current levels. But given that domestic gas production is limited, demand for imported LNG would surge three-fold to 65 billion cubic meter, or over 50 million tonnes. Collaterally, to import this LNG, India’s regasification capacity will have to increase to 60 million tonnes compared with 25 million tonnes now. Crisil Research said its analysis shows that would entail investments of Rs30,000-35,000 crore. And for all that gas to be consumed, 9,000 km of pipelines would have to be laid in east and south India, which would cost another Rs25,000- 30,000 crore. Crisil Research said to ramp up gas usage, LNG import and pipeline infrastructure needs to be expanded significantly.
Source: The Economic Times

December 27, 2016. Doosan Heavy Industries and Construction has been awarded a $2.3 bn contract to build 2,640 MW of coal-fired power plants in India. The contract was awarded by the Uttar Pradesh government to Doosan Power Systems India (DPSI) for the construction of build two thermoelectric power plants in the region. Under the contract, Doosan will build two power generators, each with 660 MW capacity, at the Obra-C coal-fired electrical power plant in Sonebhadra. The firm will also build another two generators, each with 660 MW capacity, at the Jawaharpur coal-fired electrical power plant in Etah.
Source: Energy Business Review
December 22, 2016. The government has allowed public and private power producers to swap their coal supplies with a view to reducing the cost of electricity by ensuring more efficient fuel usage. It may eventually extend the facility to other coal-consuming industries. The government’s latest move is an extension of its May 4 decision allowing states freedom in utilising coal allotted to their power stations, a move that Power and Coal Minister Piyush Goyal had then said would reduce cost of generation by 40-50 paise per unit and lead to savings of Rs25,000 crore per annum in 4-5 years by enabling supplies from mines closer to the plant. Under the coal use flexibility plan announced in May, all long-term coal linkages -supply quotas from specific mines -of individual power plants in a state are clubbed together and put under the charge of the state government or its nominated agency. Similarly coal linkages of individual power plants of central generation utilities would be clubbed together and put under the charge of the entity. States or the central utilities are then free to make better use of the allotted coal by using them to fire more efficient plants for higher generation rather than waste them in old, inefficient plant for less-than-desired output. They can also swap supplies to rationalise transportation of coal from mines nearer to the plants. In case a state decides that it could get better value by sourcing power generated using this coal to fuel a private power station, the electricity has to be procured through bidding amongst competing private sector plants. The state has to then mention upfront the source, quantity, quantum and delivery point for the power. In case a state or central utility decides to move around coal among its own plants, the deciding criteria would be on plant efficiency, coal transportation cost, transmission charges and overall cost of power. Earlier, the government had allowed swapping of coal mines by users so that transportation cost can be reduced for generation of power. The government has allowed coal swapping in 19 blocks, which brought down the cost of power generation as users were able to source fuel from mines located closer to them.
Source: The Times of India
December 21, 2016. The state government has decided to allow Jindal Steel and Power Ltd (JSPL) power plant to use Jitpur coal block for its 1,600 MW power plant located at Godda. Godda BJP MP Nishikant Dubey said the decision taken would help the revival of the plant that was stalled after the Centre cancelled the permission to use coal blocks by the company earlier. Coal blocks in Godda are owned by the Jharkhand Mineral Development Corp.
Source: The Economic Times
December 27, 2016. In a move that could bring relief to many residents affected by power related issues in developer areas like DLF, Ardee City, Unitech, Sushant Lok, Palam Vihar, among others, Haryana Electricity Regulatory Commission is planning to bring an amended Act regulating single point connections. The residents of developer areas had filed a complaint at the CM Window, alleging that they were being made to pay higher electricity bills, as the builders had taken a load of only 5MVA against the required 15MVA, and thereafter, were dividing the load among 2,500 houses against the 1,500 houses officially sanctioned. They also alleged that the developers were availing a 4% discount for bulk supply without passing it on to residents. On top of that, the developers were making the residents pay an extra 12% service charge. According to the electricity board, the discom supplies power to the developer (single point) in these areas, and then the developer distributes it among residents.
Source: The Economic Times
December 26, 2016. The burden of subsidising the power bills of agricultural and low-income families is set to move from industrial consumers to large domestic and commercial consumers of electricity. The government plans to introduce a new tariff structure to charge more from large domestic power consumers rather than industrial units that currently share the cross subsidy burden. Most states categorise households consuming more than 800 units of power a month as large domestic consumers. The government is also working on simplifying tariff patterns by classifying consumers in two to three categories and sub-categories to bring transparency in power billing. Nowhere in the world except India are power consumers charged for regular payments and bulk consumption. These patterns have never been altered though tariffs have changed over the years. Encouraging industrial units to increase power usage is the need of the hour since India has moved away from being a power-deficit country to a power-surplus country, the power ministry said. Industrial units can absorb the excess generation capacity of power plants operating at about 60% of capacity due to lack of demand from distribution utilities and an ongoing economic slowdown.
Source: The Economic Times
December 26, 2016. NTPC said its total installed capacity increased to 48,028 MW following the commissioning of 800 MW unit at Kudgi in Karnataka. NTPC has a capacity of over 23,000 MW under implementation at 23 locations across the country, including 4300 MW being undertaken by joint venture and subsidiary companies. NTPC wants to be the world’s leading power company in a bid to energise India’s growth and plans to become 130 GW company by 2032.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
December 25, 2016. The inter-ministerial panel formed to look into the issues pertaining to Tilaiya Ultra Mega Power Project (UMPP) –relinquished by Reliance Power — has failed to make any headway in the matter relating to the bank guarantee and has sought fresh comments from the power ministry and PFC. The coal ministry had earlier issued a show-cause notice to Reliance Power, seeking reasons for delays in developing coal mines allocated for Tilaiya UMPP. The panel was of the view that the comments received from the power ministry and and the Jharkhand government did not reveal anything specific so as to facilitate decision making on the issue of release/deduction of bank guarantee. The power ministry had clarified that with regard to development of coal blocks earmarked for UMPPs, it was no way involved and the actual responsibility for the mines development was of the procurers of this project.
Source: The Indian Express
December 23, 2016. India has agreed to export to Nepal additional 240 MW of electricity — 80 MW immediately from January and 160 MW from February — in a bid to lessen the power woes of the Himalayan nation. An agreement was signed to this effect in New Delhi between Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) and NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN), a wholly-owned subsidiary of India’s state-owned power major NTPC. The NEA is Nepal’s state-owned electricity company. The import will be made through Dhalkebar-Mujjafpur Cross Border Transmission line which was inaugurated in February 2016. The fresh agreement on power purchase from India would to some extent address the problem of blackouts in the country, the NEA said. Nepal is reeling under a huge power crisis. The country suffered power cuts up to 15 hours every day until last year — mostly in winter season. To cope with this perennial power crisis, Nepal in September signed an agreement to import additional 250 MW electricity from India through various cross-border transmission lines. It was decided that India will install additional 100 MVA transmission line in Muzaffarpur in its side to ease the export to Nepal. Currently, Nepal has been importing 345 MW electricity from India.
Source: Business Standard
December 22, 2016. Twenty government departments have surfaced in the defaulters’ list of Power Corp department, in Bijnor, Rajasthan. An amount of Rs12 crore of electricity bills are pending from 20 government departments. The education department tops while the health department is second on the list. The Power Corp has issued notices to the defaulters. While the Power Corp was sailing smoothly as a lot of consumers were depositing their dues of electricity bills at the office of Power Corp after demonetisation, the government departments are the ones who have troubled them.
Source: The Economic Times
December 22, 2016. Power consumers are likely to gain to the extent of Rs69,310 crore from the reduction in electricity tariff enabled by the auction of nine coal blocks to power sector firms so far, the power ministry said. The auction proceeds from 83 coal mines allocated so far are estimated at over Rs3.95 lakh crore over the life of the mines, which will be available to the coal bearing states. The actual revenue generated from these coal mines up to October 2016 is Rs2,779 crore excluding royalty, cess and taxes, the ministry said. The ministry informed the production of raw coal in the country during April-November 2016-17 was 391 million tonne as compared to 385 million tonnes during the corresponding period of previous year, an overall growth of 1.6 percent. The ministry said special measures such as spot e-auction and linkage rationalization were undertaken to clear the accumulated stock of coal. While the ministry highlighted the progress made by the coal sector over the past year, the industry expressed displeasure on various counts. The government had earlier allowed public and private power producers to swap their coal supplies with a view to reducing the cost of electricity by ensuring more efficient fuel usage. It may eventually extend the facility to other coal-consuming industries.
Source: The Economic Times

December 21, 2016. The government launched a mobile application to track its ambitious household electrification programme. The Centre has shifted focus to 100% household electrification in all states from rural electrification programme where a village is declared electrified if 10% of households and all public places have electricity access. Data of about 6 lakh villages, with more than 15 lakh habitations having 17 crore people, has been mapped on the mobile application Garv II for tracking progress on household electrification. Power Minister Piyush Goyal said status of village-wise works sanctioned under the Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY) and release of funds to states has also been mapped in Garv-II to monitor progress of works in each village.
Source: The Economic Times
December 21, 2016. Power Minister Piyush Goyal urged central electricity transmission utility Power Grid Corp of India Ltd (PGCIL) and state transmission companies to unlock capital that has accrued over years in transmission assets. Global investors may get to own power transmission lines in India as the government is looking at monetising the assets by offering equity to international pension funds aimed at mopping up Rs10,000-12,000 crore investments. The proposal aims at unlocking value of the existing power transmission lines to generate revenues that can be re-invested in strengthening transmission system and other infrastructure projects. PGCIL is India’s central transmission utility that owns and operates 131,728 circuit-Kilometer of transmission lines and 213 substations across the country with an inter-regional capacity of over 61,000 MW.
Source: The Economic Times
December 27, 2016. Tenughat Dam, a prime tourist spot in the state, is all set to get illuminated with solar lights. The stretch leading to the dam will be decked out in solar lights like the enchanting Marine Drive in Mumbai. The district administration has sent a proposal in this regard to the state government. The administration has plans to install solar lights in all the villages in the 11 panchayats in the Jhumra Hills.
Source: The Economic Times
December 26, 2016. In what would further encourage investments in renewable energy projects, the state government has exempted electricity duty of 40 paise per unit for rooftop solar and captive units. The decision is expected to help Rajasthan reach closer to 2300 MW rooftop solar capacity by 2022, a target given to it by the Centre. The duty cut is expected to have a positive impact on the new capacity lined up. Recently, Rajasthan Renewable Energy Corp (RREC) issued rate contract order for 25 MW rooftop plants and empaneled companies to design, supply and install these projects. People interested to put up rooftop plants can reach these vendors who are also required to guarantee 5 years of maintenance.
Source: The Economic Times
December 26, 2016. The government’s thrust on cutting emission, backed by investments committed by public sector enterprises would lead to an action packed 2017 for the sector, Praj Industries said. State run-oil marketing companies (OMCs) Indian Oil Corp and Bharat Petroleum Corp are in pact with the Pune-headquartered engineering company Praj Industries to set up plants to manufacture the so-called second generation (2G) ethanol from non-edible agricultural waste. The two OMCs along with Hindustan Petroleum Corp are expected to set up multiple ethanol units based on this technology with an aggregate investment pegged at around Rs5,000 crore.
Source: The Economic Times
December 26, 2016. The automated control systems for two nuclear power plants in Tamil Nadu`s Kudankulam will start arriving in India from Russia 2018 onwards, the Russian State Nuclear Corp (Rosatom) said. Automated control systems are key components needed to ensure the safe operation of the nuclear power plant. These systems for the 1,000 MW units – 3 and 4 would be manufactured by a Rosatom affiliate — Automated Control Systems. According to the Russian company an agreement to supply automated control systems was signed between Rosatom-Automated Control Systems and Atomstroyexport — the latter responsible for nuclear power plant construction. The agreement said that the equipment supply for Kudankulam units 3 and 4 would begin in 2018 and 2019, respectively. After that the installation and setup would begin. India’s nuclear power plant operator, Nuclear Power Corp of India Ltd (NPCIL) is setting up 1,000 MW units at Kudankulam in Tirunelveli district, around 650 km from here. The company has completed two units and construction activities for the third and fourth units have started. The general agreement for the construction of Units 3 and 4 was signed with Rosatom, in 2014. At present, the implementation of the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project (KNPP) involves the construction of six power units equipped with VVER-1000 reactors. The road map for cooperation between Russia and India in the sphere of nuclear power provides for the construction of a total of 12 power units in different locations in India, including the site of the KNPP.
Source: Zee News
December 26, 2016. Punjab deputy Chief Minister (CM) and SAD president Sukhbir Badal and his Union Minister wife, Harsimrat Kaur Badal, laid the foundation stone of a Rs600 crore, seocnd-generation ethanol bio-refinery at Tarkhanwala village in Bathinda. The two SAD heavyweights conducted the state government even after Oil Minister Dharmendra Pradhan could not make it to the event. To produce 100 kilo litres of ethanol every day, the plant will be using 400 metric tonnes of bio mass, including farm stubble.
Source: The Economic Times
December 25, 2016. A solar energy products exhibition was organised recently to generate awareness about the long-term benefits of solar energy. The exhibition was jointly organised by the Jammu Kashmir Energy Development Agency (JAKEDA) with some private partners. Participants appreciated the steps taken by the concerned authorities. Solar geysers, lights, bulbs, lanterns and heating systems were put on display and they felt these items would be very useful during the winter season in the Kashmir Valley.
Source: The Economic Times
December 25, 2016. Asserting that the present generation has the duty to leave behind a better place to live in for the next generation, Minister of State for Power, Coal, New and Renewable Energy and Mines Piyush Goyal said by 2022, India will be one of largest installations of renewable energy in world. Goyal also said Prime Minister Narendra Modi is committed towards ramping up renewable energy. Under its plan, Goyal said, the government is also committed to set up solar plant of one lakh megawatt to meet its security needs. Goyal said India is also considering to expand its hydro power capacity which currently stands at 25 MW. Goyal expressed optimism at world’s commitment under the Paris declaration and the Conference of the Parties (CoP) 21 to fight against climate change.
Source: The Indian Express
December 25, 2016. The Pune city has won three awards for Smart City project in a competition organised by Business-World Awards 2016, Pune Smart City Development Corp Ltd said. The PMC has laid emphasis on transport, water, road and solar systems. A special purpose vehicle formed for smart cities mission is running these projects.
Source: The Economic Times
December 23, 2016. The city plans to generate electricity by using solid waste collected from 80 wards by adopting green technology. Addressing a meeting of Meerut Municipal Corp (MMC) officials, divisional commissioner Alok Sinha announced that 900 tonnes of solid waste, collected every day from 80 wards under MMC, will be used to produce 12 MW of power for the city. The commissioner said the MMC will ensure that waste is collected from each house in the city. Representatives of private companies also addressed the meeting and gave a PowerPoint presentation on their solid waste management techniques. 12 MW power will be generated on a daily basis, and the total cost of setting up the power plant will be around Rs275 crore. The plant will be set up under the public-private partnership (PPP) model. Pick-up trucks used to collect garbage from people’s houses will be fitted with global position system (GPS) devices so that their movements can be tracked.
Source: The Economic Times
December 23, 2016. Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL) has set up a 3.5 MW solar energy project to power its airport facility in the eastern suburb of this tech hub. Spread over 23 acres with 12,985 solar modules installed, the single-axis tracker based project is the first at an airport in the country. The plant can generate up to 24,000 units of electricity per day depending on sunlight. The Gurgaon-based Amplus Energy Solutions, which bagged the order through a competitive bidding, has set up the project on turnkey basis at the HAL airport used for military aircraft test flights, VIP aircraft and charted services. As part of its commitment to harness renewable sources for its growing energy needs, the company is setting up 50 MW capacity solar plant in two phases over the next two years, with 35.8 MW on open lands and 9.2 MW on roof-tops. The company has also commissioned a 6.3 MW wind power plant at Harapanahalli in Davangere district, about 300 km from Bengaluru, for its captive power needs.
Source: The Economic Times
December 23, 2016. While battery manufacturers and solar power companies are struggling to develop batteries that would be cheap, smaller in size and can store power for days, an engineering college in Kolkata has devised a combo of solar based generation and power storage system that can supply power perpetually 24 hours a day all through the year at a fraction of conventional battery cost. It is scalable to any size and are suited for any hilly area as well as multi storeyed buildings. A 100 kilowatt pilot project is already being planned in hills of East India, while its smaller version, producing 100 watts of power 24×7 is now running in Kolkata on a four storeyed building. The system consists of a solar pump basically solar modules that would generate power during day and run a water pump. It also consists of two water tanks at two different elevations. The upper tanks would release water at half the speed at which it receives water from the lower pump. The falling water would rotate a turbine an equipment that generates electricity when rotated by an external force falling stream of water from the elevated tank in this case. During day, water from the lower tank would be pumped to the upper tank. A portion of this water also flows down simultaneously into the lower tank generating power. The rest of the water in the elevated tank keeps flowing down during night, thus producing power the entire day. According to experts it is a variant of pumped storage system added with solar generators and filled with rain water doing away with a steady flow of water in the lower tank.
Source: The Economic Times
December 23, 2016. Holding his ground on the solar panel scam, which had rocked Kerala during the Congress-led UDF rule, former Chief Minister (CM) Oommen Chandy said that he had not committed any crime. In his second deposition before the commission, headed by retired high court judge Justice Sivarajan, the senior Congress leader claimed that all the charges levelled against him were legally proved wrong. The commission had directed Chandy to be present for the cross-examination. He was cross-examined by the commission in January last in Thiruvananthapuram, when he was the CM.
Source: The Economic Times
December 23, 2016. Solar power generator Azure Power said it has bagged a 50 MW project which was recently put up for auction by Solar Energy Corp of India (SECI) under the National Solar Mission (NSM). Azure Power secured 50 MW of the total 100 MW capacity auctioned by SECI and will supply power to SECI for 25 years, it said. The project will be built in the Ananthapuramu Solar Park, which is being developed by the Solar Park Implementation Agency (SPIA), Andhra Pradesh Solar Power Corp Ltd (APSPCL). The tariff will be Rs4.43 per unit ($0.067) with an additional support of Rs12.7 million per MW ($0.19 million) from the Government of India in terms of Viability Gap Funding (VGF). This makes the levelised tariff of this project significantly higher than the levelised tariff of the lowest bid, including VGF, under SECI auctions in NSM Phase II Batch III. With a portfolio of over 1,000 MW, Azure Power has developed, constructed and operated solar projects of varying sizes, from utility scale to rooftop, since its inception in 2008.
Source: The Economic Times
December 21, 2016. Those looking for a bright spot in the global warming picture might want to pay closer attention to India. For several years, demand for electricity in the world’s second-most populous country has trailed forecasts, data compiled by India’s Central Electricity Authority show. While the reasons for the mismatch are complex, the gap raises the prospect that India won’t need to burn as much coal to meet its future energy needs. Rather, much of it is going to come from solar panels and lanterns, both of which can be supplied off grid. Millions in India still are waiting to connect to the grid as routine power shortages often lead to blackouts. It may not be the traditional power companies that meet their needs. Instead, emerging technologies such as solar lanterns and rooftop photovoltaics are becoming the energy of choice — and are starting to bite into traditional sources of demand. As solar and energy storage technologies improve, some of the 300 million not connected to the grid may eventually get their electricity through off-grid installations and appliances, Nitin Zamre, managing director for India at ICF International Inc., said. India’s power demand is a major variable in the debate about how to rein in global warming. It accounted for almost 7 percent of global emissions in 2012, World Resources Institute data show. Under the Paris Agreement signed by more than 190 countries, India has promised to boost the amount of power coming from sources other than fossil fuels to 40 percent from about 30 percent. Prime Minister Narendra Modi is working to make rooftop solar a major energy source with a program that’s enticing overseas investment. Meanwhile, India’s traditional energy producers are also under pressure. With distributors unable to buy as much power as they’d like, traditional power plants are being forced to generate less than their rated capacity. Modi’s push to install as much as 175 GW of renewables by 2022 has added to competition between power generators. Major conventional-energy generators in India are also getting into the renewables game as solar costs fall — giving the country an even better chance of controlling emissions.
Source: Bloomberg

December 21, 2016. The Haryana government is in talks with companies to produce bio-fuel from paddy stubble and also has plans to provide agriculture implements to farmers at subsidised rates to keep a check on the practice of burning straw in the State, Chief Minister Manohar Lal Khattar said. Khattar said that agriculture implements at subsidised rates will help farmers collect paddy straw, which can be used to make bio-fuel. Khattar said that construction work on the Kundli-Manesar-Palwal Expressway has started and it would significantly reduce vehicular pressure on Delhi. Khattar said that movement of vehicle had started between Palwal to Manesar and construction work on the Kundli-Manesar stretch would be completed at the earliest. Gurugram Development Authority has also prepared a plan to purchase 500 CNG buses to promote public transport in the NCR area.
Source: The Hindu
December 27, 2016. Venezuela said it will cut 95,000 barrels per day (bpd) of oil production in the New Year in fulfillment of a producers’ deal to reduce global output and strengthen prices. January 1 marks the start of the pact by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and several non-OPEC producers to lower production by almost 1.8 million bpd. Oil Minister Eulogio Del Pino said the output deal should lead to a re-balancing of inventories, after which he forecast Brent crude would settle at a price range of around $60-$70 a barrel and Venezuela’s crude basket between $45-$55 a barrel.
Source: Reuters
December 27, 2016. The finance ministry of Mexico has decided to delay the announcement of winners for the next phase of its oil and gas (O&G) exploration and production round, from 22 March 2017 to 19 June 2017, to allow more companies to participate in the auction and to incorporate modifications. The 15 shallow water blocks, located off the coasts of Vera Cruz, Tabasco and Campeche, hold nearly 650 million barrels of oil equivalents of crude oil in proven reserves.
Source: Enerdata
December 26, 2016. Russia’s largest oil producer Rosneft has agreed to buy oil services firm Targin from Sistema conglomerate for up to 4.1 billion roubles ($67.4 million), Rosneft said. Rosneft said the number of drilling rigs will increase by 19 percent following the deal.
Source: Reuters
December 26, 2016. Libya’s national oil company National Oil Corp (NOC) has resumed oil production at its major oil field of Sharara, which had been closed since November 2014, due to a pipeline blockade by local armed factions loyal to rival Libyan alliances. The pipeline leading to Sharara and neighbouring El Feel field has been reopened, allowing NOC to restart Sharara production at a pace of 58,000 barrels per day (bpd). The nominal production capacity of the Sharara oil field stands at 330,000 bpd and that of the El Feel field at 90,000 bpd. Libya’s oil production has recently doubled to 600,000 bpd as forces controlling the eastern Oil Crescent changed.
Source: Enerdata
December 25, 2016. Israeli conglomerate Delek Group’s gas and oil exploration units, Delek Drilling and Avner Oil Exploration, approved a merger aimed at reducing costs and attracting new investors. Delek Drilling said that shareholders of both companies approved the merger, which will see all assets and liabilities of Avner transferred to Delek Drilling and Avner will be dissolved. The companies in April began the merger process. Delek Drilling and Avner each hold 15.625 percent in the Tamar natural gas field off Israel’s Mediterranean coat and 22.7 percent each in the nearby Leviathan field, which is slated to start production in 2019 or 2020.
Source: Reuters
December 24, 2016. The Croatian government will buy Hungarian oil group MOL’s 49 percent stake in oil and gas company INA, Croatian Prime Minister (PM) Andrej Plenkovic said. MOL and INA have locked horns for years over control of the Croatian oil company. Plenkovic said the buy-out was in Croatia’s best interests after a United Nations arbitration commission ruled that evidence presented by Croatia in a lawsuit against MOL were insufficient to prove that certain contracts made in 2009 were the result of corrupt activities.
Source: Reuters
December 23, 2016. Oil major BP has agreed with Azerbaijan to extend a contract to develop the country’s biggest fields by a quarter of a century to 2050 in a move to unlock billions of dollars of fresh investments in the Caspian Sea deposits. The existing production sharing deal was due to expire in 2024 and talks to extend it have been slow because of disagreements between partners in the BP-led consortium. The extension of the Azeri contracts adds to the flurry of deals BP signed in recent weeks, including buying stakes in gas exploration areas off the coast of Mauritania and Senegal, and renewing an onshore oil concession in Abu Dhabi. BP said the consortium and Azeri state oil firm SOCAR signed a letter of intent to continue developing the giant Azeri-Chirag-Guneshly (ACG) offshore fields until 2050. With current output of 620,000 barrels per day, the fields have produced a total of over 3 billion barrels of oil since the start of the project, with around $33 billion of investment. Their remaining reserves are estimated to contain several more billions of barrels of oil.
Source: Reuters
December 23, 2016. The United States (US) Department of Energy expects to begin sales of roughly 8 million barrels of sweet crude from the country’s emergency oil reserve in early to mid-January, according to a notice sent to potential bidders. The Strategic Petroleum Reserve oil will come from the Big Hill and Bryan Mound, Texas storage sites, and West Hackberry, Louisiana facility, the notice said. Delivery of the oil will begin on March 1 but buyers can take the oil as early as February, the notice said. The Energy Department said it would sell $375 million worth of crude oil, or about 8 million barrels at prices, from the emergency reserve this winter after Congress passed a temporary spending bill authorizing the sale. It is the first of several planned sales over the coming years that could total up to $2 billion worth of oil, intended to raise funds to modernize the reserve. There are roughly 695 million barrels of oil in the reserve, a string of heavily guarded salt caverns on the Louisiana and Texas coasts.
Source: Reuters
December 22, 2016. The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) committee responsible for monitoring compliance with a global agreement to reduce oil output will meet in the first half of January, Kuwait’s Oil Minister Essam Abdul Mohsen Al-Marzouq said. Marzouq later clarified that the meeting would take place in the “beginning” or “first half” of January. The OPEC and non-OPEC producers reached their first deal since 2001 to curtail oil output jointly and ease a global glut after more than two years of low prices. OPEC has a long history of cheating on output quotas. The fact that Nigeria and Libya were exempt from the deal due to production-denting civil strife will further pressure OPEC leader Saudi Arabia to shoulder the bulk of supply reductions.
Source: Reuters
December 21, 2016. Malaysia’s state-owned energy company Petroliam Nasional Bhd (Petronas) signed an agreement to study two oil fields in Iran, joining international companies from Russia to France that plan to help boost the Persian Gulf nation’s oil and gas production. Petronas signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to assess the South Azadegan and Cheshmeh Khosh oil fields, the National Iranian Oil Co. said. In the past month, Iran has signed up Royal Dutch Shell Plc to Russia’s Gazprom Neft PJSC and Total SA to study its oil and gas potential after sanctions on its economy were eased in January. The agreement marks a return to Iran for Petronas, which bought crude from Iran before international sanctions were imposed, according to Iran oil ministry. The study of the two oil fields will take six months, and should be finished in the second quarter, Petronas said.
Source: Bloomberg
December 27, 2016. Russia activated a pipeline carrying Russian gas to Crimea with President Vladimir Putin hailing it as a step that would power economic growth on a peninsula Moscow annexed from Ukraine in 2014. Crimea has no land border with Russia, and Moscow has struggled to meet its energy needs, which were previously met by Ukraine.
Source: Reuters
December 27, 2016. Qatargas has announced the start-up of commercial operations at Laffan Refinery 2, marking the expansion of its refining capacity in Qatar. The project, which is located in the Ras Laffan Industrial City, has a refining capacity of 146,000 barrels per day of condensate procured from the non-associated natural gas reserve North Field. According to Qatargas, the new condensate refinery along with Laffan Refinery 1 is strategically significant owing to its role in diversifying Qatar’s energy mix. Laffan Refinery 2, which is the expansion phase of the existing condensate refinery, was undertaken by Japanese engineering firm Chiyoda in collaboration with Taiwan based CTCI for nearly $600 mn.
Source: Energy Business Review
December 26, 2016. Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (TEPCO) will enter the city’s metropolitan gas retail market next July, it said, opening a new stage of competition with Japan’s biggest city gas operator Tokyo Gas. TEPCO Energy Partner Inc, Tepco’s retail unit, will work with gas operator Nippon Gas, which already has 320,000 city gas retail customers, to offer maintenance and other services. The pair aim for about 500,000 customers by the end of March 2018, including Nippon Gas’ existing customers, and to boost that to one million by the end of March 2020, or about 10 percent of Tokyo Gas’ customer base, TEPCO Energy Partner said. The move chimes with Japan’s plan for nationwide liberalization of its 2.4 trillion yen ($20 billion) retail gas market in April 2017. Competition between utilities and gas operators was spurred in April when Japan’s $70 billion retail electricity market was opened up. Under the latest agreement, TEPCO will provide piped gas equivalent to about 275,000 tonne a year of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from next April to Nippon Gas which has been buying LNG from Tokyo Gas.
Source: Reuters
December 25, 2016. Algeria’s state energy producer Sonatrach Group plans to increase output of natural gas and crude oil by 20 percent in the next four years as new projects start up, Salah Mekmouche, the company’s vice president of exploration and production, said. Sonatrach will bring on stream Tiguentourine, In Salah and Timimoune natural gas projects as well as oil wells of the Berkine basin, after spending $9 billion a year on exploration and development projects since 2015, Mekmouche said. Sonatrach also plans to increase production from old oil wells in Hassi Messaoud, he said. Sonatrach will produce 69 million tons of oil equivalent this year, up from 67 million tons last year, according to company data. Gas output will increase to 132.2 billion cubic meters from 128.3 billion in 2015, the data show.
Source: Bloomberg
December 21, 2016. Indonesia’s Donggi-Senoro liquefied natural gas (LNG) plant has secured buyers for 31 cargoes of LNG it plans to export next year. The plant will produce 40 cargoes in 2017 leaving nine cargoes that will be sold in the spot market, including to domestic buyers.
Source: Reuters
December 21, 2016. The China-backed Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) has approved a $600 million loan to finance a natural gas pipeline from Azerbaijan through Turkey, it said, taking its total loans in its inaugural year to $1.73 billion. Once completed, the Trans Anatolian Natural Gas Pipeline Project will transport natural gas from fields in Azerbaijan into Turkey and then markets in Southern Europe, AIIB said. The latest loan was granted to Azerbaijan state-owned company Southern Gas Corridor (SGC) to build the 1,850 kilometre pipeline, part of a project that also includes developing Shah Deniz 2 gas field in the central Asian nation, AIIB said.
Source: Reuters
December 21, 2016. China’s state oil and gas majors are set to import record levels of liquefied natural gas (LNG) this month, betting on robust demand during the cold winter months and helping lift Asian prices to their highest in nearly two years. Trade flows data shows 7.33 million cubic metres (mcm) of LNG, equivalent to 3.33 million tonnes, are heading to China for delivery this month. This includes 10 cargoes from Qatar, an unusually high number even for the world’s largest LNG exporter. The trade flow data puts China on track to import more than 20 million tonnes this year, about 13 percent of the country’s total annual gas consumption of about 197 billion cubic meters (bcm), or 152 million tonnes. The buying spree may give Asian LNG prices LNG-AS further upward momentum. They are currently at $9.30 per million British thermal units (mmBtu), the highest since January 2015 and more than double levels in April. Aside from cold weather, November’s bigger-than-expected imports were due to growing use of long-term contracts by oil and gas majors and buoyant manufacturing levels, analysts said.
Source: Reuters
December 23, 2016. Peabody Energy Corp failed to explain how it will cover future mine cleanup costs in a reorganization plan filed, triggering concerns over the company’s use of “self-bonds.” Under a federal program called “self-bonding,” large miners like Peabody have been allowed to extract coal without setting aside cash or collateral to ensure mined land is returned to its natural setting, as required by law. The practice came under scrutiny following bankruptcy filings by some of the largest United States coal miners because, without collateral set aside for mine reclamation, taxpayers are potentially exposed to billions of dollars in cleanup costs. Environmental groups have been following the bankruptcy to see whether Peabody replaces roughly $1 billion of self-bonds with other guarantees, as rival Arch Coal Inc did in its October bankruptcy reorganization.
Source: Reuters
December 27, 2016. Sri Lanka’s electricity regulator informed the power and energy ministry that urgent steps must be made to buy new power plants, postpone maintenance work at the available power plants and increase rooftop solar generation to avoid a power crisis in the first quarter of 2017. The Public Utilities Commission of Sri Lanka (PUCSL) said that the full availability of Lakvijaya coal plant, the country’s only coal power plant, was a key factor in January 2017. The PUCSL suggested to looking into the possibility of shifting any maintenance at the available power plants to avoid shutting down during the critical period January to April. The Ceylon Electricity Board was also suggested to take immediate action to purchase shortage in generation from available plants and the CEB and the Sustainable Energy Authority should “expedite connection” to start commercial operations under small scale generation on Standardized Power Purchase Agreements.
Source: Business Standard
December 27, 2016. Iran plans to increase its power generation capacity to 100 GW by 2025, of which 12 percent would be nuclear power, the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran (AEOI) said. AEOI said that the country’s nominal power generation capacity stands at 75-80 GW currently. Iran plans to increase the number of nuclear power plants to 12. According to the report released by energy ministry, Iran’s nominal power generation capacity stands at 75.916 GW – up by 1.8 GW since the beginning of the current fiscal year on March 21. During the nine months of the current fiscal year, Iran generated 226 billion kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity, the report said.
Source: AzerNews
December 27, 2016. Panasonic Corp will invest more than 30 billion yen ($256 million) in a New York production facility of Elon Musk’s Tesla Motors to make photovoltaic (PV) cells and modules, deepening a partnership of the two companies. The United States (US) electric car maker is making a long-term purchase commitment from Panasonic as part of the deal, besides providing factory buildings and infrastructure. The two companies said they plan to start production of PV modules in the summer of 2017 and increase to 1 GW of module production by 2019.
Source: Reuters
December 26, 2016. China is reducing the amount of money it pays to newly completed solar and wind power generators for their electricity, in order to reflect declines in construction costs, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) said. The nation will cut tariffs paid to solar farms by as much as 19 percent in 2017 from this year’s levels, and by as much as 15 percent for wind mills in 2018 from current prices, according to the NDRC. The changes will help reduce subsidies paid to new photovoltaic and wind power projects by about 6 billion yuan ($863 million) annually, the NDRC said. China will also encourage local authorities to continue making use of auctions to select renewable energy developers, in order to further lower power prices, according to the NDRC. Reductions to renewable power prices will be smallest in regions in China that have the calmest wind and the weakest solar radiation, according to the NDRC.
Source: Bloomberg
December 26, 2016. Power cuts are common in Uganda with several businesses suffering thousands of losses. In Soroti village located in the eastern part of Uganda, power shortage is common just like any other town in the country. The east African nation decided to invest in a $19 million solar plant that lies in a 33 acre piece of land. The plant is able to produce 10 megawatts of power that can be fed in the national grid. According to the Eren Renewable Energy, thousands of people in Soroti village will benefit from this new plan. The inhabitants are hoping that a new solar power plan will help solve this problem for good.
Source: AfricaNews
December 26, 2016. Vietnam’s national power utility Electricity of Vietnam (EVN) has officially commissioned the 1,200 MW Lai Chau hydropower project on the Da River. The project, consisting of three 400 MW units, entered construction phase in 2011 and was put into commercial operation one year ahead of schedule.
Source: Enerdata
December 26, 2016. The United States (US) Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) has issued two Combined Licenses for Duke Energy’s William States Lee III nuclear project in South Carolina, authorising the company to build and operate two AP1000 reactors at the site, near Gaffney, South Carolina. The licenses contain conditions, including specific actions associated with the post-Fukushima requirements for Mitigation Strategies and Spent Fuel Pool Instrumentation and a pre-startup schedule for post-Fukushima aspects of the new reactor’s emergency preparedness plans and procedures. Duke Energy initially submitted the application in December 2007. The two reactors are now expected to be commissioned between 2024 and 2026.
Source: Enerdata
December 26, 2016. The Energy Regulatory Commission (ERC) of Thailand plans to open bidding for the development and operation of 1,000 MW of renewable power capacities in 2017. Solar, biomass-fired, biogas-fired and waste-to-power projects will be offered feed-in tariffs in the bidding round, with the first one for 519 MW of solar projects expected in the second half of 2017. The ERC will also open bids for 400 MW of biomass-fired projects and for 63 MW of waste-to-power projects.
Source: Enerdata
December 25, 2016. China’s largely rubber-stamp parliament passed a law that will levy specific environmental protection taxes on industry for the first time from 2018, as part of a renewed focus on fighting the country’s pollution woes. Anger has risen in the world’s second-largest economy at the government’s repeated failure to tackle land, water and air pollution, with large parts of northern China enveloped in dangerous smog in recent days. The tax rate will be 1.2 yuan ($0.17) per unit of atmospheric pollution, 1.4 yuan per unit of water pollution, 5 yuan per tonne of coal waste and 1,000 yuan per tonne of “hazardous waste”. Industrial noise polluters will also be levied 350 yuan per month if they exceed limits by 1-3 decibels, 700 yuan for 4-6 decibels and 11,200 yuan per month for 16 decibels and more. The law goes into effect on January 1, 2018. China has not previously imposed any specific environmental taxes, and the new levy will replace an earlier system of miscellaneous charges that are regarded as far too low to deter polluters.
Source: Reuters
December 23, 2016. French utility Engie is preparing to pull out of a Turkish nuclear power project as it no longer fits with the group’s strategy. Engie is undergoing a restructuring that includes € 15 billion ($15.72 billion) worth of asset sales – of which 41 percent have already been signed – and € 22 billion of investments, as well as cost savings aimed to have a net cumulative impact of 1 billion euros on core earnings by 2018.
Source: Reuters
December 22, 2016. China launched a global carbon dioxide monitoring satellite via a Long March-2D rocket. The 620 kg satellite TanSat was sent into a sun synchronous orbit about 700 km above the earth and will monitor the concentration, distribution and flow of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, Yin Zengshan, chief designer of TanSat at the Chinese Academy of Sciences micro-satellite research institute, said. The satellite will help understanding of climate change and provide independent data. During its three-year mission, TanSat will thoroughly examine global carbon dioxide levels every 16 days, accurate to at least 4 parts per million (ppm). China is the third country after Japan and the United States (US) to monitor greenhouse gases through its own satellite.
Source: New Kerala
States with more than All India Per Capita Domestic LPG Consumption of 14.2 Kg/Year/Person
| State/UT |
Per Capita Domestic LPG Consumption/Sales (Kg/Year) per Person |
| Himachal Pradesh | 16.5 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 17.3 |
| Karnataka | 18 |
| Telengana | 18.1 |
| Sikkim | 18.2 |
| Maharashtra | 18.3 |
| Mizoram | 19.5 |
| Kerala | 19.9 |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli | 19.9 |
| Uttarakhand | 20.2 |
| A & N Islands | 21.3 |
| Tamil Nadu | 21.6 |
| Haryana | 23 |
| Daman & Diu | 24.2 |
| Puducherry | 26 |
| Punjab | 26.5 |
| Goa | 29.4 |
| Chandigarh | 33.6 |
| Delhi | 42.2 |
Per Capita PDS Kerosene Sales/Consumption
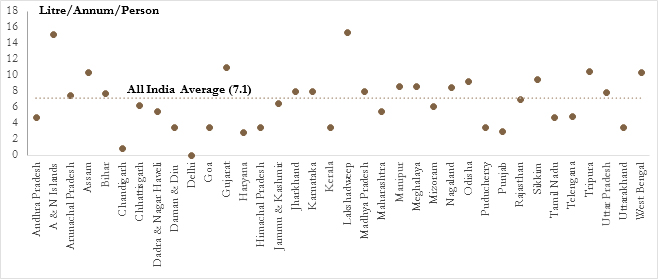
Source: Rajya Sabha Unstarred Question No.3173

Publisher: Baljit Kapoor
Editorial advisor: Lydia Powell
Editor: Akhilesh Sati
Content development: Vinod Kumar Tomar
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.