-
CENTRES
Progammes & Centres
Location

POWER SURPLUS LEADING TO POWER STRESS
The Revised Framework for Resolution of Stressed Assets issued by the RBI has forced the electricity sector towards NPAs and the new guidelines will only deepen the sector’s crisis, a Parliamentary panel has noted. India has around 175,000 MW of operational coal-based power generation capacity. Of this, around 60,000 MW capacity is under financial stress. Lenders have exposure to around ₹3 trillion of these stressed assets. With a view to clean-up the books of the banks, RBI had issued the revised framework which substituted the then existing guidelines with a simplified generic framework for resolution of stressed assets.
The government is likely to recommend that bankruptcy proceedings for stressed power plants should kick in after 360 days of default, giving relief to banks and companies that are struggling to meet the 180-day deadline set by the RBI in its controversial 12 February circular. The recommendation is expected to be presented to the Allahabad High Court which is hearing petitions against the circular and had asked the government to present its views after consulting all stakeholders. Separate recommendations are likely to be made for power projects depending on their operational status and resolution plans drawn by the lenders. Stressed operational projects and those under execution may be recommended for an extra 180 days over and above the 180-day deadline expiring 27 August. Special dispensation has been sought for projects resolved through CIL supplies (Shakti scheme) and those already in NCLT. A high-level committee to address cross-sectoral issues including delayed payment of private power companies is also being mulled. The power ministry and private power firms have demanded that stressed power projects should not be categorised as stressed in 90 days of default, while the deadline of 180 days to resolve a bad loan, after which liquidation process is immediately triggered, be extended to 270 days.
India may be looking at a huge electricity surplus in most part of the country in the current financial year, according to the latest data released by the power ministry’s technical planning wing CEA. The country is likely to experience energy surplus of 4.6 percent and peak power surplus of 2.5 percent in the fiscal year through March 2019, the CEA has said. Three states are expected to witness peak time power surplus of more than 30 percent including Tripura at 30.6 percent surplus, Himachal Pradesh at 35.7 percent and Sikkim at 79.2 percent, apart from areas served by Damodar Valley Corp at 40.4 percent. However, five states are likely to have peak power deficit of more than 15 percent — Punjab with 19.6 percent power deficit, Bihar at 18.9 percent, Uttar Pradesh at 17.4 percent, Assam at 17.4 percent and Jammu and Kashmir at 15.1 percent. In 2017-18, CEA had projected an all-India peak power surplus of 11,471 MW or 6.8 percent but the country suffered from a peak power deficit of 2 percent. Experts said the Indian power system is becoming energy surplus but peak deficit due to increased share of renewables and reducing share of hydro and gas-based power generation. CEA said the assessment of the anticipated power supply position for 2018-19 has been made taking into consideration power availability from various stations in operation and renewable energy sources apart from fuel availability and anticipated water availability at hydro stations.
Average spot price of power increased 39 percent to ₹3.46/kWh in July over a year ago at IEX. The price however declined 7 percent sequentially compared to ₹ 3.73/kWh in June this year. It said ‘One Nation, One Price’ was realised for 21 days last month. The DAM experienced minor transmission congestion of 6 percent mainly in import of power towards northern region. According to the National Load Dispatch Centre statistics, the all India peak demand touched 168 GW on July 10, 2018, about 1 percent decline over the previous month. The electricity market at IEX TAM and DAM combined traded 4,148 mu last month vis–vis 5,053 mu in June, and 3,729 mu in July last year. Good monsoon rains dampened the power demand as well as prices in July this year vis–vis the preceding month. The DAM traded at 4,028 mu in July registering a decline of 19 percent over 4,965 mu in June, and 10 percent increase over 3,669 mu in July 2017, it said. On a daily average basis about 130 mu were traded during the month with average daily sell bids at 237 mu and average daily buy bids at 161 mu, it said.
The CEA has undertaken a study to ascertain the cheapest power mix in 2030. The outcome of the study will also act as components to the regulators in determining power tariffs. According to estimates by the power ministry, the share of renewable energy in India’s electricity mix is set to increase to around 55 percent by 2030. At present, renewables account for nearly 20 percent of the total installed capacity. India has committed to produce about 40 percent of its installed electricity capacity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030. It has also set a target of adding 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022. Meanwhile, the CEA is also closely working with stakeholders in building a cost-effective power evacuation infrastructure in Leh and Ladakh region of Jammu and Kashmir. It can be executed by a combination of underground cables and towers installed by airlifting, he said.
Bangladesh, which is importing around 700 MW of power from India, is looking to ramp up its electricity import from the country, the neighbouring nation said. The neighbouring country is aiming at importing 10,000 Mw from India. Power sector cooperation between the two countries is “not limited to transmission and supply only.” India is “supporting its neighbouring country to enhance the capacity building”, particularly, human resource development for power generation, transmission and distribution.
Bihar initiated power projects worth over ₹75 billion and it is anticipating that each household in the state would be electrified by the end of this year. Three power units in the state – Kanti, Navinagar and Barauni – have been handed over to the NTPC Ltd which was likely to “ensure better power generation and availability of electricity to consumers in Bihar at cheaper rates”. Subsidy to domestic consumers besides developing special “agriculture feeders” to cater to the electricity requirements of those involved in farming is expected to improve efficiency in the electricity sector.
The MERC has allowed Adani Power to recover additional expenses incurred by its subsidiary APML due to introduction of the GST. The company put the total impact of the GST to be ₹0.35/kWh which amounts to about over ₹4.025 billion till February 2018. APML had filed a petition with the MERC in April to adjust tariffs of electricity sold to the state from its 3,300 MW Tiroda power plant. The company sought the electricity regulator’s approval to offset financial consequences of GST and evacuation facility charge by CIL.
Power discoms in Delhi sold 615.5 mu of electricity to customers outside the state during April-June despite the AAP-led government’s allegation that the capital was staring at power crisis in peak summer season due to coal shortage at plants. According to official data, discoms in Delhi sold 296.228 mu of electricity in June 2018 against 233.578 mu in May, registering an increase of 26.8 percent. Among distribution companies, BYPL sold 144.14 units, BRPL sold 4.29 mu and TPDDL sold 106.381 mu in June. In May, BYPL sold the maximum 130.047 mu, BRPL sold 16.594 mu and TPDDL sold 64.071 mu to outside customers. BSES said that due to the nature of the power business in India, power demand is arranged keeping in mind the peak power demand. In June, the AAP government wrote to the Power Minister that Delhi was staring at a power blackout due to the fast depleting coal stockpiles at power plants in the city and urged for action with the Railways which transports coal to the national capital.
Faced with reduced supply of electricity by private sector companies under power purchase agreements, GUVNL has invited bids to procure 1,000 MW power on short-term basis through tariff based competitive bidding. The apex electricity utility intends to procure 1,000 MW, which includes 500 MW round the clock and 500 MW for twelve hours, for the months of September, October and November. For December, GUVNL has invited bids for 250 MW round clock power and 500 MW for twelve hours. Meanwhile, the power demand across the state increased to 13,500 MW. The demand had declined to 11,000 MW after heavy rains lashed the state.
Goa said that to improve the power situation in the state a 10-15% hike in the electricity tariff was needed. The electricity department is “seriously working” on improving the power equipment in the state. The department has issued various work orders to the tune of ₹4.1 billion, as also kept ₹1.13 billion for underground cabling, ₹7.55 billion to take up priority work and ₹750 million for automating the electric distribution network. Additionally, this year, the government has kept budgetary support of ₹3.17 billion for various subsidies, including power connections for households and agricultural farms. Work worth ₹4.11 billion is underway. The government will come out with a policy to regularise meter readers and line helpers.
Iran said it had resumed supplies of electricity to Iraq and other neighbouring states 10 days earlier, after shortages in Iraqi cities sparked unrest in July. Tehran stopped supplying electricity to Iraq in July due to unpaid bills and because of a rise in Iranian consumption during the summer. The power shortage in Iraq sparked protests in Basra and other cities, as people blamed what they called an inept and corrupt Iraqi government. A number of protests have also broken out in Iran in recent months over regular power cuts and water shortages. Saudi Arabia offered to sell electricity to Baghdad at a discount, part of an effort by the kingdom to curb the influence of its rival Iran in Iraq.
Brazil’s Eletrobras (Centrais Eletricas Brasileiras) has delayed the auction of a power distributor based in the state of Amazonas to 26 September from 30 August, while keeping the original date for three other units, the power generation company said. Amazonas Distribuidora de Energia will be put on the block in September while Eletroacre, Ceron and Boa Vista Energia will be auctioned off in August, the company said. Eletrobras is seeking to offload heavily indebted distributors ahead of government plans to privatize the overall company.
A Bosnian regional government agreed to guarantee a €614 million ($700 million) loan from China’s Exim bank to help Bosnian utility EPBiH to add a new generating unit at its Tuzla coal-fired power plant. The amount covers 85 percent of the total value of a contract signed last November for the largest investment into Bosnia’s postwar energy infrastructure, the government of autonomous Bosniak-Croat Federation said. In 2014 EPBiH picked a consortium of China Gezhouba Group and Guandong Electric Power Design to add the 450 MW unit, but the project has been delayed by red tape and negotiations over financing. Under its guarantee terms, the government cited a 20-year loan repayment, including a five-year grace period, and a one-off payment by EPBiH of 47.6 million Bosnian marka ($27.7 million) into a regional guarantee fund. The guarantee deal is expected to receive the required approval from parliament if the issue is put to the lawmakers before Bosnia’s 7 October general election. The government said the new unit at the 715 MW Tuzla plant is necessary to replace its three outdated units, adding that the latest environment-friendly technologies will be used in its construction.
In Australia residential consumers are paying 18 percent lower since 2012 and 8 percent below their global counterparts. According to a survey done by Australian-based consulting firm IEC, Meralco’s tariffs have decreased to P 7.77 per kWh in January 2018 from January 2012’s price point of P 9.57 per kWh. The bad news is Australia is still the third highest electricity rates in Asia behind Japan and Singapore. Japan and Singapore were reported to be among the top Asian countries with the highest electricity rates, placing Meralco’s average tariff 24th highest out of 46 markets surveyed. The study identified markets such as Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Korea and Taiwan as having the lowest electricity rates due to annual subsidies amounting to $ 800 billion from their respective governments. These subsidies are in the form of cash grants, subsidized fuel or deferred expenditure. To reduce energy costs for the consumer, IEC recommended a focus in adding retail competition on top of more power generation facilities.
The Asian Development Bank has approved more than $375 mn made up of a loan and grants to help Bangladesh provide electricity to all its citizens. The package will go towards a project to develop two power lines in support of the government’s national target of electricity for all by 2021. The government of Bangladesh has pledged to address infrastructure deficiencies, including modern and affordable energy services. About 35 million people in the country are without access to electricity. The government will contribute $174.5 mn towards the total cost of the project, estimated at $532 mn, which is due to be complete at the end of June 2023.
The German government said it took a minority stake in electricity transmission firm 50Hertz for “national security” reasons, thwarting Chinese investors from buying into the strategic company. Berlin has therefore tasked a public bank with purchasing a 20-percent stake put up for sale by Australian infrastructure fund IFM and which has been sought by China’s State Grid. The Chinese group had already tried to take a minority stake in 50 Hz. But their first attempt was blocked as 50 Hz’s majority shareholder — Belgian power transmission system operator Elia — snapped up the stake and expanded its holdings to 80 percent.
State-sponsored Russian hackers appear far more interested this year in demonstrating that they can disrupt the American electric utility grid than the midterm elections, according to US intelligence officials and technology company executives. By comparison, according to intelligence officials and executives of the companies that oversee the world’s computer networks, there is surprisingly far more effort directed at implanting malware in the electrical grid. The Department of Homeland Security reported that over the last year, Russia’s military intelligence agency had infiltrated the control rooms of power plants across the US. In theory, that could enable it to take control of parts of the grid by remote control.
RBI: Reserve Bank of India, NPAs: non-performing assets, MW: megawatt, CIL: Coal India Ltd, CEA: Central Electricity Authority, kWh: kilowatt hour, IEX: Indian Energy Exchange, DAM : day-ahead market, GW: gigawatt, TAM: term ahead-market, mu: million units, MERC: Maharashtra Electricity Regulatory Commission, APML: Adani Power Maharashtra Ltd, GST: Goods and Services Tax, discoms: distribution companies, AAP: Aam Aadmi Party, BRPL: BSES Rajdhani Power Ltd, BYPL: BSES Yamuna Power Ltd, TPDDL: Tata Power Delhi Distribution Ltd, GUVNL: Gujarat Urja Vikas Nigam Ltd, IEC: International Energy Consultants, Hz: Hertz, US: United States
28 August. Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd (BPCL) will be expanding the storage capacity of its Cherlapalli LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) bottling plant. The company, which caters to 22 lakh individual LPG customers in Telangana, added 2 lakh connections last fiscal. This year, thanks to Ujjwala Scheme, it has been able to provide over 1.5 lakh connections in the state. BPCL state head (LPG) S Dhanapal said currently only 2% of its customers use the app and that the company would like more people to make use of it for a hassle free experience while making payments, applying for a new connection, among others.
Source: The Economic Times
28 August. Vedanta Ltd has bagged 41 out of 55 oil and gas exploration blocks offered in India’s maiden open acreage auction, upstream regulator DGH (Directorate General of Hydrocarbons) said. Oil India Ltd (OIL) won nine blocks, while Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) managed to win just two. GAIL (India) Ltd, upstream arm of Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd (BPCL) and Hindustan Oil Exploration Company (HOEC) received one block each, DGH said, giving out the list of winners of Open Acreage Licensing Policy (OALP) round-1. Vedanta, which had put in bids for all the 55 blocks, won the right to explore and produce oil and gas in 41 of them. Prime Minister Narendra Modi has set a target of cutting oil import bill by 10 percent to 67 percent by 2022 and to half by 2030. Import dependence has increased since 2015 when Modi had set the target. India currently imports 81 percent of its oil needs.
Source: Business Standard
28 August. Geleki Toilyakhetra Suraksha Vikas Mancha, an umbrella organisation of 19 different social and youth organisations, has protested the ONGC (Oil and Natural Gas Corp)’s stance over the move of the Ministry of Petroleum and Hydrocarbons to hand over the Geleki oil field to Schlumberger Overseas SA for enhancing production from the mature field terming it as a ploy to privatise the PSU (Public Sector Undertaking) in phases. The Mancha has been spearheading a movement to stall alleged government plans to privatise aging oil fields in Assam against the interests of the local communities and the state. It said that ONGC authority did not have a formal meeting with the Mancha prior to giving out the press release and it is very surprising that Geleki, one of the most high yielding oil fields in the country now is being sought to be given to a private company which allegedly does not have a good track record with the Assam Asset itself. The ONGC authority also clarified that ONGC signed the Summary of Understanding with Schlumberger Overseas SA to enhance production, strengthen surface and sub-surface activities by inducing state of the art technology provided by Schlumberger, a global leader in the sector.
Source: The Assam Tribune
27 August. Diesel prices hit a record high of Rs 69.46 per litre while petrol rates inched towards Rs 78 a litre mark after a fall in rupee made imports costlier. Diesel price was hiked about 14 paise per litre and petrol by 13 paise, according to price notification of state-owned fuel retailers. The increase pushed diesel price to its highest ever level of Rs 69.46 a litre in Delhi. In Mumbai, the fuel now costs Rs 73.74 a litre. Fuel prices in Delhi are the cheapest in all metros and most state capitals due to lower sales tax or VAT (Value Added Tax). Diesel price had previously hit its highest level on May 29 when it reached Rs 69.31 a litre mark in Delhi. Petrol in Delhi costs Rs 77.91 per litre, and Rs 85.33 in Mumbai. The rates are however lower than the peak hit on May 29 when they touched Rs 78.43 a litre in Delhi and Rs 86.24 in Mumbai. Petrol price has risen by Rs 0.77 a litre in Delhi in last 12 days. Diesel rates have gone up by Rs 0.74 per litre since then. State-owned oil firms had in mid-June last year dumped the 15-year practice of revising rates on 1st and 16th of every month in favour of daily price revisions. The centre currently levies a total of Rs 19.48 per litre of excise duty on petrol and Rs 15.33 per litre on diesel. On top of this, states levy VAT – the lowest being in Andaman and Nicobar Islands where a 6 percent sales tax is charged on both the fuel. Mumbai has the highest VAT of 39.12 percent on petrol, while Telangana levies the highest VAT of 26 percent on diesel. Delhi charges a VAT of 27 percent on petrol and 17.24 percent on diesel. The central government had raised excise duty on petrol by Rs 11.77 a litre and that on diesel by Rs 13.47 a litre in nine installments between November 2014 and January 2016 to shore up finances as global oil prices fell, but then cut the tax just once in October last year by Rs 2 a litre.
Source: Business Standard
25 August. Over 70,000 LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) connections have been provided under Ujjwala Yojna in Himachal Pradesh, Chief Minister (CM) Jai Ram Thakur said. Reviewing the progress of Central and state governments’ welfare schemes, Thakur said 73,074 LPG connections have already been provided to eligible families in the hill-state. More households will get the connections by the end of next year, he said. The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) under which women belonging to BPL (below poverty line) families will be provided with clean cooking fuel was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 1 May 2016 in Ballia, Uttar Pradesh. The scheme aims to provide LPG connections to five crore BPL households by 2019 across the country and offers assistance of Rs 1,600 for one connection.
Source: Business Standard
22 August. Alinz Portable Petrol Pumps said that it has tied up with Czech firm Petrocard to set up four manufacturing units in India to make machines for such pumps at an investment of Rs 1,600 crore. The concept of portable petrol pumps is new to India, which has been approved by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Alinz Managing Director Inderjeet Pruthi said. A portable petrol pump is an automatic self-service machine dispensing petrol, diesel and kerosene. The payment are cashless, through facilities like e-wallets, he said. These pumps will be a boon for people living in rural areas, mountains regions and remote locations, he said. They can be set up in just about 400 square kilometres as against huge land requirement for normal gas stations. Besides, he said, it is a good opportunity for those also looking to start a business. To set up a new pump an amount of Rs 90 lakh to Rs 1.20 crore would be required and as per communication with the banks they are ready to finance 80 percent of the project.
Source: Business Standard
27 August. GAIL (India) Ltd is currently is currently executing new 5,000 kilometre (km) of trunk pipeline across the country at an estimated cost of Rs 25,000 crore, Chairman and Managing Director (CMD) B C Tripathi said. Tripathi said the company is also investing around Rs 3,500 crore in the current financial year along with its joint venture partners and its subsidiary firm in setting up city gas distribution networks. GAIL had first started allowing open access to other entities for its pipelines in 2004. However, applications for access had to be given physically. The launch of the online portal for common carrier capacity is a step towards a functioning natural gas trading hub, the company said. Guidelines set by Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB), the country’s downstream oil and gas regulator, stipulate providing 25 percent of the total pipeline capacity as common carrier capacity, for providing non-discriminatory open-access on first-come-first-served basis for transporting third party gas for a period of less than one year. According to Tripathi, of the total earmarked common carrier capacity under GAIL’s pipelines, almost 33 percent of the capacity was used by third party transporters during the last financial year ended March 2018. Tripathi said that apart from re-negotiation of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) contracts the company has started supplying gas through its own ships in the European and Middle-East markets based on delivered-ship basis. Tripathi announced the first phase of Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga project that involves setting up gas pipelines will be commissioned in the current calendar year ahead of schedule. GAIL is the country’s largest natural gas company and operates more than 11,400 Km of natural gas pipelines across the country.
Source: The Economic Times
27 August. Royal Dutch Shell said it will acquire French oil major Total SA’s 26 percent stake in the company that operates 5 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) Hazira LNG (liquefied natural gas) terminal in Gujarat. The size of the deal was however not disclosed. Hazira LNG & Port venture comprises two companies — Hazira LNG that operates an LNG regasification terminal in Gujarat and Hazira Port, which manages a direct berthing multi-cargo port at Hazira. This portfolio action is consistent with Shell’s strategy to deepen its presence in the gas value chain in India, the fourth largest LNG consumer in the world, Royal Dutch Shell said.
Source: Business Standard
22 August. India has sought re-negotiation of the natural gas price it is to source through a proposed $10 billion Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India (TAPI) pipeline in view of the slump in global energy markets. The four nations to the pipeline projects had in 2013 signed a gas sale purchase agreement (GSPA) that benchmarked the price of natural gas that Turkmenistan is to export at 55 percent of the prevailing crude oil price. This translates into a price of about $7.5 per million metric British thermal unit (mmBtu) at current oil prices at the Turkmen border. Added to this would be transit fee and transportation charges which would jack up the rates to over $10.5 per mmBtu at the Indian border. For a consumer, the price would be around $13 per mmBtu after adding local taxes and transportation charges. The price of Turkmen gas is more than double of the $3.6 per mmBtu rate paid for post natural gas producers in India. Turkmenistan would export 90 million standard cubic meters per day of gas through TAPI, with Afghanistan getting 14 million metric standard cubic meter per day (mmscmd) and India and Pakistan 38 mmscmd each. India had previously used its position as world’s fastest-growing energy consumer to renegotiate gas import deals with Australia, Russia and Qatar.
Source: Business Standard
28 August. Higher demand for thermal power and lower-than-required growth in domestic coal output may push up coal imports to 62 million tonnes (mt) this fiscal, Credit rating agency India Ratings and Research (Ind-Ra) said. According to Ind-Ra, imported coal requirement is likely to increase to 62 mt this fiscal from 56 mt in FY2018 to meet the incremental power generation. According to Ind-Ra, in a scenario of lower-than-required growth in domestic coal output, short-term power prices would remain firm and are likely to be determined by the marginal cost of energy production undertaken using imported coal.
Source: Business Standard
27 August. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will help India’s largest power generation utility, NTPC Ltd, to use its technology to reduce pilferage of coal when transporting them on wagons on railway tracks. Following the successful pilot project undertaken by ISRO on one such coal wagon train through its NavIC (Navigation in Indian Constellation) or Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, NTPC wants to incorporate this on a permanent basis. This seven-satellite system aims at providing India a satellite system so that it becomes independent of the Global Positioning System (GPS) of the United States. The problem of coal being stolen has been a perennial problem with NTPC, particularly in areas in Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal. Many police cases have been booked in these states for coal thefts by unknown persons. Despite Railway Protection Force personnel providing security, the large numbers who come to take away the coal when stoppages occur far outnumber the security provided. The pilot done by ISRO on one train heading to West Bengal for nearly a year by attaching a NavIC system onto the wagon revealed where exactly the train had an unscheduled stop and the number of minutes it halted too. The issue of coal thefts plagues energy companies in the Eastern part of the country with a coal mafia said to rule roost. Coal is stolen enroute as well as when loading them. The largest state-owned producer of coal, Coal India Ltd has deployed vehicle tracking systems and GPS at its mines to handle the issue. Some companies have applied for permission to use drones to tackle the menace. NavIC Systems are now being deployed across different spheres.
Source: The New Indian Express
25 August. With MAHAGENCO (Maharashtra State Power Generation Company) deciding to import coal, the claims of Western Coalfields Ltd (WCL) and other coal companies regarding supply of adequate coal have fallen flat. The generation company has recently floated tenders for importing 2 million tonnes (mt) coal for new units of Koradi, Chandrapur and Bhusawal power plants. Imported coal is costlier than domestic coal and consumers will have to pay for it by way of higher power tariff. MAHAGENCO has not been importing coals since the last three years. NTPC Ltd is also bringing in coal from abroad after a gap of four years. This happens at a time when the coal ministery has claimed the country has produced record coal. Import of coal also raises question mark over MAHAGENCO’s decision to sell coal to private power companies. The coal meant for one unit each in Bhusawal and Nashik power plants has been provided to Dhariwal plant (185 MW) near Chandrapur and Ideal Energy plant (250 MW) at Bela (Nagpur district). The tender process will be completed in September and the imported coal will reach MAHAGENCO’s power plants in late October or November. WCL had claimed in an affidavit before the high court that coal dispatch to power plants should be 119 railway rakes (wagons) per day. Central Railway (CR) had earlier claimed there was an increase of 29% in coal rakes (wagons) supplied by it to WCL in 2017-18 as compared to 2016-17. The number of rakes supplied to Parli power station in Marathwada increased by 773% from 26 to 227 while the increase for Koradi was 148%. The overall loading for MAHAGENCO power stations by Nagpur division of CR had risen from 9.6 rakes per day in 2016-17 to 12.4 rakes per day in April-January of 2017-18.
Source: The Economic Times
22 August. Coal India Ltd (CIL) arm CCL (Central Coalfields Ltd) said its 17 out of the 21 ongoing mining projects worth Rs 4,095.5 crore are facing delays due to various reasons including non-grant of green clearances. Of the 21 projects, Parej East and Hurilong projects could not be started due to non-grant of environment and forest clearances, CCL said. Kalyani open cast project, one of the ongoing projects, will be started after green clearances, it said. As on March 31, 2018 there are 21 ongoing and 34 completed mining projects under CCL with sanctioned capacity of 112.85 million tonnes (mt), it said.
Source: Business Standard
22 August. The Kawai plant has not imported any coal in March-April this year, while it had imported 2.8 million tonnes (mt) and 1.6 mt of coal in FY17 and FY18 respectively. Adani Power has shut down a 660 MW unit at its Kawai power plant in Rajasthan due to shortage of coal. The shutdown underscores the ongoing issue of coal shortage at power plants, mainly due to insufficient railway rakes to ferry the fuel. The Kawai power plant was one of the ten electricity generation stations to receive assurance on coal supply under the scheme to harness and allocate koyla transparently in India (Shakti scheme), which was specifically designed to salvage power plants with power purchase agreements but without fuel supply agreements. Under Shakti, linkages have been granted to 10 power plants with 11,549 MW capacity. The power ministry had claimed that since five stressed projects with 8,490 MW capacity would receive coal under Shakti, these plants should be taken out of the list of the 34 stressed assets (38,870 MW). To be sure, the Kawai plant is not among the 34 stressed power projects. The Rajasthan Electricity Regulatory Commission allowed Adani Power Rajasthan, which runs the 1,320 MW Kawai power plant, to recover the additional cost on account of having to import coal due to reduced supplies from Coal India Ltd. The company estimated the additional cost due to coal shortage to be Rs 1,221 crore per annum since 2014.
Source: The Financial Express
28 August. India signed a $250 million Development Policy Loan (DPL) to improve the performance of Rajasthan’s electricity distribution sector under the states “24×7 Power for All” programme. The agreement signed between the Central government, Rajasthan’s state government and the World Bank is the second in the series of two operations planned for a comprehensive turnaround of Rajasthan’s electricity distribution sector. The first loan closed in March last year. The electricity distribution companies (discoms) in Rajasthan provide electricity to about 9.5 million customers. The key areas under the programme include strengthening governance in the distribution sector in the state, reducing energy procurement costs and improving the operational performance. It will also involve financial restructuring and recovery in the sector by transferring considerable amounts of the discoms debt to the state. Economic Affairs Joint Secretary Sameer Kumar Khare said the programme will contribute to the state’s fiscal sustainability. The loan has a three-year grace period and a maturity of 21 years.
Source: Business Standard
27 August. In a rare move, the government has issued a direction to power regulator Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) to allow changes in any central or state government duties to be passed in electricity tariffs to consumers post bidding. The industry welcomed the government’s move and said it will expedite procedures, helping a big chunk of power projects stuck due to such regulatory issues. The power ministry said the delay in decision making was affecting the power sector and was one of the factors causing stress. The power ministry has ordered that the central commission will only determine the per unit impact of such change in taxes, which will be passed on. State power distribution companies may submit objections in 21 days. The order on tariff pass through will be effective from the date of change in taxes. In cases where CERC (Central Electricity Regulatory Commission) has already passed an order, that order will apply to all cases and no additional petition should be filed. The 40th Standing Parliamentary Committee has sad total outstanding loans of scheduled commercial banks to the power sector (including renewables) stood at Rs 5.65 lakh crore at the end of March. Nearly 80% of this is accounted for by public sector banks and almost a fifth of this exposure is stressed on various counts, the committee report said.
Source: The Economic Times
27 August. Power Minister M M Mani said that the department suffered a loss to the tune of Rs 400 crore following the devastating floods. About 25 lakh power connections have been snapped across the state. Despite staring at a herculean task to recoup the loss, the electricity board contributed Rs 50 crore to the chief minister’s distress relief fund (CMDRF). Now, board employees are being assisted by their counterparts from Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka for restoration works. Even the service of retired board employees has been sought. Thousands of transformers, hundreds of sub stations and several power generating centres were damaged, mainly in Idukki, Pathanamthitta and Ernakulam. Several transformers were switched off as a precautionary measure during the floods. This had led to a temporary disruption in power distribution.
Source: The Economic Times
24 August. State Bank of India (SBI) Managing Director (MD) Arijit Basu said that about 7-8 power sector projects worth Rs 170 billion (Rs 17,000 crore) are expected to be resolved soon as lenders are nearing consensus on these. There are about 34 stressed power projects and the combined value of their outstanding loans is about Rs 1.74 trillion (Rs 1.74 lakh crore).
Source: Business Standard

23 August. In a major relief to state-run power utility Gujarat Urja Vidyut Nigam Ltd (GUVNL), Adani Power has restored the supply of 2,000 MW since the past 15 days. GUVNL has power purchase agreements of 2,000 MW with Adani Power, 1,000 MW with Essar Power Gujarat and 1,805 MW with Tata Power. Essar discontinued supply from December 15 last year, while Adani stopped supply from January 20 this year without any prior notice to GUVNL or the Gujarat Electricity Regulatory Authority (GERC). Essar, however, has not restored its supply. The electricity demand had shot up to more than 16,000 MW before the state received good rainfall in July, raising concerns about meeting the rising gap. However, with the north, central and southern Gujarat and Saurashtra receiving good rains in past several days and the availability of 2,000 MW of power from Adani Power, GUVNL in not purchasing power the exchanges.
Source: Business Standard
22 August. The electricity bills paid by as many as 1,300 consumers for nearly 10 years in Hathras were allegedly pilfered by engineers and employees of the UPPCL (Uttar Pradesh Power Corp Ltd) causing revenue loss to the tune of several hundred crores of rupees to the state exchequer. The state government has now ordered a vigilance probe into the case. The incident came to light earlier this month when several consumers in UP’s Hathras district under Dakshinanchal Distribution Company (DDC) approached the Uttar Pradesh Power Corp Ltd claiming that their names were missing from the records even though they have been depositing their bills since 2008-09. A stunned UPPCL brass immediately initiated a preliminary probe and matched the online consumers with the actual consumers at the ground only to find that around 1,300 consumers were given electricity connections without keeping their records. UP Energy Minister Srikant Sharma said the department has constituted a vigilance inquiry into the incident and the culprits will be brought to book. Initial investigations into the incident have revealed that a section of Hathras covering few villages was unelectrified and was, therefore, classified as ‘Dark Zone’ in 2008. The villagers, however, got poles erected and wires stretched to wheel in electricity into the villages over a period of time. Sharma said the entire exercise appears to have been done in connivance of the officials of the then Dakshinanchal distribution company. UPPCL said the villagers who were given electricity connections were issued a ‘pass book’ to keep records of the bills they paid. Sharma said that directions have also been issued to UPPCL to identify the officials who were facing inquiry in the previous SP and BSP regimes but have not been brought to book.
Source: The Economic Times
28 August. Mytrah Energy, Hyderabad-based renewable energy company, announced it has commissioned a 103.5 kilowatt (kW) solar power project for Suretech Hospital and Research Centre, a nursing training institute in Nagpur, Maharashtra. The rooftop solar project is expected to help reduce the hospital’s annual electricity bill, around Rs 15 lakh based on the current tariff. As part of the agreement, Mytrah will provide maintenance service for the plant for the next 25 years. The power producer said the project will help Suretech meet its power needs through green energy and reduction cost incurred in electricity consumption.
Source: The Economic Times
28 August. The South Western Railway (SWR) has installed solar panels in 19 buildings, including railway stations, workshops and offices, with a total capacity of 3,605 kilowatt peak (kWp). The annual energy requirement of KSR railway station is 3.13 million units and about 13.9% of it is now being met by solar panels. SWR said these solar panels generate about 3 million units per annum on an average, saving revenue of about Rs 70 lakh. SWR hopes to meet the full energy requirement of Hubballi and Mysuru workshops with solar energy, making them carbon neutral. In addition to the 12 railway stations in SWR that have solar panels, it has identified 60 more stations where solar panels will be installed during 2019-20, increasing the total capacity to 4,685 kWp, which translates to about 7 million units on an average per year, contributing 15% of annual energy requirements (other than for running of trains) of SWR. The annual energy requirement of SWR is about 47 million units, which includes 17 million units for Bengaluru division. Rooftop solar panels installed at platform 7 and 8 at Bengaluru City railway station
Source: The Economic Times
28 August. The next time the floodlights are up for a day-night match at the Brabourne stadium, it will be solar power panels on the roof that will be powering them. The stadium, which has several sports activities inside the Cricket Club of India (CCI) complex and is mostly used for first-class cricket matches, earned the distinction of becoming the first cricket stadium in the world to generate 865 kilowatt (kW), which translates to 11.5 lakh units per year, of solar power. It amounts to 30% of the overall power consumption of approximately 35 lakh units per year. Praising CCI for the big step taken to address climate change, Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis threw open the facility and said it was good as a solar power plant atop the stadium with 2280 solar panels spread over the entire circular roof around the public stands. Fadnavis said a plant over a stadium that can save power bills worth Rs 1.25 crore is praiseworthy. The Chinnaswamy stadium in Bengaluru had around 430 kW power from solar panels. The generation of solar power will reduce carbon emissions from the thermal power generation that can be equated with planting 1,600 new trees every year in the initial period. The CCI club and the stadium consumes power worth Rs 5 crore every year. Fadnavis said setting up such a large power plant in 120 days was a record in itself. Though floodlights will require generators, normal power and other back-ups going by the intensity of power needed by them, indirectly more than the same amount of green power would have already been supplied to the grid. In effect, it will be green power that will be fed to the stadium and other club areas. While Tata power executed the project, the Excelsior Engineering Solutions acted as the project consultant. The solar panels were imported from China.
Source: The Economic Times
28 August. Merino Panel Products Ltd (MPPL) announced the launch of a 5.5 MW captive open access solar power plant in Hisar. MPPL will draw more than 9 million units (kWh) of electricity from this plant every year for consumption in its manufacturing unit in Bahadurgarh, Haryana. Not only is this plant first of its kind in terms of the power delivery model, it is also the first to use single-axis tracking at this scale (5.5 MW) in the State of Haryana. This design enables the plant to deliver up to 15% more energy than the more common fixed-tilt plants. In a recent order, Haryana Electricity Regulatory Commission (HERC) has waived all transmission and distribution charges on Solar Open Access plants, thus, making this a very well timed investment for MPPL.
Source: Business Standard
27 August. Locals opposing the construction of Jaitapur nuclear power plant in coastal Konkan held a protest march, opposing land acquisition for the project. Villagers, including women in large numbers, gathered at Madban village in Ratnagiri district and shouted slogans against the proposed power plant. Almost 80 percent of the land acquisition of the total 930 hectares owned by 2,500 persons, has been completed. However, some farmers and villagers are opposing the project, citing forced rehabilitation and loss of livelihood. The proposed nuclear power plant will take over land that currently belongs to the villagers in five different fishing villages: Madban, Varliwada, Karel, Niveli and Mithgavane. In March, French Ambassador to India Alexandre Ziegler said construction of the Jaitapur nuclear power plant is expected to begin this year-end. India and France had inked an agreement to expedite the project. On completion, the Jaitapur project will be the largest nuclear power plant in the world, with a collective capacity of 9,900 MW.
Source: Business Standard
27 August. Indian billionaire Gautam Adani’s energy unit is nearing a deal to acquire a 1,370 MW thermal power plant backed by GMR Infrastructure. Adani Power Ltd will take over about Rs 38 billion ($543 million) of loans out of a total of Rs 58 billion that GMR Chhattisgarh Energy owes. Adani Power will also assume non-funded liabilities of about Rs 14 billion. The Reserve Bank of India has been looking to restructure stressed loans that have already pushed dozens of companies into bankruptcy. GMR Chhattisgarh comprises two 685 MW coal-power units that started operations in 2015 and 2016.
Source: Business Standard
27 August. India’s first Biofuel-powered flight was successfully tested for domestic operations between Dehradun and New Delhi. The Bio-fuel is expected to reduce India’s dependency on Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) and help bring down air fares. Oil Minister Dharmendra Pradhan said that ATF price is the key component in the aviation industry, and in the coming days, India is hoping to reduce its import dependency in this area. Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said the government is working to bring down the cost of this fuel. Minister of Civil Aviation Suresh Prabhu emphasised that the use of alternative fuel would benefit the consumers. Expressing happiness over the success of the test flight, Chairman and Managing Director of SpiceJet, Ajay Singh said that this will eventually help in bringing down the air fares. Made from Jatropha crop, Biofuel has been developed by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research-Indian Institute of Petroleum (CSIR-IIP), in Dehradun. It has been recognised by American Standard Testing Method (ASTM) and meets the specification standards of Pratt and Whitney and Bombardier for commercial application in aircraft. SpiceJet had last year placed orders for 205 Boeing 737 Max fuel-efficient planes that are expected to reduce fuel consumption by about 15% and will leave 40% lesser noise footprint. SpiceJet said that the company intends to use the mixture of 75% ATF and 25% Biofuel in its operations. According to International Air Transport Association (IATA), aviation industry contributes to 2% of the total greenhouse gas emissions in the world. The advantage of Biofuel as compared to ATF is that it reduces carbon emissions and enhances fuel efficiency.
Source: Business Standard
25 August. The Solar Energy Corp of India (SECI) is likely to revise downwards its 2,500 MW wind-solar hybrid project tendered in June to 1,200 MW, as evacuation-related challenges continue to affect the sector. The SECI had earlier deferred the last bidding date from 8 August to 7 September. The SECI plans to amend the standard bidding document for the project and has proposed to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) to introduce a separate bidding guidelines for hybrid wind-solar power projects. The plan to reduce the capacity comes in the wake of cancellation of wind and solar auctions in the last two months as developers faced evacuation-related issues and the difference in tariffs of first and second bidder was too wide. A lot of developers did not have commitment from the central or state transmission utilities to evacuate power from the project site. The 2,500 MW wind-solar hybrid tender was invited by the SECI in June with 8 August as the last date for submission of bids. However, the date was later extended to 7 September after developers requested change in bidding documents. The ceiling tariff for the project is Rs 2.93/kWh.
Source: The Financial Express
24 August. Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister (CM) N Chandrababu Naidu inaugurated a 2 MW floating solar power plant built on Mudasarlova reservoir. The power plant envisages saving the burning of 1,540 tonnes of coal a year and release of 300 tonnes of carbon dioxide. As part of the ‘Smart City’ initiative, the solar power plant was built in 20 acres of the reservoir, among the oldest man-made water bodies, on the outskirts of the city, at a cost of ₹ 11.34 crore. The works were executed by DES Engineers of Hyderabad under the supervision of AECOM, consultants for the Smart City projects. The works for the plant began in May this year and prior to it, the reservoir was de-silted at a cost of ₹ 20 lakh.
Source: The Hindu
24 August. The government announced the country’s first wind power project connected to the Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) was commissioned by Ostro Kutch Wind Private Ltd in Gujarat. Solar Energy Corp of India (SECI) had conducted the first auction of wind power projects in February last year in which tariff of Rs 3.46 was discovered, much lower than the feed-in tariffs in vogue at the time. Companies placed bids for 1,000 MW capacity of projects to be connected on ISTS where power generated in one resource-rich state could be transmitted to other renewable deficient states. Five firms including Mytrah, Inox, Ostro, Green Infra and Adani won the bids. The energy generated from this project is being purchased by Bihar, Odisha, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh.
Source: The Economic Times
24 August. Power trading solutions provider PTC India announced that it has operationalised the flow or supply of 126 MW inter-state wind power commissioned capacity to different beneficiary states under government scheme. The power will flow (be supplied) to Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and Odisha, PTC India said. According to PTC India, the commissioned capacities are part of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy Wind Scheme (Tranche-I) of 1050 MW in Jun 2016. The Solar Energy Corp of India (SECI) had conducted the competitive bidding and e-reverse auction for selection of wind project developers in Feb 2017 and the tariff discovered was Rs 3.46 per kilowatt hour (kWh) setting a new benchmark for the wind sector at that time, it said.
Source: Business Standard
24 August. To promote green energy and reduce overdependence on coal-fired power generation, Yogi Adityanath government is fast changing gears to promote setting up of solar power parks in the private sector. The government would handhold solar power projects by allowing both ‘open access’ facility and guaranteeing full power evacuation and purchase by state-owned power utilities. The state is sanguine about the economically backward Bundelkhand and Purvanchal regions for solar parks owing to easy availability of land. The private developer or consortium would be selected after a bidding process and the projects would be expected to be completed in 18-24 months for a speedier generation. Nodal agency Uttar Pradesh New and Renewable Energy Development Agency (UPNEDA) has issued draft guidelines for private solar parks and invited suggestions from stakeholders before it is finalised and implemented under the existing solar power policy, which was announced in December 2017. Under solar parks draft guidelines, the state would purchase cent percent power generated from these plants, while it would also allow the sale of power to any third party buyer through open access model as per the business strategy of the private developer. The solar parks could also be developed by availing the applicable grants under the union ministry of new and renewable energy scheme. Currently, the grant is subject to a ceiling of 30 percent of the project cost or Rs 1.2 million per MW. However, the developer is free to exercise the choice of open access too, where it could sell power to any other company/utility within or outside the state. Yogi government is targetting a total investment of Rs 500 billion in the solar power space in the next 5 years. It has even proposed a Green Energy Corridor in Bundelkhand at an investment of Rs 40 billion, to be funded by the Centre in part. Besides, the government is eyeing solar energy generation of 10,700 MW by 2022 in UP.
Source: Business Standard
23 August. Ambient air pollution shortens an average Indian’s life by over 1.5 years, say scientists who suggest that better air quality could lead to a significant extension of human lifespan around the world. Researchers said that if PM (particulate matter) 2.5 concentrations worldwide were limited to the World Health Organization (WHO)’s air quality guideline concentration of 10 microgrammes per square cubic metre, the global life expectancy would be on average 0.59 year longer. The benefit of reaching the stringent target would be especially large in countries with the highest current levels of pollution, with approximately 0.81.4 years of additional survival in countries such as India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and China. This is the first time data on air pollution and lifespan has been studied together in order to examine the global variations to find out how they affect the overall life expectancy. The researchers from University of Texas at Austin in the United States looked at outdoor air pollution from PM smaller than 2.5 microns. These fine particles can enter deep into the lungs, and breathing PM2.5 is associated with increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, respiratory diseases and cancer. PM2.5 pollution comes from power plants, cars and trucks, fires, agriculture and industrial emissions. They found that the life expectancy impact of ambient PM2.5 is especially large in polluted countries such as Bangladesh (1.87 years), Egypt (1.85 years), Pakistan (1.56 years), Saudi Arabia (1.48 years), Nigeria (1.28 years), and China (1.25 years). India had a life expectancy impact of 1.53 years, according to the study.
Source: Business Standard

23 August. External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj urged the Indian diaspora to utilise opportunities in India in the area of solar power. India has been promoting the use the solar energy in developing countries and was the leading force behind establishment of the International Solar Alliance.
Source: Business Standard
23 August. The government has imposed restriction on import of bio-fuels including ethyl alcohol and other denatured spirits, bio-diesel, petroleum oils and oils obtained from bituminous minerals other than crude, through an amendment in import policy. The import of these items, which was free earlier, will now only be allowed for non-fuel purpose on actual user basis. Import policy of bio-fuels revised from ‘free’ to ‘restricted’ and allowed for non-fuel purpose on actual user basis as per the National Bio-Fuel Policy, the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) said in a notification. In another notification, the government said export of beach sand minerals has been brought under state trading enterprise and shall be canalised through Indian Rare Earths Ltd. Export of rare earth compounds classified as beach sand minerals, permitted anywhere in the export policy, will now be regulated.
Source: The Economic Times
23 August. In what could set the template for other state governments that find themselves facing the hump of safeguard duty on solar gear, the Madhya Pradesh (MP) government has revised the conditions for its rooftop solar tender. The state was in the middle of a tender when the Centre on July 30 notified a safeguard duty ranging from 15-25 percent on solar cells and panel. The state has amended Clause 3.29 of the request for proposal, dealing with tax and duties, through a corrigendum to the tender. The MP government had floated a tender to put up 28 megawatt peak of rooftop solar projects through renewable energy service company (RESCO) model. The amended clause specifies how changes in tax would be passed on in the tariff. This adjustment in tariff because of change in capital cost can be done till three months before the project’s scheduled commissioning specified in the power purchase agreement.
Source: Business Standard
22 August. Renewable energy company Siemens Gamesa has announced the commissioning of 3.375 MW of wind-solar hybrid power pilot project for NTPC Ltd. This being smart grid based renewable energy’s (SGRE’s) first hybrid project for the thermal power giant. The Wind Solar Hybrid project consists of an SG 2.0-114 wind turbine in hybrid with 1.375 MW High Efficiency HiT solar panels, which was executed in Bijapur District in Karnataka. This is the first pilot renewable energy hybrid project in India that was developed from the engineering design stage by Siemens Gamesa. Present in India since 2009, the accumulated base installed by Siemens Gamesa recently topped the 5-GW mark.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
22 August. Adani Green Energy has set up a wholly-owned subsidiary to generate wind energy. Adani Wind Energy (GJ) Ltd (AWEGL) has been incorporated as Adani Green’s 100 percent subsidiary, and is yet to commence its business operations.
Source: Business Standard
22 August. A part of kerosene subsidy savings in India could be invested in helping the vulnerable section of society access clean lighting through off-grid solar lighting technologies, a new study by leading think tanks International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) and The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) explored the business model for a ‘kerosene-solar subsidy swap’ has suggested. It said a shift to solar lighting will reduce the need for ongoing expenditure on subsidies because any government support would help cover one-off capital costs, not consumption costs. Their report released said since 2013-14 the central government has cumulatively saved Rs 26,470 crore by gradually reducing kerosene subsidy expenditure. This makes sense fiscally and environmentally but leaves some households with high lighting costs. The report also reviews the suitability of Uttar Pradesh and Odisha to host a subsidy swap pilot study, assessing the real-world impact of increased adoption of solar energy and a reduction in kerosene consumption. Moreover, almost 51 percent of subsidised kerosene is lost and marketed for other purposes. Policy makers are aware of these problems, and the government has been winding down kerosene subsidy expenditure through increased prices, reduced allocation of subsidised fuel to states and by encouraging cities such as Chandigarh and New Delhi to voluntarily give it up.
Source: Business Standard

22 August. The use of agricultural residues in power plants can help reduce pollution in the Delhi-NCR region by 8 percent by 2025, a new study, conducted jointly by The Energy and Resources Institute and Automotive Research Association of India, has suggested. The study suggests several measures that could help in reducing pollution by 2025. It indicated that up to 26 percent of pollution in the city in summer is caused by internal factors like vehicular emissions and this goes up to 36 percent in winter. The study suggested that use of agricultural residues in power plants can help cut down pollution by 8 percent by 2025. Last year, the Union power ministry directed the state-run power producer NTPC Ltd to blend crop residue with coal at its plants to reduce stubble burning on agricultural lands, which triggers thick smog in Delhi every year. Increasing LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) penetration in the NCR by 75 percent by 2025 and 100 percent by 2030 could help reduce pollution by 6 percent, the study suggested. A switch from solid fuels to gas can bring down the PM (particulate matter) 2.5 and PM10 levels by 12 percent by 2025, it said. The study used two approaches to assess the pollution level in the Delhi-NCR region. The first was Receptor Modelling, under which the PM10 and PM2.5 levels were monitored at 20 locations across the city and the second model used advanced chemical transport approach to ascertain the emission factors. The study found that the industries operating in the NCR contribute significantly to Delhi’s pollution, apart from biomass burning in rural kitchens and agricultural fields.
Source: Business Standard
28 August. Iran’s crude oil and condensate exports in August are set to drop below 70 million barrels for the first time since April 2017, well ahead of the 4 November start date for a second round of US (United States) economic sanctions. The US has asked buyers of Iranian oil to cut imports to zero starting in November to force Tehran to negotiate a new nuclear agreement and to curb its influence in the Middle East. The total volume of crude and condensate, an ultra-light oil produced from natural gas fields, to load in Iran this month is estimated at 64 million barrels, or 2.06 million barrels per day (bpd), versus a peak of 92.8 million barrels, or 3.09 million bpd, in April, preliminary trade flows data showed. The National Iranian Oil Company has slashed its crude prices to keep buyer interest amid the August export drop.
Source: Reuters
28 August. Petrobras, Royal Dutch Shell, Total and Repsol have registered to bid on oil cargo the Brazilian government will be auctioning, Pre-sal Petroleo SA, the state company managing contracts to develop the coveted offshore pre-salt layer, said. The oil cargo is the government’s share of production in the Mero, Lula and Sapinhoa fields in the Campos and Santos offshore basins. A previous attempt by the government to sell its share of the oil failed. The auction will take place on 31 August.
Source: Reuters
28 August. Investing $8 billion in Brazil’s waning offshore Campos Basin could boost its oil production by 230,000 barrels of oil equivalent per day (boepd) by 2025, consultancy Wood Mackenzie said in a report. Oil majors have already plowed billions into Brazil, now Latin America’s top producer, to lock in stakes in its pre-salt offshore oil play, where billions of barrels of oil are trapped beneath a thick layer of salt under the ocean floor. Meanwhile, oil and gas production in the Campos Basin, where activity began about forty years ago, has fallen by a third over the last seven years to 1.3 million boepd, raising the specter of hefty outlays to close down operations. Under a more optimistic scenario, where Brazil boosts its recovery factor in the basin to levels seen in the Gulf of Mexico and the North Sea, 5 billion barrels of additional oil could be recovered, it estimates.
Source: Reuters
27 August. French energy group Total is not looking at investing in the US (United States) shale oil industry, the company’s Chief Executive Officer Patrick Pouyanne said. Patrick Pouyanne made the comment when asked whether peer BP’s $10.5 billion acquisition of US shale assets from BHP Billiton had made the sector more attractive. BP’s acquisition of about 500,000 producing acres marked a turning point for the group since the Deepwater Horizon disaster in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010, for which the company is still paying off more than $65 billion in penalties and clean-up costs.
Source: Reuters
27 August. Iraq’s state oil marketer SOMO is close to a deal with China’s state-run Zhenhua Oil to boost the OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) member’s crude oil sales to the world’s top oil importer. Iraq is the second-largest producer in the OPEC. The move will bolster Iraq’s position in Asia, the world’s biggest and fastest-growing oil-consuming region, which already takes 60 percent its oil exports at some 3.8 million barrels per day (bpd). It is not clear where the JV (joint venture) would be located, but the port city of Tianjin, near Beijing, was under discussion. Singapore is also among the options. China is under the pressure to cut oil purchases from Iran, OPEC’s third-largest producer, as the United States re-imposes sanctions on Tehran and threatens to choke off the Islamic republic’s oil exports to zero. The SOMO-Zhenhua deal would give China another crude supply option as the Iran and U.S. oil flows are threatened. Last year, Zhenhua won a term contract to supply diesel fuel to SOMO for the first time, and it also recently entered a deal to develop Iraq’s East Baghdad oilfield.
Source: Reuters
27 August. Oil company Chevron estimated 2018 oil production in Indonesia at 218,300 barrels per day (bpd), lower than 247,300 bpd in 2017, company data distributed to a parliamentary committee showed. The outlook includes output projections from four oil blocks in Indonesia, including the East Kalimantan block, whose contract expires in October. Chevron’s Rokan alone is expected to produce 203,800 bpd. In the first half of the year, Chevron Pacific Indonesia oil lifting was 207,148 bpd, according to data from Indonesia’s upstream oil and gas regulator (SKKMigas).
Source: Reuters
26 August. South Sudan has resumed pumping 20,000 barrels per day (bpd) of crude from Toma South oil field, where production had been suspended since 2013, the Sudanese Oil Minister Azhari Abdulqader said. South Sudan’s oil output currently stands at 130,000 bpd and is expected to reach 210,000 bpd by year-end, he said. South Sudan’s oil is shipped to international markets via a pipeline through Sudan.
Source: Reuters
22 August. OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) and other oil exporting producers are expected to agree on a mechanism to monitor their crude production before the end of the year, Kuwaiti Oil Minister Bakhit al-Rashidi said. A committee set up by the OPEC and allied non-OPEC exporters would review their crude output at a meeting in Algeria next month, he said. The committee that will meet in Algeria on 23 September, known as the JMCC, is chaired by Saudi Arabia and includes OPEC members Algeria, Kuwait, United Arab Emirates and Venezuela, as well as non-OPEC members Oman and Russia. Iran asked to attend the meeting to defend its market share which could be impacted by US sanctions due to take effect on its oil industry in November.
Source: Reuters
27 August. ExxonMobil said it has commenced a A$120 million ($88 million) offshore exploration drilling off Australia’s southeast coast to search for new sources of natural gas. ExxonMobil Australia is also actively considering a potential gas import project to bring additional supply to the country’s east coast market, Chairman Richard Owen said.
Source: Reuters
22 August. China’s Sinopec Corp has teamed with Zhejiang Energy Group Co Ltd on a 3 million tonne per year liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminal in east China, with the first phase set for operation at end-2021. The project, to be built in Wenzhou of Zhejiang province, includes four tanks each able to store 200,000 cubic meters of LNG, a berth to dock tankers of 30,000 cubic meters to 266,000 cubic meters, as well as a 26 kilometre (16 mile) pipeline. The two companies launched new entity Zhejiang Zheneng Wenzhou LNG Co Ltd that is 51 percent owned by the Zhejiang group, 41 percent by Sinopec and 8 percent by a local investment firm, Sinopec said. The Wenzhou terminal puts the Zhejiang group into China’s so-called “second-tier” of LNG players, which are local-government-backed city gas distributors that are emerging as new merchants in the global gas market.
Source: Reuters
25 August. A vessel hauling a shipment of coal from the United States switched its destination to South Korea from China, according to ship tracking data, a day after China imposed 25 percent tariffs on the US (United States) fuel. The Underdog was loaded with 63,000 metric tonnes of coal on 23 July in Long Beach, California, and sailed to China, where it arrived off the coast of Nanshan on 17 August. The Underdog was one of several U.S. cargoes that have rerouted amid the US trade dispute with China. Last month, a coal cargo on the Navios Taurus shifted to Singapore after originally heading to China. US coal exports to China dropped in July, with only two other tankers, the Navios Altair I and Glory, departing from California to China, and carrying a combined 128,000 metric tonnes of coal. No ship with US coal departed for China in August. The US shipped 3.2 million tonnes of coal to China last year, up from less than 700 tonnes in 2016, making it China’s seventh largest supplier.
Source: Reuters
28 August. The Transmission Company of Nigeria (TCN) has stepped up effort to boost electricity supply in the country with the commissioning of three new transformers in Lagos, Niger and Ekiti States. The new power transformers will increase electricity transmission capacity from 200 megavolt-ampere (MVA) to 300 MVA in Ejigbo Substation, 60 MVA to 120 MVA in Bida Substation and from 80 MVA to 140 MVA in Ado Ekiti Transmission Substation. TCN said the newly installed transformers were in addition to the several power transformer projects executed in the last one year in various substations across the country.
Source: Premium Times
27 August. China Machinery Engineering Corp (CMEC) will complete a project for the construction of a third unit at Serbia’s Kostolac B coal-fired power plant in 2020, CMEC Chairman Zhang Chun said. CMEC signed in November a contract for the construction of a 350 MW unit in Kostolac B which will produce 2.5 billion kilowatt hour of electricity annually. A total of $613 million (€527.7 million) will be invested in the construction of the new unit as part of the second phase of a project for the overhaul of Kostolac B at a total cost of $715.6 million, the government said.
Source: SeeNews
24 August. ScottishPower will increase its standard variable gas and electricity prices by an average of 3.7 percent from 8 October, the firm said. The increase is due to a rise in wholesale energy costs of more than 20 percent since April, ScottishPower said.
Source: Reuters
22 August. The Jamaica government said the construction of a multi-million dollar power plant in St. Catherine, southeast of the capital could provide the impetus for increased local and foreign direct investment into the country. The 190 MW power plant being constructed by the Jamaica Public Service is estimated to cost $330 million and is being financed by largely by local investors. Prime Minister (PM) Andrew Holness said that the development, which is two months ahead of schedule and within budget, is a major achievement for Jamaica, as not only will it ensure the country’s energy security, but for the average consumer, it will inevitably see a reduction in your electricity prices.
Source: Trinidad & Tobago Express
28 August. Norway’s Equinor said it is considering whether to build a pioneering offshore wind farm with floating turbines to supply electricity to two North Sea oilfields as part of a strategy to curb greenhouse gas emissions. Norway’s greenhouse gas emissions have remained high despite pledges for deep cuts under international accords such as the Paris climate deal. Last year, Norway’s annual emissions were 2.4 percent above 1990 levels at 52.4 million tonnes. The company’s first floating offshore wind farm began operating off Scotland last year, supplying electricity to the onshore market. Equinor has also announced plans for bottom-fixed offshore wind projects in the United States, Poland and Britain. A final investment decision on the plan for Snorre and Gullfaks, known as the Hywind Tampen floating wind farm, will be made in 2019, Equinor said.
Source: Reuters
27 August. Russia’s state civil nuclear power corporation Rosatom has started to load nuclear fuel at the fourth power unit of the Tianwan Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) in China, Rosatom said. Overall, 163 fuel assemblies are planned to be loaded into NPP’s fourth power unit. Nuclear fuel loading signifies the start of the stage of the power unit’s launch into operation. In the next stage, the power unit will be launched with its connection to China’s power grid. The second stage of Tianwan NPP (the third and fourth power units) is being built with the assistance of ASE, Rosatom’s engineering division. Currently, three VVER-1000 power units built under the Russian project are operational at the Tianwan NPP. NPP is the largest facility of the Russian-Chinese economic cooperation. The first stage of NPP (the first and the second power units) was launched in 2007. The launch of the third power unit of NPP dates back to December 2017.
Source: Financial Tribune
27 August. South Africa has cancelled plans to add 9,600 MW of nuclear power by 2030 and will instead aim to add more capacity in natural gas, wind and other energy sources, Energy Minister Jeff Radebe announced. Africa’s only nuclear power has an installed capacity of 1,860 MW but plans under the government of former President Jacob Zuma to have six times that output by 2030 hit hurdles over cost and other issues. The plan also showed that electricity demand on the grid has been declining. Russian state-owned firm Rosatom was seen as a frontrunner to build the additional nuclear capacity. Several meetings between Zuma and Russian President Vladimir Putin led to speculation that Rosatom had secured the deal before the launch of the public tender.
Source: Reuters
25 August. Exxon Mobil Corp has been looking to buy renewable energy for delivery in Texas. The largest US (United States) oil company sent out a request for proposals with a 8 June deadline, inviting solar or wind power suppliers to pitch contracts that would last 12, 15 or 20 years. Exxon, based in Irving, Texas, is seeking at least 100 MW and would consider proposals for more than 250 MW. Exxon has been slow to follow Big Oil rivals such as Royal Dutch Shell Plc and BP Plc into renewable energy technologies. But as the price of renewable power declines, the company may see the value in consuming wind or solar, even if it eschews producing that kind of energy.
Source: Bloomberg
25 August. Iran has resumed talks with Russia to build a new nuclear power plant capable of generating up to 3,000 MW of electricity, Energy Minister Reza Ardakanian said. The Islamic Republic currently has the capacity to produce 1,000 MW of nuclear electricity. Iran already runs one Russian-built nuclear reactor at Bushehr, its first. Russia signed a deal with Iran in 2014 to build up to eight more reactors in the country. The United States in May pulled out of a deal between Tehran and major powers to limit Iran’s nuclear ambitions, and Washington imposed new sanctions on Tehran in August.
Source: Reuters
24 August. The European Union (EU) will scrap import controls on solar panels and cells from China in September, rejecting a request from EU producers who argue that the bloc will be opening its doors to a flood of dumped products. The EU first imposed anti-dumping and anti-subsidy measures for Chinese solar panels, wafers and cells in 2013 and extended them in March 2017 by 18 months, signaling that they should then end. Chinese manufacturers are allowed to sell solar products in Europe free of duties if they do so at or above a minimum price that has progressively declined. If sold for less than that price, they are subject to duties of up to 64.9 percent.
Source: Reuters
23 August. Biofuel producer and oil refiner Neste sees good opportunities for its renewable jet fuel despite a canceled pilot project in Switzerland. The Finnish company is hoping to get a boost for its biofuels business in the coming years from proposed reductions of CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions in aviation. The pilot project was due to replace at least 1 percent of jet fuel used at Geneva airport with Neste’s biofuel, until Swiss authorities told Neste they had decided not to back the scheme. The International Civil Aviation Organization is targeting carbon-neutral growth in aviation from 2020. Alongside Neste, at least one other company, US (United States) AltAir Fuels, has tested biofuel for aircraft with pilot projects.
Source: Reuters
22 August. Britain’s Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) has notified EDF Energy Nuclear Generation Ltd and Doosan Babcock of its intention to prosecute both companies over a non nuclear-related health and safety matter, the ONR said. The charge relates to an incident in April at the Hinkley Point B nuclear plant owned by France’s EDF, which resulted in injury to a Doosan Babcock employee.
Source: Reuters
22 August. Four of Japan’s biggest nuclear operators and plant builders have started talks on a potential partnership in atomic energy, as the sector struggles to reboot in the wake of the Fukushima disaster seven years ago. Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings Inc (TEPCO), Hitachi Ltd, Toshiba and Chubu Electric Power Co Inc have signed an initial agreement that will be fleshed out in discussions. The companies had begun talks on an alliance that would initially focus on decommissioning old reactors. That could be extended to building and maintaining nuclear plants, with the moves likely to spur a broad realignment in Japan’s nuclear industry. Japan’s nuclear sector provided about 30 percent of the country’s electricity supply before a tsunami and earthquake caused reactor fuel meltdowns at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi station in March 2011. The disaster highlighted regulator and industry failings and turned swathes of the public against nuclear power, with all reactors needing to be relicensed by a new regulator to meet tougher safety standards. Japan had 54 operational reactors before the disaster, but utilities have announced plans to decommission nine units in the aftermath, in addition to the six reactors at Fukushima, where a decades long clean-up is in progress.
Source: Reuters
As on 31 March 2018
| Fuel Type | Installed Capacity (MW) |
| Coal | 1, 97, 172 |
| Oil/Diesel | 838 |
| Gas | 24, 897 |
| Nuclear | 6, 780 |
| Hydro | 45, 293 |
| Renewables | 69, 022 |
| Total Generation Capacity (Utilities) | 3, 44, 022 |
Installed Capacity: Utilities and Captive
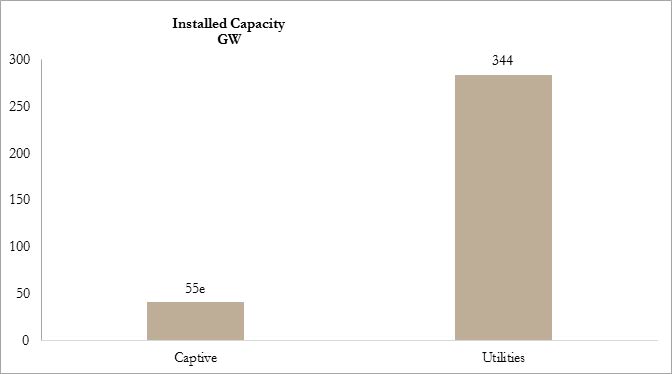
e: Estimated
Source: Central Electricity Authority
Publisher: Baljit Kapoor
Editorial Advisor: Lydia Powell
Editor: Akhilesh Sati
Content Development: Vinod Kumar Tomar
|
OBSERVER RESEARCH FOUNDATION 20, Rouse Avenue, New Delhi- 110 002 PHONE: (011) 3533 2000, FAX: (011) 3533 2005 E-Mail: [email protected] |
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.