World Food Safety Day is celebrated annually on 7 June, with the purpose to promote awareness and action on food safety. World Food Safety Day was established by the
United Nations General Assembly in December 2018 to highlight the importance of safe food for public health and well-being. The day aims to draw attention to the global need for safe, nutritious, and sustainable food, as well as to promote efforts to prevent, detect, and manage foodborne risks.
Food safety is a critical global concern as unsafe food can lead to food-borne illnesses, which can have severe health consequences. An estimated 600 million people—nearly 1 in 10—die each year from food-borne illnesses, while 420,000 people lose their lives each year, resulting in a loss of 33 million years of healthy life. Unsafe food also has
economic implications, as it can adversely impact trade and tourism, affecting both national economies and the livelihoods of individuals involved in the food industry. The
cost of unsafe food is estimated to be US$ 110 billion annually in lost productivity and healthcare costs in low-income and middle-income nations.
Food safety is a critical global concern as unsafe food can lead to food-borne illnesses, which can have severe health consequences.
Each year, World Food Safety Day focuses on a specific theme to address different aspects of food safety.
The theme for World Food Safety Day 2023 is “Food Standards Save Lives”. Food standards are a set of regulations designed to ensure the safety and quality of food products and thus, it plays a crucial role in protecting public health and saving lives. They provide a framework for farmers and processors to ensure the safe and hygienic handling of food products. The Food Code, also known as the “
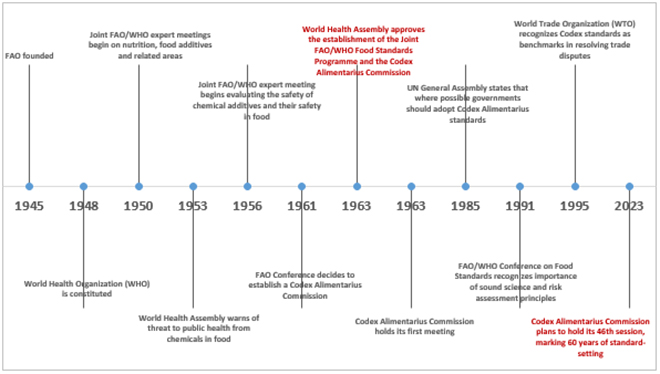
Codex Alimentarius”, is an international set of standards, regulations, and codes of practice designed to safeguard consumers’ health and promote ethical practices in the food industry. The Codex Alimentarius Commission was established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1963 to safeguard consumer health and promote ethical standards in the food industry. The
Codex standards are the cornerstone of food safety, having been in place for over 60 years. Every year, the 'food code' continues to expand, with new standards being established and existing standards being updated as new information becomes available.
 Source: WHO-World Food Safety Day 2023
Source: WHO-World Food Safety Day 2023
WHO’s
Global Strategy for food safety 2022–2030 calls on member states to adopt, adapt, and reinforce their national food safety frameworks with an integrated approach by harmonising food safety and quality; environment; agriculture; and health. As Codex standards and Codex texts are non-binding, they must be codified as national laws or regulations to be enforceable. In India, food standards and regulations are governed by the
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI). The FSSAI plays a key role in ensuring food safety and promoting public health through monitoring and supervision of food-related activities. It is important for food businesses and consumers in India to be aware of these
standards and regulations and ensure compliance to maintain food safety. Other than preventing food-borne illnesses, food standards set guidelines and regulations for food production, processing, handling, and storage; maintaining the quality and nutritional value of food; labelling allergenic ingredients and managing potential allergen cross-contamination; food fraud prevention for economic gain; and facilitating international trade by promoting a level playing field for producers and ensuring that food products meet safety and quality requirements across different countries. By adhering to common standards, countries can establish mutual trust in each other's food safety systems, facilitating the import and export of food products while safeguarding public health.
The FSSAI plays a key role in ensuring food safety and promoting public health through monitoring and supervision of food-related activities.
The
Codex offers a set of science-based standards to the international community that can assist countries in achieving a number of Sustainable Development Goals—SDG 1 (No Poverty) by translating global food safety standards into national law. This allows local traders to enter new markets and expand their business, thus, indirectly achieving SDG 2 (Zero Hunger). It achieves SDG 3 (Good Health & Well Being) by protecting consumer health and strengthening food safety systems to reduce the prevalence of food-borne illnesses; SDG 8 (Decent Work & Economic Growth) by encouraging fair trade practices in the food sector by removing trade barriers and obstructions; SDG 12 (Food Waste & Management of Chemicals) through accurate and reliable food labelling; and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the SDGs) by working together to ensure that no one gets left behind when it comes to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals for 2030.
Food Safety is an important public health concern and is an essential component of achieving food security.
Food safety and security complement each other and contribute to our sustainable future. The security dimension focuses on access and affordability, ensuring that everyone in the world has access to enough food. Food safety safeguards food from contamination or deterioration to ensure that consumers have access to nutritious and safe food.
To feed 10 billion people in 2050, we need new solutions for our food security and sustainability in the future without sacrificing food safety to meet the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Food safety safeguards food from contamination or deterioration to ensure that consumers have access to nutritious and safe food.
By prioritising food safety, we can mitigate
health risks, minimise food waste, build consumer confidence, support agricultural productivity, and facilitate trade. These efforts collectively contribute to achieving food security, where all individuals have access to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food to meet their dietary needs and preferences. Overall, food standards serve as a crucial framework for ensuring the safety, quality, and integrity of our food supply. By complying with these standards, food producers, processors, distributors, and retailers contribute to the prevention of food-borne illnesses and contribute tothe consumers’ well-being.
Shoba Suri is a Senior Fellow at the Observer Research Foundation
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.



 World Food Safety Day is celebrated annually on 7 June, with the purpose to promote awareness and action on food safety. World Food Safety Day was established by the
World Food Safety Day is celebrated annually on 7 June, with the purpose to promote awareness and action on food safety. World Food Safety Day was established by the 
 PREV
PREV


