-
CENTRES
Progammes & Centres
Location

In 2015, the United Nations General Assembly unveiled the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through the 2030 Agenda, an ambitious resolution to foster inclusive global development. These 17 goals, encompassing 169 defined targets, provide a comprehensive framework for measuring development in both inclusive and sustainable terms, considering the dimensions of space (equity) and time (sustainability). However, in the post-pandemic world, prioritising the SDGs is imperative from a strategic standpoint, particularly given the current trajectory that suggests the world is falling short of attaining all 17 SDGs.
Sustainable business practices remain integral to the achievement of these SDGs and these have garnered increased significance in recent years. These practices, which have long existed, are now recognised for their critical role in mitigating adverse impacts on our planet and securing humanity's future. They encapsulate strategies enabling companies to boost profitability and address the three pillars of sustainability—economic, environmental, and social.
The private sector and multilaterals play crucial roles in advancing global SDG objectives, with a notable shift away from a singular focus on short-term profit maximisation.
As such, the relationship between business performance and sustainable development involves a two-way causality. The private sector and multilaterals play crucial roles in advancing global SDG objectives, with a notable shift away from a singular focus on short-term profit maximisation. Instead, businesses are increasingly prioritising sustainability parameters to formulate long-term strategies.
This shift is motivated by several factors. Firstly, addressing SDGs helps mitigate long-term risks stemming from environmental, political, and social dimensions, safeguarding market competitiveness ahead of regulatory policy implementations. Secondly, achieving the SDGs fosters transparency in sustainability risks and impacts, reducing information asymmetry and enhancing governance processes. Additionally, aligning business solutions with SDGs creates opportunities for market expansion, revenue maximisation, and job creation through strategic partnerships. Lastly, deepening partnerships for SDGs, when integrated into national and corporate budgets, enhances business competitiveness, market resilience, and overall company goodwill.
While many studies delve into various facets of supply chain practices, a noticeable gap exists— the absence of a comprehensive framework applicable across diverse industries. Today's global economy relies on intricate supply chain networks as the backbone for delivering products and services. Supply Chain Management (SCM) orchestrates the seamless flow of goods and services, managing relationships among manufacturers, intermediaries, and end-users. As these supply chains expand into complex and opaque networks, challenges abound. Resource scarcity identification, population growth, urbanisation trends, market dynamics, internationalisation, shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and risks pose formidable obstacles. These challenges necessitate innovative solutions for effective supply chain management.
Supply Chain Management (SCM) orchestrates the seamless flow of goods and services, managing relationships among manufacturers, intermediaries, and end-users.
Digitisation is a transformative force that has granted organisations a comprehensive, real-time view of their supply chains. It empowers organisations to optimise inventory, streamline delivery, and minimise waste, aligning with SDG 12 (Sustainable Consumption and Production). Moreover, it is a conduit for embracing and executing supply chain integration through digital technologies. Digital technologies, including automation, data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT), are instrumental in elevating overall supply chain performance and enhancing efficiency.
This technology adoption facilitates real-time data access, seamless communication, and streamlined processes. The result? Enhanced competitiveness through meeting customer demand effectively, reducing costs, and improving overall viability. Research conducted in the Western Balkans region revealed that the timely exchange of precise information among participants resulted in a decrease in waste, thereby, enhancing the sustainability of the perishable supply chain. The duration of product flow through the chain decreased by 11 percent, and inventory costs were reduced by 8.69 percent for the producer and 20.60 percent for the retail sector.
Recent research indicates the potential of digital technologies to enhance sustainability performance within supply chains. This guidance becomes particularly valuable for organisations considering Artificial Intelligence-based technologies. Digitisation has also paved the way for new business models, such as the circular economy, focusing on waste reduction, resource conservation, and sustainable value creation.
Two prevailing digital technologies, IoT and Big Data Analytics (BDA), stand out in the contemporary business landscape. The IoT, a network of interconnected devices collecting and transmitting data, provides real-time insights into operations. An assessment conducted jointly by Accenture and the World Economic Forum reveals that when digital technologies are expanded across various sectors, they have the potential to contribute a significant portion—up to 20 percent—of the emissions reduction required by 2050 to align with the International Energy Agency's net-zero pathways in the energy, materials, and mobility sectors. The rapid adoption of digital technologies in these sectors can already result in emissions reductions ranging from 4 to 10 percent.
Industry 4.0's role in sustainable supply chain management is examined, with businesses anticipating that digitalisation will enhance sustainability through big data analytics for energy management and knowledge transfer within the chain.
Simultaneously, blockchain technology gains attention for its potential to revolutionise supply chain management through transparency and data sharing. As digitisation transforms collaboration within supply chains, sustainability takes centre stage. Industry 4.0's role in sustainable supply chain management is examined, with businesses anticipating that digitalisation will enhance sustainability through big data analytics for energy management and knowledge transfer within the chain.
Traditionally, supply chain management prioritised efficiency and profitability. However, the spotlight has shifted towards sustainability, embracing environmental, social, and economic dimensions. This shift is particularly evident in emerging economies like India, China, and Southeast Asian nations, where measuring supply chain performance has become crucial for analysing and enhancing overall performance. A systematic review reveals the need for measurement matrices and management frameworks to advance performance, emphasising the growing concern for sustainability.
Sustainable supply chains are built on three crucial pillars, which collectively form the foundation for a balanced and resilient supply chain network: a) Economic sustainability, which ensures long-term profitability by managing risks, minimising disruptions from environmental and social factors, and safeguarding reputation; b) Environmental sustainability, which minimises carbon footprints and transforms business practices into positive environmental contributions; and c) Social sustainability, contributing to social well-being by upholding human rights, promoting fair labour practices, and emphasising social responsibility.
Figure 1: A framework of Supply Chains’ Impacts on Sustainability
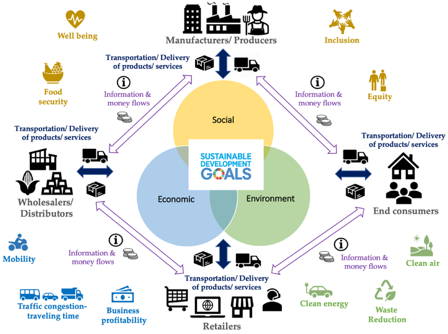
Source: Salinas-Navarro et. al.
In conclusion, sustainable operations and supply chain management are not merely altruistic endeavours but fundamental components of responsible and forward-thinking business strategies. Embracing sustainability across manufacturing, logistics, procurement, and sourcing is a fundamental shift towards a more resilient and ethical business world. This strategic imperative not only enhances profitability, resilience, and competitiveness but also positively impacts the planet and society as a whole. As businesses navigate the challenges of the 21st century, sustainability is not just a choice but the way forward.
Soumya Bhowmick is an Associate Fellow with the Centre for New Economic Diplomacy at Observer Research Foundation
Indrani Mukherjee is a Research Intern at Observer Research Foundation
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.

Soumya Bhowmick is a Fellow and Lead, World Economies and Sustainability at the Centre for New Economic Diplomacy (CNED) at Observer Research Foundation (ORF). He ...
Read More +
Indrani Mukherjee is a Research Intern at Observer Research Foundation ...
Read More +