With its vast and diverse economy, India has witnessed significant shifts in employment dynamics over the years. The economy's employment landscape is evolving, with numerous sectors offering substantial growth potential. As India continues on its path of economic development, the following opportunity sectors in the Indian economy are expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the country's employment outlook.
(1) Digital services
India's leadership in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) has fostered innovation and led to the integration of digital technologies across various sectors, creating a demand for skilled professionals in software engineering, data science, and digital marketing. The digital economy can potentially create 60 to 65 million jobs by 2025, most requiring functional digital skills. This trend is aligned with the broader global shift towards digitalisation, where India's expertise and workforce are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of work.
Figure 1: Sector-wise growth rate of India’s IT industry (in percentage)
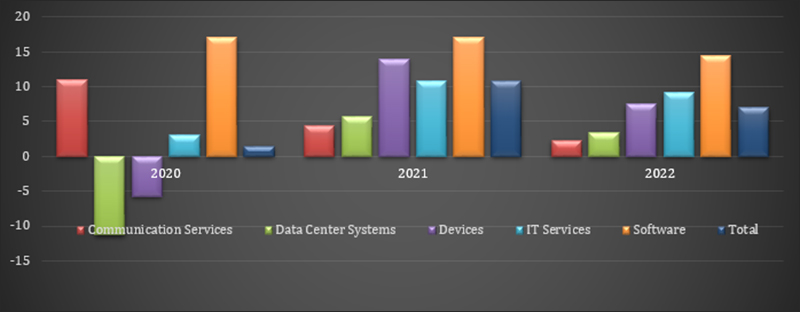
Source: Department of Commerce, USA
(2) Financial services:
The financial services sector in India is undergoing significant expansion, driven by increasing demand for banking and insurance services. Moreover, the emergence of fintech innovations is reshaping the industry and opening new employment opportunities. Firstly, the shift towards digital banking creates a demand for professionals skilled in mobile and online banking technologies, customer experience design, and cybersecurity. Second, the insurance sector is witnessing a transformation with technology integration. Expected to grow to US$ 250 billion by 2025, the insurance sector will be pivotal, with an opportunity of US$ 78 billion in additional life insurance premiums from 2020-30.
(3) Health services:
The Indian healthcare sector is undergoing significant growth driven by various factors. Firstly, an ageing population is increasing the demand for healthcare services, particularly for age-related and chronic illnesses. Secondly, heightened healthcare awareness has increased the need for medical services, preventive care, and regular check-ups. Technological advancements, including telemedicine and health apps, have enhanced healthcare accessibility, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, with telemedicine gaining prominence for remote consultations. The hospital industry, valued at US$ 61.79 billion in 2017, is expected to reach US$ 132 billion by 2023.
(4) Hospitality services:
India's tourism industry is on the cusp of significant growth, providing employment prospects in hotel management, travel agencies, culinary arts, transportation, and related services. The rebound of the tourism sector after the pandemic is poised to contribute to economic development and job creation. Additionally, tourism-related services, including souvenir shops and entertainment, further expand employment opportunities. With a current market size of US$ 23.5 billion and a promising CAGR of 4.73 percent, the industry is expected to grow to US$ 29.61 billion by 2028.
Table 1: Targets of Draft Tourism Policy, 2022
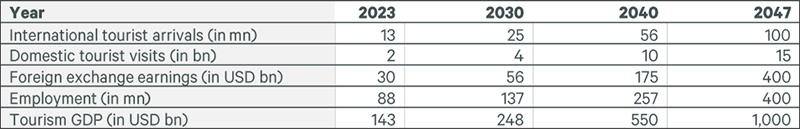
Source: CBRE
(5) Consumer retail services:
The Indian retail sector is undergoing a significant transformation with the increasing dominance of e-commerce and organised retail. Digital marketing has also become pivotal in the e-commerce era, with positions such as SEO specialists, content creators, social media managers, and digital advertising experts actively contributing to businesses' online presence. This retail sector transformation is reshaping the job landscape in India, fostering diverse opportunities in logistics, warehousing, digital marketing, and related fields, thereby bolstering the Indian job market. Expected to grow at a CAGR of 25 percent, with India’s thriving middle-class population, the retail market can grow up to US$ 1.1 trillion by 2027 and US$ 2 trillion by 2032.
(6) Global capability centres:
India's Global Capability Centers (GCCs) are essential components of the IT-enabled services sector, playing a vital role in supporting multinational companies' back-office operations globally. This sector is a significant driver of employment in India, offering diverse job opportunities. Firstly, GCCs provide customer support services, employing individuals with strong communication skills and language proficiency. Second, they offer IT consulting services, creating jobs for software engineers, system analysts, cybersecurity experts, and project managers. And, third, finance and accounting teams within GCCs hire accountants, financial analysts, and auditors.
(7) Renewable energy:
India has made substantial progress in advancing clean energy solutions, particularly in renewables, which promote environmental sustainability and generate significant employment, primarily in solar and wind power. Renewable energy expansion can create millions of jobs, focusing on skilled workers for installation, maintenance, and research in green energy technologies. This trend aligns with global shifts towards clean energy, where sectors like solar photovoltaic, hydropower, biofuels, and wind power drive job growth in the renewable energy field. In 2022, the solar industry alone employed an additional 52,080 people. As the sector grows, it can potentially employ 1 million people by 2030.
(8) E-commerce:
The expansion of online shopping has driven demand for efficient logistics and delivery services, creating jobs for thousands of delivery partners and gig workers. E-commerce companies are significant employers, requiring a diverse range of professionals, including IT experts, digital payment specialists, and merchandisers. The e-commerce market in India is expected to surge to US$ 200 billion by 2026, a substantial rise from its 2020 figure of US$ 46.2 billion.
(9) MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises):
Micro, Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) are integral to India's economy, contributing more than 30 percent to the GDP, with a substantial share in exports. They are a crucial source of employment, supporting millions of livelihoods, second only to agriculture. Moreover, MSMEs serve as a breeding ground for entrepreneurship, innovation, and broader economic engagement, making them a vital component of India's economic landscape. MSMEs have employed a record 123.6 million people between July 1, 2020 and August 1, 2023.
Figure 2: Distribution of Employment in the MSMEs
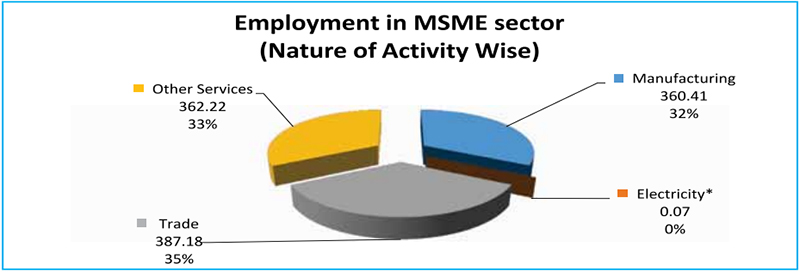
Source: Ministry of MSME, Annual Report
(10) Startup ecosystem:
India's thriving startup ecosystem owes much of its success to the government's introduction policies, such as the Startup India Initiative of 2016 and tax incentives that relieve financial burdens on startups, fostering innovation and expansion. India's concerted efforts to improve its business environment have elevated its status as an appealing destination for startups, further fuelling the development of Indian towns and cities like Bengaluru, Mumbai, Chennai, Gurgaon, etc., entrepreneurship hubs—aiding job creation, and enhancing India's global competitiveness in the startup arena.
Figure 3: Jobs created by Startups
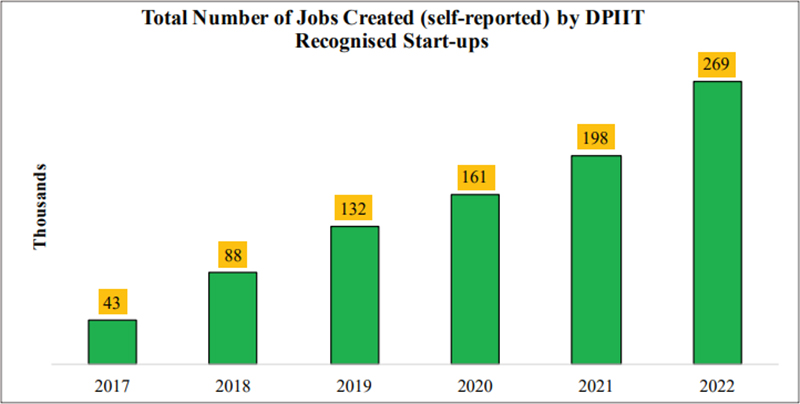
Source: Indian Economic Survey, 2022-23
In summary, India's employment landscape is experiencing a significant transformation across various sectors. Ranging from digital services to a thriving startup ecosystem, the country is poised for substantial job creation. With government initiatives and a dynamic workforce, India is well-positioned for diverse and robust employment growth as it continues its vision of becoming the world's third-largest economy by 2027-28.
Soumya Bhowmick is an Associate Fellow with the Centre for New Economic Diplomacy at the Observer Research Foundation.
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.








 PREV
PREV


