Blue foods rank among the most traded food commodities worldwide, playing a vital role in global food security and nutrition while supporting the livelihoods of millions. Approximately 3 billion individuals rely on blue foods for about 20 percent of their animal protein consumption, and fishing supports the livelihoods of 10-12 percent of the global population. The blue economy represents an innovative strategy for balancing economic growth, societal well-being, and environmental conservation through oceanic resources. It involves employing science-backed management methods to ensure sustainable harvesting, protect fish stocks, and preserve marine biodiversity. Sustainable seafood production, rich in vital nutrients like protein and omega-3 fatty acids, is a key focus of the blue economy. Efficient utilisation of aquatic resources not only meets the dietary demands of a growing populace but also lessens negative environmental impact compared to land-based protein sources.
The blue economy represents an innovative strategy for balancing economic growth, societal well-being, and environmental conservation through oceanic resources.
The blue economy concept focuses on the connection between human activities and the environment, especially in coastal regions. Although humans have relied on and inhabited coastal areas for millennia, the blue economy represents a contemporary approach aimed at fully integrating oceanic resources into all economic levels, ranging from local to national scales. Its objective is to formulate a deliberate and efficient sustainable development strategy.
The blue economy, initially valued at US$ 1.5 billion, is forecasted to reach US$ 2.5-3 trillion by 2030. There is a growing interest in leveraging the potential of the blue economy to alleviate poverty in the least developed countries and small island developing states, as well as to facilitate a blue recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. The African Union's Agenda 2063 views the blue economy as the next frontier. Evidence shows exponential growth in several marine sectors, notably the seafood industry, the fastest-growing segment in the food industry, and coastal tourism, the fastest-expanding sector in tourism.
Blue foods play a crucial role in advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) related to poverty reduction and hunger eradication by fostering a sustainable and fair food system. They not only offer nutritious foods rich in micronutrients and animal protein, aiding in reducing infant and maternal mortality rates and supporting cognitive function (SDG 2 - Zero Hunger, SDG 3 - Good Health and Well-being), but also contribute to sustainable food production with minimal greenhouse gas emissions (SDG 12 - Responsible Consumption, SDG 14 - Life Below Water, SDG 15 - Life on Land) and provide livelihoods for small-scale farmers (SDG 1 - No Poverty, SDG 8 - Decent Work and Economic Growth, SDG 10 - Reduced Inequalities).
Blue foods play a crucial role in advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) related to poverty reduction and hunger eradication by fostering a sustainable and fair food system.
The concept of blue food carries significant potential for bolstering global food security and sustainability by leveraging the abundance of marine resources. Oceans and aquatic environments offer a wide range of seafood, algae, and other aquatic organisms that can serve as nutritious and sustainable food sources. Harnessing this potential helps diversify the food supply, easing pressure on traditional land-based agriculture and fostering a more resilient global food system.
The sustainability of blue food stems from the ability of marine ecosystems to regenerate when managed responsibly. It also aligns with sustainable fisheries and aquaculture practices, promoting biodiversity conservation and minimising adverse environmental impacts. Recognising and utilising the nutritional richness of marine resources, blue food presents a promising pathway to address food security challenges while advancing long-term sustainability objectives.
The sustainability of blue food stems from the ability of marine ecosystems to regenerate when managed responsibly. It also aligns with sustainable fisheries and aquaculture practices, promoting biodiversity conservation and minimising adverse environmental impacts.
Blue foods play a crucial role not only in providing food and nutritional security to billions of people but also in sustaining the livelihoods, economies, and cultures of many riparian and coastal communities. Unlike foods sourced from land-based animals, blue foods exhibit remarkable diversity, often containing essential micronutrients and fatty acids, and can be produced using environmentally-friendlier methods. Fig. 1 illustrates how blue foods are central to transforming food systems. Therefore, recognising the importance of blue foods for food and nutrition security provides a critical rationale for safeguarding the integrity and diversity of aquatic species and ecosystems.
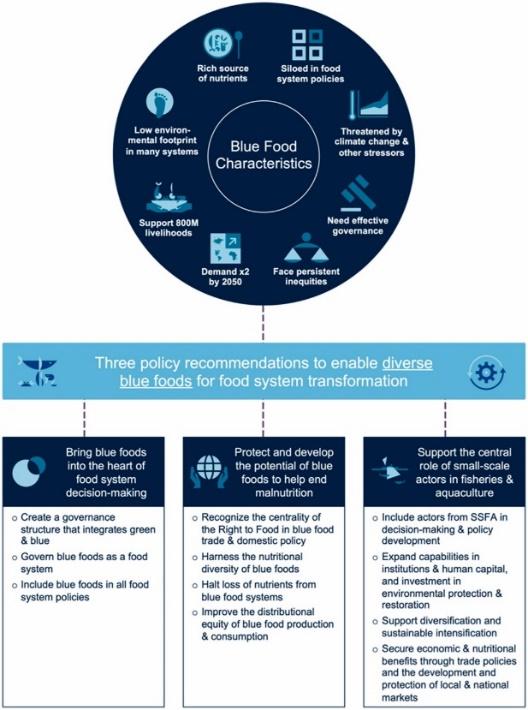
Role of blue foods in the Global Food System
The potential of blue foods to enhance food security and sustainability presents a promising pathway for addressing critical global challenges. It calls for a holistic approach that integrates environmental, social, and economic considerations.
-
Promoting sustainable practices by encouraging and incentivising sustainable fishing, aquaculture, and seaweed farming practices to ensure the long-term health of marine ecosystems and biodiversity.
-
Investing in research and innovation in blue food production technologies, such as aquaponics, integrated multi-trophic aquaculture, and sustainable seafood processing, to enhance productivity while minimising environmental impacts.
-
Strengthening governance and regulation at local, national, and international levels to manage marine resources sustainably, prevent overfishing, and address pollution and habitat degradation.
-
Supporting coastal communities, small-scale fishers, and aquaculture farmers to improve livelihoods, ensure equitable access to resources, and enhance resilience to climate change impacts.
-
Promoting awareness and consumption about the nutritional benefits and sustainability of blue foods, promoting local and traditional blue food consumption, and encouraging sustainable seafood choices.
As we draw closer to 2030 and the deadline to attain the SDGs, by adopting a holistic approach that integrates environmental, social, and economic considerations, the potential of blue food to enhance food security and sustainability can be realised, contributing to a resilient and thriving food system for present and future generations.
Shoba Suri is a Senior Fellow at the Observer Research Foundation.
Subhasree Ray is the Lead, Nutrition & Wellness (Corporate Medical Services), at Reliance Industries Limited.
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.




 PREV
PREV



