COMMERCIALISING COAL MINING: TOO MUCH TOO LATE?
Coal News Commentary: January – February 2018
India
Private companies would soon be able to mine and sell coal in India, alongside CIL. Four years after enabling commercial mining and sale of coal through the Coal Ordinance (Special Provisions), 2014, the Cabinet approved a bidding process for commercial mining. The auction would be on a transparent online platform and the government would not get any share from commercial mining. The government would conclude the auction in 2018-19, so that production can start in two to three years. The mines and auction platform is yet to be identified. In 2015, the government had allowed allotment of coal mines to states for mining and commercial sale to medium, small and cottage industries. Commercial mining is not expected to have any bearing on CIL’s production targets. CIL aims to touch 1 bt of production in 2019-20. CIL has been the dominant commercial miner in India for 41 years and has a market share of 80 percent. Another permitted player is Singareni Collieries, a venture of CIL and the Telangana (earlier Andhra) government. The rest of the requirement is met through import and production from captive mines. This news attracted unexpected attention from even international mainstream television news channels. Experts said that the World’s third largest coal user opening its mines to commercial mining carried the connotation of an open invitation to commit the crime of coal mining but they pointed out that reality is less dramatic. Demand for electricity and consequently the demand for coal is growing much slower than originally thought. Domestic companies which made suicidal bids for coal blocks are walking away from their projects even if it is at a cost. Many observed that opening up coal mining for commercial mining is probably too much too late.
Coal, as a primary source of energy, will continue for some more time in India and its demand in the non-regulated sector is expected to be higher than the regulated sector like power, the study – ‘Coal Vision 2030′ said. Overall coal demand is estimated to be 900-1,000 million mtpa by 2020 and 1,300-1,900 mtpa by 2030. CIL has commissioned the study to assess the future demand scenarios for the coal sector in India up to 2030. By 2030, of the overall coal demand, thermal coal demand is estimated to be 1,150-1,750 mtpa and the balance is coking coal demand. The Coal Vision Document 2030 suggests that no new coal mines need to be allocated or auctioned beyond the current pipeline. According to the document, total capacity of mines allocated and auctioned, including CIL, SCCL and Neyveli Lignite, as on date is about 1,500 mtpa at the current rated capacity. In the short term, coal production is likely to be significantly lower than the potential, although demand may be met. Majority of the mines currently auctioned or allocated (including CIL, SCCL) are scheduled to be completed by FY20. Based on the current status of these blocks, it is estimated that captive or commercial coal blocks may contribute 90-170 mtpa by 2020. However, this does not exclude the possibility of coal deficit at consumers’ end driven by evacuation constraints, marketing policies and mismatch between regions of production vis-a-vis consumptions. Coal mining companies need to ensure continuous monitoring and portfolio planning to avoid coal deficit.
CIL’s decision to move to the global standard of charging customers based on the actual consumption of the GCV of coal may work in the company’s favour only if it can control quality and assure supplies in the higher bracket of a said coal grade. The current pricing mechanism, according to CIL, is based on considering the mid-point of the GCV range of a particular grade. Thus, if the miner supplies coal that is higher than the mid-point GCV, it loses revenue. Under the new mechanism, this would change. GCV is the amount of heat released by the complete combustion of a unit of natural gas or coal. To elucidate this fact, the official pointed out that G11 grade of coal has a GCV range of 4,000-4,300 kcal. The price of G11 has been fixed at ₹ 955 per tonne considering the mid-point GCV to be 4,150 kcal. Under the new mechanism, which will be effective from the 2018-19 financial year, the consumer will be charged based on the actual GCV consumption, which eliminates the scope of losing revenue. Coal consumers have been complaining a lot about the quality of Indian coal alleging not only about grade slippages but pointing that the coal supplied is towards the lower end of the contracted GCV range. The Coal Consumers Association said that although India has the world’s fifth-largest coal reserves at 308.80 bt the coal seams in the country are laden with stone bands and layers. Thus, the deposits are not as pure or refined as is the case with Australia, South Africa or other producers. CIL said that the revision in the billing policy was imminent as it brings the miner at par with global practices and would benefit the consumers. However, CIL will continue to have the current 17 coal grades in place. Nevertheless, analysts caution CIL of revenue shortfall in case the exact contracted GCV is not supplied.
In order to boost coal supplies to power plants, the government has decided on various steps including the use of dedicated rail transportation and setting up of power projects only within 500 km from coal mines. It has also decided that all power plants within 20 km from pit-head of coal mine will construct elevated closed belt conveyors within next 2 years. As per the estimates on the basis of power consumption growth, the requirement of domestic coal in 2018-19 would be about 615 mt which means that 288 rakes of coal per day would be required from CIL.
CIL will produce 513 mt of coal in 2018-19 and offer 12 mt via e-auction to meet the power sector’s demand. The balance amount to meet the power industry’s demand of 615 mt of coal would come from Singareni Collieries and captive coal blocks, CIL said. Captive mines allotted to private power developers and states would collectively contribute 105 mt by 2021-22 from 37 mt currently. CIL is expected to close the current financial year with 500 mt production. After facing coal deficit in the last quarter, which led to power generation loss, the ministry of power has asked CIL and the Railways to ensure supply of 615 mt of coal with the movement of 288 rakes every day.
The Competition Commission of India dismissed allegations of unfair business practices against CIL with regard to sale of coking coal. The complaint filed by Jharkhand-based Industries and Commerce Association was also against BCCL and coal ministry, apart from CIL. Industries and Commerce Association’s members, which are involved in the manufacture and sale of hard coke, were buying coking coal from BCCL under the distribution system of ‘linkage’ till the introduction of National Coal Distribution Policy in October 2007. Under the new policy, they were required to receive 75 percent of their coal requirement through FSA at notified prices to be fixed by CIL and balance 25 percent through e-auction or import. The first FSA expired in 2013 and the second one is due to end in 2018. The coal ministry had issued guidelines in February 2016 to CIL regarding auction of linkages for non-regulated sectors.
CIL charted a company-wise plan for enhanced loading of 288 rakes a day. Of the eight subsidiaries of CIL, Mahanadi Coalfields Ltd would load the highest number of rakes per day, at 76. It would be followed by South Eastern Coalfields (57 rakes per day). Production from captive coal blocks awarded to private power developers and states is expected to improve. The coal ministry auctioned the 29 coal blocks to the private sector and allotted 11 mines to states through India’s first e-auction. A portal is being developed wherein the status of coal availability at siding/ mine, availability of railway rakes being supplied to the power plants and the status of coal stock at the power plants would be monitored on an almost real-time basis.
The country’s coal import increased by 12.4 percent to 18.49 mt against 16.44 mt in the same month of the previous fiscal, according to m-junction, a leading name in the e-auction space. On a month-on-month basis, however, there was a flat growth in non-coking coal, it said. Overall, coal and coke imports in April-January of 2017-18 stood at 179.5 mt, marginally lower than 180.8 mt recorded for the same period last year. India is expected to see a rise in coal imports.
The BJP promised to resume mining in the state, if voted to power. In its Vision Document the BJP promised to put back on track the coal mining issue in 180 days of forming the government. Coal mining in Meghalaya is ostensibly part of the “customary tribal rights” that has been temporarily banned by the National Green Tribunal in the state from April 17, 2014, after tribal Dimasa groups filed an application before it alleging that the water of the Kopili river was turning acidic due to coal mining in Jaintia Hills. Environmental activists said that the was a case of double standards as the BJP is presenting a green image to overseas observers.
Indian resources conglomerate Adani Enterprises Ltd is looking to buy mines in countries such as Indonesia, the company said, despite its struggles to develop a controversial coal project in Australia. The company already owns a coal mine in Indonesia, but has been unable to secure financing for the long-delayed Carmichael mine in Australia amid numerous court challenges from environmental groups concerned about climate change and potential damage to the Great Barrier Reef. Adani is also India’s biggest trader of coal, with volumes of 81 mt in the fiscal year that ended on March 31, 2017, sourced mainly from Indonesia and Africa. India, the world’s second biggest coal importer after China, brought in a total of 190 mt last fiscal year. The company’s market share in coal trading in the country was going to increase after it extended to retail markets, especially brick kilns and sponge irons. The company has also recently started trading coal in Sri Lanka and Bangladesh, in addition to its operations in Thailand, Taiwan, Vietnam and China.
Adani has failed to meet financial and jobs creation milestones through its $16.5 billion Carmichael coal mine project in Queensland, the Australian state’s premier said and asked the Indian energy giant to fulfil its commitment. Adani Australia disclosed that it was currently employing 800 people working across operations and projects in Queensland and had invested over $3.3 billion in Australia. The Australian government had said it would not finance a vital rail-link project that supports Carmichael coal mine. The Adani Group has for over five years battled the opposition to any expansion of the Abbot Point port, saying it will cut into the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. The Adani group entered Australia in 2010 with the purchase of the greenfield Carmichael coal mine in the Galilee Basin in central Queensland, and the Abbot Point port near Bowen in the north.
Reliance Power said CIL has been directed by the Delhi HC to immediately commence coal supplies to the Unit-I of Butibori power project. Reliance Power has set up 2 x 300 MW Butibori Plant near Nagpur through its subsidiary Vidarbha Industries Power Ltd, which is supplying its entire power to Reliance Infrastructure Ltd (Distribution Utility), which distributes electricity to over 2.8 million consumers in Suburban Mumbai under a long-term Power Purchase Agreement approved by Maharashtra Electricity Regulatory Commission. While coal is being supplied to Unit 2 by CIL through its subsidiary Western Coalfields Ltd, the supply was not commenced to Unit 1 of the Butibori Plant despite a valid LoA issued by the CIL subsidiary pursuant to the recommendations of Standing Linkage Committee (Long Term) comprising of coal ministry, power ministry, CIL, Central Electricity Authority and Railways among others, in 2008, the company said. The LoA had promised supply of 1.23 mtpa of coal for Unit 1, it said. The coal supply issue was pending for nearly four years after the commissioning of the unit and commencement of power supply to Reliance Infrastructure Ltd in April 2014 under a long-term Power Purchase Agreement approved by Maharashtra Electricity Regulatory Commission. The Delhi HC, has noted that the Butibori Plant has fulfilled the pre-requisite of SHAKTI Policy, wherein FSAs are to be signed with existing LoA holders, and has a case for having an FSA executed in its favour, it said. After the directions of Delhi HC, both units of Butibori Plant would be getting assured coal supplies from Coal India subsidiaries under 100 percent FSA/MoU and mitigate the uncertainties in supply of 600 MW quality and reliable power to citizens of Mumbai, it added.
Faced with delays in key approvals and sudden change in tariff terms, Essar Power has decided to surrender the Tokisud North coal block in Jharkhand in which it has already invested ₹ 4.9 billion. The move will cripple the company’s 1,200 MW Mahan plant in Madhya Pradesh. The Ruias-run company has made significant progress in developing the coal block, which has extractable reserves of 52 mt, and won through a competitive bidding process in February 2015 offering ₹ 1,100 a tonne, the highest in the industry. Surrendering the coal block will hit its 1,200 MW, ₹ 80 billion Mahan Power Plant, which had been shut between September 2014 and May 2016 after the Supreme Court had cancelled all the 204 coal blocks allotted by the previous Manmohan Singh government citing corruption. The Mahan plant resumed operations in May 2016 after Essar Power procured coal through government conducted e-auctions and the company hopes to rework the power purchase agreement with the MP discom accordingly. The coal ministry had issued a termination notice to the Tokisud North coal mines and asked them to forfeit ₹ 2.61 billion bank guarantee for non-payment of upfront amount for the block.
The Central Bureau of Investigation has launched an investigation into alleged irregularities in the invoicing of inferior quality coal imported from Indonesia which was passed on to state run power generation companies, NTPC Ltd and Aravali Power Company as ‘superior quality’, causing a loss of ₹ 4.87. The over-invoicing of imported coal imported between 2011-12 and 2014-15 was done in connivance with officials of NTPC, MMTC and also APCPL, a joint venture of Delhi and Haryana government with NTPC, a probe by directorate of revenue and intelligence in the matter had revealed. NTPC, MMTC and APCPL operate coal-based thermal power plants for which they import coal through global tenders. MMTC and CEPL emerged successful bidders for the supply of coal.
Rest of the World
China’s thermal coal futures hit record highs after four top utilities warned of potential heating and electricity shortages and as the worst blizzards this winter continued to blast some central and southern provinces. China’s State Power Investment Corp, China Datang Corp, China Huaneng Group and China Huadian Corp asked the government to boost supplies of coal and temper a months-long rally in prices. Thermal coal futures have jumped over 10 percent this year, extending a months-long rally, as utilities rush for supplies to deal with soaring power demand as cold weather sweeps across swathes of the nation.
China will add at least 200 mt of rail freight capacity in 2018, including at least 150 mt of thermal coal capacity. China is trying to push more transportation of goods from coal to agricultural produce onto the rail network and reduce transport by road as part of its effort to reduce pollution. The government and rail operator are prioritising current coal deliveries for power plants. Currently coal stocks at power plants nationwide are enough for 15 days.
China National Coal Group Corp, or ChinaCoal, expects to launch 15 coal mines with total capacity of 54.7 mt in 2018, the company said. Coal mines will be in Inner Mongolia, Shanxi and Shaanxi regions of northwestern China. The company has ordered 23 of its coal mines to keep production open during the upcoming Lunar New Year holiday, adding an average of 50,000 tonnes of daily output compared to the holiday last year. ChinaCoal also said it will not hike physical coal prices before early March to ensure coal supplies. Moves came after utilities warned of tight coal supplies amid soaring coal prices and heavy snow storm across the country. China’s No.2 coal producing province Shanxi asked coal miners to shorten or cancel Lunar New Year holiday.
China plans to increase high-quality coal supply by allowing mines to boost capacity if they shut outdated production processes, the latest effort by authorities to further streamline the industry and stabilize coal prices. Coal companies will be encouraged to close inefficient and polluting mines and replace them with larger ones if they meet certain standards, the NDRC said. The incentives are the latest of several measures taken by China to foster closer ties among coal mines, coal-related businesses and power utilities as it looks to stabilize coal prices. Last year, China’s top coal miner Shenhua Group Corp took over China Guodian Group Corp and created world’s largest power utility. To halt the price surge and ensure coal supplies to utilities amid frigid weather, the NDRC ordered the major coal port of Qinhuangdao, in China’s northeastern Liaoning province, to cap FOB thermal coal prices at 750 yuan a tonne from February 5. China aims to eliminate all coal mines with a capacity of less than 90,000 tonnes this year. Industry experts said more than 1,000 mines with a combined capacity of around 150 mt of coal capacity are expected to shut in 2018.
China will carry out “special action” in 2018 to crack down on illegal coal mining to ensure safe mine operations and reduce output capacity, the State Administration of Work Safety said. Coal mines that fail to meet safety measures or operational standards will be ordered to close and rectify violations. 219 coal mining accidents in 2017 and 375 fatalities, down dearly 30 percent from 2016. Annuals deaths in the coal sector have fallen steadily from a peak of nearly 5,000 in 2003. The office of work safety will also carry out inspections to shut so-called “zombie” mines and cut excess capacity at mines. China aims to eliminate all coal mines with a capacity of less than 90,000 tonnes a year to reduce safety risks at coal mines. Some regions have said they plan to raise the threshold to 150,000 tonnes or more.
Protesters gather near the government house to protest the construction of a coal power plant in Bangkok, Thailand. Protesters seeking to stop construction of coal-fired power plants in the country’s south have claimed victory, as the energy ministry agreed to order news assessments of the health and environment impacts of the projects. Thailand’s Energy Minister Siri Jirapongphan told protesters that the health and environmental impacts of two planned coal-fired power plants in the south will be reassessed impartially, an announcement the group termed a victory. The ministry agreed not to proceed with either project if the new review finds them unsuitable. The proposed Krabi plant would generate up to 800 MW and the Songkhla one 2,200 MW of power.
Mongolia’s coal exports dropped by nearly a quarter in January from a year earlier, with deliveries disrupted by ongoing congestion at the border with key trading partner China. The fall was part of a 6.3-percent year-on-year decline in overall mineral exports, according to Mongolia’s National Statistics Office data. The nation’s January coal exports dropped 24.1 percent to 1.995 mt with their value down 18.45 percent at $138 million, the data showed. China was the destination of 90 percent of Mongolia’s total exports in January. In late December, Mongolia suspended coal deliveries to clear the key supply road of a dangerous queue of traffic that at times stretched 100 km into the Gobi desert. The government also plans to open a new route for coal trade to reduce congestion. According to Chinese customs data, Mongolian coal shipments to its southern neighbour fell 18.6 percent in December, 2017 to 2.83 mt though volumes rose 27.6 percent to 33.6 mt over the year as a whole. The Mongolian data showed that the value of gold exports from the country climbed 49.3 percent year-on-year in January to $27.16 million.
Australia’s top coal hauler, Aurizon Holdings Ltd, is on course for a showdown with the world’s biggest coal exporters after a regulator capped the revenue it can charge at A$1 billion ($783 million) less than the company sought. BHP Billiton, Glencore, Anglo American, Peabody Energy and others face cuts of nearly a tenth of their coal export volumes from Queensland state, the country’s biggest coal exporter, after Aurizon said the tough revenue cap would cut throughput on its network. The expected drop in coal traffic would be worse than last year’s losses after Cyclone Debbie, which cut exports by 16 mt and sent prices for metallurgical coal, used in steel-making, skyrocketing. The cuts would lower throughput on the network that transports nearly all of Queensland’s coal output by 20 mtpa, or about 9 percent of total coal traffic.
Japanese trading house Mitsubishi Corp reported a 12-percent rise in April-December profit and raised its full-year forecast again, boosted by stronger-than-expected coking coal prices. Coking coal prices had been higher-than-expected, partially due to stronger appetite from Chinese buyers.
Taiwan has detained a local businessman on suspicion of buying coal from North Korea in violation of United Nations sanctions, prosecutors said. A Taiwanese man surnamed Chiang allegedly carried anthracite from North Korea on a vessel hired through mainland China last August and September, with the cargo sold in open waters off Vietnam. Prosecutors also said three others were being investigated on suspicion of forgery and violating laws on terrorism financing, and have been released on bail.
NATIONAL: OIL
Saudi keen to have stake in west coast, Kakinada project: Oil Minister
February 23, 2018. World’s largest oil company Saudi Aramco is interested in acquiring a stake in India’s proposed Rs 1.8 lakh crore refinery in Maharashtra and Rs 33,000 crore petrochemical complex in Andhra Pradesh, Oil Minister Dharmendra Pradhan said. After talks with Saudi Arabia’s Energy Minister Khalid A Al-Falih, he said the oil kingpin is also interested in partnering in the second phase of strategic oil reserves India plans to build shortly. In Kakinada, Hindustan Petroleum Corp Ltd (HPCL) and GAIL (India) Ltd are looking at building a 1.5 million tonnes capacity petrochemical complex at the cost of Rs 33,000 crore. Pradhan said Saudi Arabia is India’s most reliable partner, supplying close to a fifth of country’s oil needs. Saudi Aramco, the Gulf nation’s flagship oil firm, sells 36.5 million tonnes of oil annually to India. Saudi Aramco had also initially shown interest in IOC’s 15 million tonnes (mt) Paradip refinery in Odisha but walked out of the project in 2006.
Source: The Indian Express
Indian state oil refiners see strong margins for 2018
February 22, 2018. India state refiners expect their profit margins to hold their strength this year as demand growth accelerates for fuel products amid a record $93 billion spent on infrastructure and stable crude oil prices. India’s sales of cars and especially motorbikes are forecast to rise rapidly, even as the development of a Delhi-Mumbai industrial corridor drives consumption of the country’s primary fuel products, diesel and gasoline. The infrastructure programme for fiscal 2018/19 calls for more than 80,000 kilometre (50,000 miles) in new highways to better connect rural areas with urban hubs. Roads and other construction require oil-based products such as tar and plastic piping, and fuel to move materials by truck and rail. India’s annual fuel demand, made up mainly of diesel and gasoline, is expected to grow 7.5 percent in 2018, according to a report by BMI Research, a unit of Fitch. That compares with 5.4 percent last year, according to government data. Refining margins also rely heavily on global crude oil prices, currently around $65 a barrel, and on the status of world inventories of refined products. Indian refiners hope global prices will remain sub-$70 per barrel as world oil production rises while new refining capacity doesn’t keep the pace. The International Energy Agency said it expects oil production to slightly outpace demand this year, especially thanks to still rising output in the United States. Hindustan Petroleum Corp Ltd (HPCL) head M. K. Surana said he expected international crude prices between $62 and $68 a barrel this year, as long as there are no geopolitical crises or technical disturbances like damage to the Forties pipeline. Based on that expectation, India’s refiners should see refining margins, also known as cracks, in the range of $7-$8 per barrel for all three state-owned refiners. India aims to increase its refining capacity by 77 percent to about 8.8 million barrels per day (bpd) by 2030, which will cost dozens of billions of dollars. Indian Oil Corp (IOC), HPCL and Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd (BPCL), that sell most of their output locally at prices linked to global rates, largely reported strong profits and margins for the October-December quarter. While Indian gasoline and diesel prices are linked to global rates, during state or central elections private rivals say state-owned firms often do not increase retail selling rates – a risk to margins, analysts point out, only if crude prices suddenly spike.
Source: Reuters
BPCL to raise $200 mn for Abu Dhabi asset purchase
February 22, 2018. Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd (BPCL) plans to raise $200 million to fund the acquisition of a 3% share in the Lower Zakum Concession, Offshore Abu Dhabi. A consortium comprising Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC)’s overseas arm, ONGC Videsh Ltd (OVL), Indian Oil Corp (IOC) and BPCL’s overseas arm Bharat PetroResources Ltd (BPRL) acquired a 10% stake in the ADNOC (Abu Dhabi National Oil Company) Group owned concession on 11 February. While OVL will hold a 4% stake, BPRL and IOCL will hold 3% each. The deal will give the Indian consortium access to about two million tonnes of annual share from the field which produces about 400,000 barrels of oil a day. Supported by political and diplomatic efforts, Indian energy companies are forming consortiums to pursue acquisitions in international oil and gas fields. India imports nearly 80% of its crude oil. ONGC and Oil India Ltd account for 70% of the total oil produced in India, while the remaining 30% comes from private sector and joint venture companies. ADNOC will also fill up India’s 1.5 million tonne strategic petroleum reserve in Mangalore, beginning May.
Source: Livemint
ONGC shortlists three oil service majors to lift output from two fields
February 21, 2018. Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) is set to hire international oil service giants for the first time to boost output from domestic oil fields in response to a government push to increase local supplies and cut expensive imports. ONGC, India’s biggest explorer, has shortlisted US (United States) oil service companies Halliburton, Schlumberger and GE subsidiary Baker Hughes to submit proposals on boosting production from two onshore fields. The three companies have until May to submit their proposals for what ONGC is calling a “production enhancement contract” for an oilfield in Assam and another in Gujarat. The government last September proposed selling a 60 percent stake in ONGC’s producing fields to foreign companies to ramp up domestic oil and gas output and meet Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s target of cutting oil imports 10 percent by 2022. India’s oil production has stalled below 1 million barrels per day (bpd) in recent years, even as oil demand has surged. That has resulted in its crude oil imports soaring, making it the world’s third-biggest importer, behind China and the United States. In January, India’s imports hit a record of almost 5 million bpd. ONGC, which the government hopes to eventually build into a global giant like Exxon Mobil or a state-owned oil major like PetroChina, has often been criticized by analysts and New Delhi for failing to increase its production. ONGC’s output – most of it from fields that have been operating for more than 30 years – is declining at the rate of 7 to 8 percent a year. A major part of the company’s capital expenditure is spent in efforts to pump more oil and gas to set off the yearly decline. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, ONGC’s standalone crude oil production stood at 20.855 million metric tonnes (417,000 bpd), a one percent fall from the previous year.
Source: Reuters
NATIONAL: GAS
RIL-BP’s $4 bn plan for developing 3 sets of discoveries in KG-D6 approved
February 26, 2018. A government oversight panel headed by DGH (Directorate General of Hydrocarbons) approved $4 billion investment plan of Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) and BP plc for developing three sets of natural gas discoveries in the KG-D6 block in the Bay of Bengal. The finds will add around 20 million metric standard cubic meter per day (mmscmd) of peak production, according to BP. RIL is the operator of block KG-DWN-98/3 or KG-D6 while UK’s BP Plc has 30 percent interest and Niko Resources of Canada the remaining 10 percent. The three set of discoveries are ones that the partners are focusing on reviving the flagging output at KG-D6. Management Committee (MC) is the final approving authority after which the companies start investing. RIL and BP had in mid-June last year announced investing Rs 400 billion in the three sets of finds to reverse the flagging production in KG-D6 block.
Source: Business Standard
Anadarko in talks with nine Indian firms to sell gas from Rovuma basin
February 26, 2018. Anadarko Petroleum Corp is in talks with nine Indian companies to sell gas from Mozambique’s Rovuma basin. The United States-based energy company, holding 26.5% stake in Rovuma, is the operator of the block. Gas from the basin is expected to flow from 2022-23, against an earlier estimate of 2019. The consortium is in talks with Petronet LNG, Oil and Natural Gas Corp, Hindustan Petroleum Corp Ltd, Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd and Gujarat State Petroleum Corp among others.
Source: Livemint
Petronet plans 20 LNG stations for buses from state roadways
February 23, 2018. Petronet LNG has planned to launch around 20 LNG (liquefied natural gas) fuel stations on a 4,000 kilometre (km) route running from Delhi to Thiruvananthapuram as part of its larger scheme in association with oil marketing companies and state roadways of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Kerala. The company has also purchased four buses from Tata Motors for its office use in Cochin that will run on gas. It is expected that around 200,000 trucks that join the fleet every year could run on LNG, as it would bring nearly 30-40% price advantage compared to other fuels. India has committed under the Paris Convention to reduce its carbon emissions by 33% to 35% by 2030. It is believed if India shifts to these many LNG vehicles, it could help India meet at least 2.5% of this commitment. India’s target is to raise the use of gas in its energy mix to 15% in three to four years from 6.5% now, to curb emissions and cut its dependence on imported oil. According to Petronet, out of the total 78 million tonnes (mt) of diesel that the country consumes every year, the share of trucks and buses comes to around 28 mt and hence a shift to cleaner gas fuel may turn advantageous for the environment.
Source: The Financial Express
Mahanagar Gas plans mobile CNG services in Mumbai
February 23, 2018. Mahanagar Gas is planning to start mobile dispensing of CNG (compressed natural gas) in Mumbai this year, especially in regions with last-mile connectivity issues and problems of land acquisition. Mahanagar Gas is also evaluating venturing out of Maharashtra and plans to bid in the next round of bidding the Government calls for. The company plans to invest Rs 500 crore in FY19 in expansion of pipelines and setting up of CNG stations. In FY18, the company has invested Rs 350 crore. The company hopes to complete FY18 with 250 CNG stations. It will add another 25 stations in FY19. It sells 30 Lakh kilo CNG per day and procures around 3 million standard cubic meters of gas per day. Besides the company is converting around 7,000 vehicles to CNG per month, up from 5,500 per month last year.
Source: The Financial Express
NATIONAL: COAL
HC pulls up Centre for capping coal mine for Sasan Power Ltd
February 27, 2018. The Delhi High Court (HC) pulled up the Centre for its decision to cap the mining of coal at 17 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) from two mines by Sasan Power Ltd, a Reliance Power subsidiary, to run their 3,960 MW power project in Madhya Pradesh. The company, in its application, has contended that the mining of 17 mtpa of coal allowed from its two blocks Moher and Moher-Amlohri in Madhya Pradesh was not enough to carry out operations till the end of this financial year. Sasan Power has claimed that if it was not allowed to mine another two mtpa, that is up to 19 mtpa, in this financial year, it will not be able to meet the requirements of its Sasan Ultra Mega Power Project (UMPP) that supplies electricity to 14 distribution companies (discoms) in seven states including Delhi. It has claimed that the approved quantity of coal would not meet the requirement for running the plant for the last 10 days of March this year, severely affecting 42 crore consumers. In its application seeking permission to mine 19 mtpa, Sasan has contended that this would also help it to maintain additional stock of coal of 1.25 million tonne for meeting any exigency which might disrupt coal production. The government had justified the cancellation, saying the unit’s coal requirement could be met by the other two mines, Moher and Moher-Amlohri extension.
Source: Business Standard
Emission study not feasible if coal operations stop at MPT: IIT-Bombay
February 26, 2018. The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Bombay, has written to the Goa State Pollution Control Board (GSPCB) stating that in case of a shutdown of coal operations at Mormugao Port Trust (MPT), the objective of a source appropriation study to quantify emission contributions from various sources which create air pollution in Vasco will not be met. The objective of MPT/GSPCB for undertaking the air pollution study was mainly to find out the extent of contribution of coal, if any, in the total pollution load of the Vasco area. The study, at a cost of Rs 94 lakh, is being conducted in view of coal pollution in the port town. GSPCB said the study is a part of the assurance given by Chief Minister Manohar Parrikar that a detailed study would be conducted in Vasco to find out the reasons behind air pollution. GSPCB said the cost of the study would be borne by MPT. The study will be carried out as per Central Pollution Control Board guidelines to ensure the required quality. Its scope includes identification of sampling locations, ambient air quality monitoring, locating pollution sources and source apportionment.
Source: The Economic Times
Government in future may auction coal mines only for commercial use: Coal Secretary
February 26, 2018. The government may in near future scrap the present system of allocating coal mines for captive use and instead only auction mines for commercial use to private as well as foreign companies with a view to boost domestic production and cut imports, Coal Secretary Susheel Kumar said. The move, which would not just help attract foreign investment but also bring in efficiency and promote competition, follows government’s decision of opening up the coal sector to commercial mining by private entities. The Cabinet had approved auctioning of coal mines to any firm bidding the highest per tonne price. At present, private sector firms are only allowed to mine coal for use in cement, steel, power and aluminium plants. Coal India Ltd (CIL) is the sole commercial miner with 80 percent market share. The government had in 2014 auctioned 29 mines to private players and states for capital use in power, steel, aluminium and cement plants. In the following year, it permitted the allotment of coal mines to states for mining and commercial sale to medium, small and cottage industries. Close to 16 mines were allotted to several states.
Source: Business Standard

Safety, minimum wages at coal mines of utmost importance: Coal Minister
February 26, 2018. The government will be mindful of minimum wages provisioning of health services and safety yardsticks at coal mines in the upcoming bidding process, Coal Minister Piyush Goyal said. He also advised the officials to ensure that due help is provided to the dependents of victims of coal mine tragedies to file their claims promptly. He stressed that the management should compassionately and proactively ensure disbursal of the claims due. It was noted that the tool of close monitoring of safety parameters across all coal mines as discussed in the last emergency review meeting held in January last year following Rajmahal mishap is worth emulation by other companies.
Source: Business Standard
Despite liberalisation, power demand to sustain Coal India’s dominance
February 21, 2018. Despite opening up of the coal sector to private miners, Coal India’s dominance in the field is expected to remain firm as the power sector will continue to bank heavily upon this state-owned coal monolith. The company has a mandate to supply at least 75 percent of the production to the power sector and the rest can be offered to others like cement and steel. With Coal India currently routing its supplies majorly to the power sector, the cement and steel plants are bearing the brunt of coal and railway rake shortage. Also, Coal India said that private companies will be more interested in short-term supply agreements which will allow them greater flexibility to react as per global trends and earn higher margins. On the other hand, Coal India will continue to focus on long-term supply agreements which warrant higher and steady offtake thereby ensuring a stable topline in the long term. Nevertheless, Coal Consumers Association (CCA) is expecting sourcing of coal to become much easier as new mines would be made operational and foresee big players including international firms entering the coal mining field. The success, however, will depend on the size of the mine and the reserve price in the forthcoming auctions. Coal Secretary Susheel Kumar said that the private companies, as well as Coal India, can also explore exports as “there is no restriction and no changes to the policy is needed to promote coal exports”. Analysts, however, are sceptical how Indian coal can fare against the black diamond from Australia, Indonesia, South Africa and others owing to its lesser gross calorific value and presence of impurities.
Source: Business Standard

NATIONAL: POWER
Intra-state network constraints affecting power supply in India: Power Secretary
February 27, 2018. India is a power surplus country but electricity does not reach all regions due to network constraints in some states, Power Secretary A K Bhalla said. He was of the view that the consumer should not suffer due to inefficiency of power distribution utilities and there should not be any unscheduled power cuts. The existing legal framework provides that the power cuts should be done only in case of technical faults or natural calamity. There is penal provision for unscheduled power cuts. But power regulators have rarely invoked that provision and penalised distribution companies. He said that the Electricity Amendment Bill will provide for 24X7 power for all from April 1, 2019. The bill will soon be discussed with the states before finalisation for approval of the Union Cabinet and introduction in Parliament. The bill is likely to be pushed for passage in the monsoon session of Parliament sometime in July this year.
Source: Business Standard
No load-shedding, power cuts in Kerala this summer
February 27, 2018. Kerala government said that there would be no power cuts and load-shedding during the coming summer months. The Kerala State Electricity Board and its officials have been asked to take precautionary and stern steps in this regard, Power Minister M M Mani said. It was the CPI(M)-led LDF government’s policy to ensure a Kerala without power cut and load-shedding, he said. The LDF government has also taken steps to re-start the construction works of the power generation projects, which had been held up during the previous UDF government’s tenure, and complete it on a war footing.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
Up to Rs 4k cashback on timely payment of BSES bills
February 27, 2018. In a move to encourage digital payment of electricity bills on time, BSES announced a cashback scheme under which consumers stand to benefit by up to Rs 4,000 on March bills, besides an added benefit on pre-payment of the April one. The Delhi-based power distribution company (discom) said that it has partnered with digital wallet company Paytm to facilitate the 40 lakh customers of both BSES discoms — BSES Rajdhani Power Ltd (BRPL) and BSES Yamuna Power Ltd (BYPL) — in the national capital. The scheme is valid up to March-end. To avail the offer, consumers have to pay their bills from the Paytm website or mobile App and use the promo code BSES2000. The minimum bill amount required to be eligible for the scheme is Rs 100, it said. The cashback will be credited into the consumer’s Paytm account within 24 hours of paying each of the bills, it said.
Source: Business Standard
In India’s power transmission sector, the seller is emerging king
February 26, 2018. In the country’s power transmission sector, the seller is emerging king. With a huge buyer interest from transmission companies and yield-based investment firms, industry experts say it may be a good time to sell transmission assets. Infrastructure investment trust (InvIT) IndiGrid signed agreements with Techno Electric & Engineering Company to buy a stake worth Rs 2.32 billion in Patran Transmission Company. IndiGrid Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Pratik Agarwal said he is on the lookout for more such assets. IndiGrid is not a lone buyer in the transmission sector where only a few assets are up for sale. He said the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board (CPPIB) and IDFC Alternatives were some of the firms interested to pick a stake in power transmission assets.
Source: Business Standard
PFC to provide Rs 502 bn financial aid to Uttar Pradesh
February 26, 2018. Power Finance Corp (PFC) said that it has inked MoUs with Uttar Pradesh power utilities for providing financial assistance of Rs 50,200 crore. The PFC has executed Memorandums of Understanding (MoU) with Uttar Pradesh state sector power utilities – UPRVUNL, UPPTCL and UPPCL – for providing required financial assistance of Rs 50,200 crore, PFC said. According to PFC, these funds would be used for upcoming greenfield and extension of thermal power generation projects at Jawaharpur, Panki, Harduagunj, Anpara and Obra; development of coal mines; Integrated Power Development Scheme, Saubhagya, DDUGJY (rural electrification); and for strengthening of transmission and distribution network in the state. The financial assistance will support the state in capacity addition of 4,760 MW; and in achievement of the objective of power for all and 24×7 quality and reliable power supply in Uttar Pradesh.
Source: Business Standard
AAP opposes move to withdraw power subsidy to SCs, economically weak
February 26, 2018. Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) has opposed the Congress government’s move to withdraw electricity concession given to scheduled castes (SCs) and economically weak consumers. AAP leader Sukhpal Singh Khaira has written to Chief Minister Amarinder Singh requesting him to withdraw the instructions issued by the Punjab government about free electricity to SC, backward classes and non-SC BPL domestic consumers. Khaira said that as per Punjab government’s earlier instructions, subsidy on account of free electricity supply up to 200 units per month was being provided to the beneficiaries but as per the new instruction issued on 17 October, 2017, that came into effect from November 1, 2017, the government has imposed limits of connected load of 1 KW and consumption not exceeding 3,000 units per annum as eligibility for availing this subsidized supply of electricity. He said that the limit of 1 KW connected load was low and would render more than 50% poor and needy families disqualified for this subsidy. He said that the government is trying to fetch money being spent on its avoidable expenses like crores of being paid to ministers and advisers, from the pockets of poor and needy people of the state. Khaira said that the Congress before assembly elections had announced to provide more facilities to the poor and needy people but has started withdrawing the facilities already given to these families. He demanded that the limit of connected load may be enhanced to 3 KW and for 200 units per month concession and the extra units may be charged as per tariff if situation demands. The condition of 3,000 units per annum must be withdrawn, he said.
Source: The Economic Times
Power projects refuse to bleed, companies snap supply in Gujarat
February 25, 2018. Faced with spiralling prices of coal, Adani Power Ltd and Essar Power Gujarat Ltd have discontinued the contracted power supply of 2,000 MW and 1,000 MW respectively, to Gujarat Urja Vikas Nigam Ltd (GUVNL). As per the data available with Western Regional Dispatch Load Centre, Gujarat bought a record 32 million units, roughly 1,333 MW, of electricity from power exchanges. Gujarat bought a record 32 million units, roughly 1,333 MW, of electricity from power exchanges. Touted to be a power-surplus state, Gujarat is forced to procure more electricity from the open market as several power plants are struggling to cope with the cost of coal and gas.
Source: The Economic Times
Exclusive police stations for power theft cases to shut in Maharashtra
February 25, 2018. The half a dozen police stations set up by state-run utility MSEDCL to probe electricity theft cases across Maharashtra will be closed and matters pending with them will be moved to local police stations. The Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company Ltd (MSEDCL) started six police stations – in Kalyan, Nashik, Pune, Jalna, Latur and Nagpur – in 2006 to investigate the cases of electricity theft. Over 1.6 lakh electricity theft cases, involving Rs 19,170.59 lakh, were registered at these police stations since their inception. As per the data available till December 2017, these police stations had solved 68,099 cases, while 87,420 power theft cases were pending with them.
Source: Business Standard
Karnataka power distribution firm’s proposal to hike tariff opposed
February 25, 2018. The Karnataka Chamber of Commerce and Industries (KCCI) has urged the Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission (KERC) to increase the quality of service and promote alternative energy sources rather than increasing power price. KCCI honorary secretary Vinay Javali said that the KCCI is not asking the government to cancel the proposal of hike of Rs 1.23 by Hescom. Javali said that the authorities should think of increasing the power generation and supply through alternative sources of power generation such as solar, wind and others.
Source: The Economic Times
Chhattisgarh government planning to electrify all households by September
February 24, 2018. The Chhattisgarh government is aiming to provide power supply to every household by September 2018. Chief Minister Raman Singh said that in the last 14 years, the state has established a new record in power generation, transmission and distribution. He said that in the last 14 years, around Rs 28,151 crore has been invested for electricity generation, which has resulted in the increase of production capacity of state electricity company by two and a half times. The Chief Minister noted that due to the production and availability of electricity, he has set a new record of meeting the maximum demand of 4,332 MW in the state. He said that according to the report of the Central Electricity Authority, in the State Sector Performance-Based Evaluation, the state’s production houses have got the distinction of being the pioneers in the country.
Source: The Economic Times
In Madhya Pradesh, 97k schools have no electricity
February 23, 2018. In a state, which is synonymous with poor social development indicators, is another shocker. Nearly 97,000 primary and middle schools go without electricity in the age of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI)— highlighting dismal infrastructure across the state. In July 2016, School Education Minister Vijay Shah had informed the state assembly that more than one lakh government primary, middle and higher secondary schools do not have power supply for past three years. After almost two years, there is hardly any change in the situation as the number bears it out. The school education department has deprived nearly one lakh primary and middle schools of the basic facility. Last year, the ministry of human resources and development ranked Madhya Pradesh third among states having poorest record of electricity provision in 28% of primary, middle, high and higher secondary schools.
Source: The Economic Times
Electricity supply to reach over 15k houses under Saubhagya
February 23, 2018. As many as 15,561 families in Aurangabad zone will soon get power connection for the first time under the Centre’s Saubhagya Yojna. The central scheme aims to achieve cent percent household electrification by providing last mile connectivity and electricity connections to all households in rural and urban areas. As part of the scheme, eligible beneficiaries will be given one power plug and one LED (light emitting diode) bulb free along with the internal house wiring. MSEDCL (Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company Ltd) said that a total of 13,253 connections for above poverty line (APL) citizens and another 2,308 for below poverty line (BPL) residents would be given under the Saubhagya Scheme. Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojna, also titled as Saubhagya scheme September 25 last year. Under the scheme, households sans power connection from rural and urban areas will be provided electricity. Free connections will be provided to prospective beneficiaries households using the Socio Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011 data. But even those not covered under this data can avail benefit of the scheme by paying Rs 500 in 10 instalments along with the electricity bills. It is mandatory for the beneficiaries of the scheme to pay monthly electricity bill. Only the households in which electricity has been permanently disconnected, living in temporary immigrants camps and houses in the agricultural land where it is not monetarily feasible to provide electricity, are excluded from this scheme. In the remote and inaccessible areas, where the conventional electrification is not possible, household will be electrified through the solar energy power packs. At such places 1 DC Fan, 5 LED Bulbs and 1 Power Plug will be provided free with the internal house wiring, MSEDCL authorities said. The houses constructed under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojna, Shabri Yojna, Ramai Yojna, Adim Yojna and other schemes will also be provided free electricity under Saubhagya scheme. On the basis of the survey done under the Saubhagya Scheme in the state, there is a target to extend power connections to 11,64,135 beneficiaries. Of these, 7,67,939 beneficiaries will be provided electricity through conventional energy sources and 21,056 will be provided through the non-conventional sources, MSEDCL authorities said. As a part of the scheme, cent percent electrification will be done in the state by the end of this year. Those who wish to get benefit of the scheme can contact the toll-free number 18002003435/ 18002333435 or the nearest state power utility office.
Source: The Times of India
70 yrs after Independence power reaches Elephanta Isle near Mumbai
February 22, 2018. Seventy years after Independence, a 7.5-km long undersea cable has finally brought electricity to the world-famous Gharapuri Isle, which houses the UNESCO World Heritage site Elephanta Caves, about 10 kilometre (km) from Mumbai, Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company Ltd (MSEDCL) Regional Director Satish Karape said. The project to electrify the island, thronged daily by thousands of Indian and foreign tourists, has cost a total of Rs 25 crore and was completed in 15 months, Karape said. Karape said that of the total project cost, the Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority gave Rs 18.50 crore while the rest had been borne from the MSEDCL’s own resources. The power connection is also expected to speed up work on the proposed 8 km long ropeway connecting Mumbai directly with Elephanta Island running above the Arabian Sea, planned by the Mumbai Port Trust, and billed as a boon to nearly two million tourists who visit it annually.
Source: Business Standard
NATIONAL: NON-FOSSIL FUELS/ CLIMATE CHANGE TRENDS
SECI allocates 50 MW wind power capacity to Odisha
February 27, 2018. The Solar Energy Corp of India (SECI) has allocated 50 MW wind power capacity to Odisha to meet the state’s Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs) for promoting the renewable energy sector. The only cost added to it is power. Under a scheme of the SECI, all the other costs are waived off. The maximum possible price discovered is Rs 2.45 per kilowatt hour (kWh) excluding the trading margin. The SECI’s trading margin will be Rs 0.07 kWh. Odisha has been a laggard compared to states such as Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Gujarat. Even if Odisha sets a target of generating 200 MW in its Renewable Energy policy 2016, not a single MW of power has been generated yet from wind energy. The state has the potential to generate 1700 MW of wind energy. The potential sites identified are Gopalpur, Chatrapur, Puri, Paradeep, Balasore, and Damanjodi. The SECI has formulated a scheme for setting up 2000 MW wind power projects to help non-windy states comply with their non-solar RPOs. The procurement of wind power from these projects will be a tariff discovered through a transparent process of bidding by the SECI.
Source: Business Standard
M&M plans to double its electric vehicles portfolio in 3 yrs
February 27, 2018. Mahindra & Mahindra (M&M), which plans to invest Rs 800 crore towards product development and capacity expansion in its electric vehicle business, aims to double its portfolio and bring on road at least four new models in the segment in the next three years. Given that incentives under the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles) Scheme are expected to be there for the duration, the company is predicting massive potential to grow electric vehicle sales. Though the government has yet to announce extension of the FAME Scheme beyond March 31 this year, there have been indications that it would eventually do so. Existing schemes are being implemented on ground and the resultant increase in electric vehicle adoption should start showing in the next one to two years, Mahindra Electric Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Mahesh Babu said. Anticipating higher demand, Mahindra has commenced work towards increasing production capacity for electric vehicles to 60,000-70,000 units a year from the current 5,000. In the ongoing financial year, the company is expecting to double sales to 2,400-2,500 electric vehicles, given the growing awareness about electric vehicles. Nearly, half these will come in from taxi operators and others in the fleet segment. Mahindra Electric, which did a pilot with 100 electric cars in association with Ola in Nagpur, has also formed an association with Uber Technologies. To begin with, the duo will deploy electric vehicles in Delhi and Hyderabad. The programme will later be extended to cover more cities. Mahindra Electric has supplied 500 electric vehicles to Lithium Urban Technologies, which provides a cab service comprising electric vehicles. It has bagged also an order for 1,000 electric cars from Bengaluru-based fleet operator Bhagirathi Travel Solutions. Babu said the government should support adoption of electric vehicles for some more time.
Source: The Economic Times
GUVNL floats wind power tender with greenshoe option
February 27, 2018. Gujarat Urja Vikas Nigam Ltd (GUVNL) has invited bids to procure 500MW of power from grid-connected wind power projects. The apex power utility in the state has also kept a greenshoe option for the additional purchase of 500 MW. This is the second such tender by GUVNL within a year’s time. GUVNL will enter power purchase agreements with successful bidders for a period of 25 years from the scheduled commercial operation date of the project. All wind power projects will be set up in Gujarat and the minimum project capacity is 25 MW. The last date for submission of bids is April 2, 2018. At present, installed wind power capacity in Gujarat is 5,339 MW. It may be mentioned that early this month, the power utility also floated a tender to purchase 500 MW of power from solar photovoltaic projects along with a greenshoe option for an extra 500MW. GUVNL had invited separate bids for 500 MW each from wind and solar developers. Six companies were selected by GUVNL in December to supply it 500 MW of wind power.
Source: The Times of India
Solar installations in India likely to fall 22 percent in 2018
February 26, 2018. Solar installations in India are expected to fall by 22 percent to around 7.5 GW in the 2018, Mercom Communications India, a subsidiary of Mercom Capital Group has said. Mercom forecasts total installations to fall by 22 percent year-on-year to approximately 7.5 GW in 2018, it said in a report. Large-scale solar projects accounted for the bulk of installations in 2017, nabbing about 90 percent of the total, with the remaining 10 percent coming from rooftop solar installations, Mercom found. Approximately 10.6 GW of large-scale solar projects were under construction, with another 4.3 GW of tenders pending auction as of December 31, 2017.
Source: The Financial Express
Avaada Power plans to invest Rs 250 bn in clean energy projects in 4 yrs
February 26, 2018. Clean energy player Avaada Power plans to invest ₹ 25,000 crore in the sector and develop 5,000 MW capacity in largely solar and wind projects in the next four years, the company said. Vineet Mittal, chairman of Avaada, said that if the group manages the 5 GW target in four years, it will demonstrate the company’s capability to global investors. Avaada is also looking at projects in South Asia and Africa as part of its overseas operations. Talking about India’s renewable energy sector, Mittal opposed trade barriers such as anti-dumping and safeguard duties on solar imports as it would lead to increased cost of power to the consumers. He suggested that the government should provide incentives such as upfront capital subsidy, interest subvention to domestic solar manufacturers to create a level-playing field with global giants in the segment. He said that the government needs to provide clarity on issues relating to the renewable energy sector to achieve its target of 175 GW installed renewable energy capacity by 2022. He said that the government needs to conduct reverse auctions in the right way because that is creating a ‘gambling habit’ among developers which has led to solar and wind tariffs hitting rock bottom.
Source: The Economic Times
J&K exploits just 16 percent of hydropower potential despite growing demand
February 25, 2018. Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) has exploited only about 16 percent of the estimated 20,000 MW of hydropower potential even as the energy demand has been growing gradually creating a wider demand-supply gap, the state economic survey 2017 said. The estimated hydropower potential of J&K is 20,000 MW, of which about 16,475 MW have been identified. However, Power Development Department (PDD) is committed to exploiting the available hydro potential to an optimum level to meet the growing demand. Various reforms are underway at the level of the state government and the Centre for making the power sector more efficient and more competitive. PDD said the biggest problem is on the distribution front as Aggregate Technical and Commercial (AT-C) losses of the state are on the higher side. The main reasons for such high losses are technical as well as commercial. To minimize losses, the system needs up-gradation and improvements, especially in existing outdated distribution network. However, with the efforts of the government the AT-C losses, which were estimated at 61.30 percent in 2014-15 were reduced to 58.82 percent in 2015-16.
Source: Business Standard
Chandigarh to become 100 percent renewable powered city
February 25, 2018. In a bid to tap its full resources and become a 100 percent renewable energy powered city, the Chandigarh administration has asked the union ministry of power to increase the quota of renewable power plants. The administration has also urged the ministry to waive-off fixed charges to the tune of Rs 50 crore that it owes for using non-renewable power plants. Ministry of new and renewal energy (MNRE) has set December 31 as deadline for UT to transform into a 100 percent renewable energy powered city. The department has purchased the required power from central generating stations, which include hydro, thermal and nuclear power stations as the UT electricity department does not generate power on its own. For this purpose, it has inked long-term purchase pacts with the power stations for which it will be liable to pay fixed charge to each generating station in addition to actual cost of power purchased. Chandigarh electricity department caters to more than 2 lakh consumers with an annual energy consumption of around 1,600 million units. In order to meet the power demand, which is estimated to be around 400 MW, the department has purchased about 202 MW from hydro stations, 80 MW has been inducted from thermal power plants, while 10 MW is procured from nuclear power stations. The electricity department has written to power ministry to transfer the power quota, which it gets from non-renewable power stations to renewable power stations. The administration has also requested the MNRE to provide 40 MW of wind energy. MNRE has directed administration to prepare a master plan for achieving the target, including solar wind, biomass and waste for energy projects.
Source: The Economic Times
India to achieve 175 GW installed renewable energy target before 2022: Government
February 23, 2018. India would achieve the target of 175 GW of installed renewable energy capacities well before 2022, New & Renewable Energy Secretary Anand Kumar said. He said that over the years the renewable energy has become cheaper and is set to replace conventional energy, which is a healthy development, and added that India has one of the fastest growing renewable energy programmes in the world. He stressed that the country would achieve its target of 175 GW of installed renewable energy capacity well before 2022. ISA (International Solar Alliance) shall help mobilise sufficient funds for solar energy projects. He said the ISA is an excellent idea which helps millions of people to provide universal energy excess.
Source: Business Standard
Separate tariff category for electric vehicles in the works: CEA
February 23, 2018. The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) is in the process of coming up with a separate tariff category for electric vehicles. Plans are afoot to consider introducing ‘Time of Day’ metering for charging such vehicles. The government has expressed its intention to make India an all-electric passenger vehicle market by 2030. The CEA is also exploring the possibility of having a battery swapping model wherein firms’ aggregate batteries, charge them and swap with discharged batteries.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
Indian scientists develop test bed to generate clean energy
February 22, 2018. Indian scientists have developed a supercritical CO2 (carbon dioxide) Brayton test facility at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) to generate clean energy from power plants, including solar thermal, the premier institute said. Touted to be the first in the country, the Brayton cycle test loop facility was unveiled by Union Minister of Science and Technology Harsh Vardhan. The facility is part of the Indo-US consortium — Solar Energy Research Institute for India and the United States (SERIIUS). Funding was provided by the Indian government’s Department of Science and Technology under the Indo-US Joint Clean Energy Research and Development Centre programme. The new-generation high-efficiency power plants with closed cycle CO2 as the working fluid have the potential to replace steam-based nuclear and thermal power plants, thus reducing the carbon foot print significantly, the IISc said. While the current day’s thermal power plants would use steam to carry the heat and turn a turbine to generate power, the research makes use of supercritical CO2 (SCO2) instead of steam to generate more power. Supercritical refers to the state of carbon dioxide above its critical temperature of 31 C and critical pressure of 73 atmospheres, which makes it twice as dense as steam.
Source: Business Standard
RInfra bags Rs 36.4 bn contract for thermal power plant in Tamil Nadu
February 22, 2018. Reliance Infrastructure (RInfra) said it has won a Rs 36.4 billion contract from Tamil Nadu Generation and Distribution Corp Ltd (TANGEDCO) for work related to Uppur Thermal power project. The contract entails design, engineering, supply, erection, testing and commissioning of BoP (balance of plant) package and allied civil works on EPC (engineering, procurement and construction) basis. The project is to be commissioned in 36 months. With this contract, RInfra’s EPC order book now stands at over Rs 150 million, it said. With a clear focus to position itself in India’s growing infrastructure sector, and a multitude of projects in the offing in areas as diverse as power, metro rails, nuclear power plants, air quality control, marine, railways, ports, and mega infrastructure projects, RInfra is targeting EPC opportunities worth Rs 2 trillion and increase the EPC order book to Rs 500 billion by FY19, it said. Recently, the company said it had secured multiple EPC orders in power sector including 2 x 250 MW lignite-based CFBC Thermal Power Project from NLC India and Flue Gas Desulphurisation works of 3 x 500 MW power plant from NTPC.
Source: Business Standard

Modi government plans Gobar-Dhan scheme to convert cattle dung into energy
February 22, 2018. First getting villagers to collect and treat it, then tapping entrepreneurs to set up plants to generate bio-gas and bio-CNG, pushing it to market through oil and gas marketing and then selling it online through e-commerce platforms— a 360 degree plan is in the works to convert cattle dung to energy and organic manure and the government is dead serious about it. Called Gobar-Dhan, the scheme roadmap is not just meant as a means to convert waste to wealth, but is an ambitious effort to clean India’s villages. According to estimates, India has about 30 crore cattle population and approximately 30 lakh tonnes of cattle dung is generated daily.
Source: The Economic Times
INTERNATIONAL: OIL
Total interested in building 150k bpd Iraq oil refinery
February 27, 2018. French oil major Total is interested in bidding to build the greenfield 150,000 barrels per day (bpd) Nassirya oil refinery in Iraq. Last year, the Iraqi oil ministry said Petrochina was also interested in the refinery project. The refinery project was originally envisioned with a 300,000 bpd capacity that would be integrated with development of the Nassirya oilfield. Bids are still open for the project and international oil companies interested in the project would be bidding as refiners only, Iraq’s Dhi Qar Oil Company said. Dhi Qar has now taken on the development of the field by itself. The field is currently producing 80,000-100,000 bpd and the company plans to double production capacity to 200,000 bpd within the next three years. But production levels are expected to remain stable this year.
Source: Reuters
US to overtake Russia as top oil producer by 2019 at latest: IEA
February 27, 2018. The United States (US) will overtake Russia as the world’s biggest oil producer by 2019 at the latest, the International Energy Agency (IEA) said, as the country’s shale oil boom continues to upend global markets. IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol said at an event in Tokyo the US would overtake Russia as the biggest crude oil producer “definitely next year”, if not this year. US crude oil output C-OUT-T-EIA rose above 10 million barrels per day (bpd) late last year for the first time since the 1970s, overtaking top oil exporter Saudi Arabia PRODN-SA. The US Energy Information Administration said that US output would exceed 11 million bpd by late 2018. Birol said he did not see US oil production peaking before 2020, and that he did not expect a decline in the next four to five years. The soaring US production is upending global oil markets, coming at a time when other major producers – including Russia and members of the Middle East-dominated Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) – have been withholding output to prop up prices LCOc1. US oil is also increasingly being exported, including to the world’s biggest and fastest growing markets in Asia, eating away at OPEC and Russian market share.
Source: Reuters
Exxon selling stake in Canada’s Terra Nova oil project
February 27, 2018. Exxon Mobil Corp is selling its entire stake in the Terra Nova oil project off the eastern coast of Canada, though the world’s largest publicly traded oil producer said it was committed to remaining an investor in the region. The project, located about 217 miles (350 kilometre) off Newfoundland and Labrador, produced about 5,000 barrels of oil per day in 2016. Exxon is selling all of its 19 percent stake in the project and initial bids are due March 30, according to data and a document from Schlumberger’s oil and gas asset sale business. The Terra Nova project consists of a floating production, storage and offloading vessel to produce oil. The project has pumped 400 million barrels of oil and consists of 30 wells that pumped about 31,000 barrels per day last year, the document said.
Source: Reuters
Norway lifts estimate for undiscovered petroleum resources by 40 percent
February 27, 2018. Norway holds 40 percent more undiscovered oil and gas resources than previously estimated, the Norwegian Petroleum Directorate (NPD) said. NPD lifted the estimate for unproven resources by 1.13 billion cubic meters (7.1 billion barrels) of oil equivalents to 4 billion cubic meters from end-2016 estimate. Unproven resources constitute about 47 percent of the total resources that remain on the Norwegian shelf, NPD said.
Source: Reuters
Saudi to supply 12 mn barrels crude to China’s Huajin in 2018 deal
February 26, 2018. Saudi Aramco has agreed to supply China’s Huajin Chemical Industries Group Corp 12 million barrels of crude oil under an annual deal for 2018, up sharply from last year. This year’s supply to Huajin, a refinery and chemical complex controlled by Chinese defense conglomerate China North Industries Group Corp (Norinco), compare to an estimated 6-8 million barrels last year. Russia beat Saudi Arabia to be the top oil supplier to China for the second year in a row in 2017. Robust demand from small, independent refineries boosted demand for Russian oil due to its smaller cargo size and proximity, while the Saudis banked on larger state refiners as key clients. In May last year, Aramco signed a preliminary agreement with Norinco to build a refining and petrochemical project in Panjin.
Source: Reuters
SK Innovation makes oil discovery in South China Sea
February 23, 2018. Korean energy chemical company SK Innovation has made an oil discovery in PRMB block 17/03 in the South China Sea. The company said it plans to drill follow-up appraisal wells to assess the reserves and commerciality of the project. This find marks SK Innovation’s first discovery in the area since its decision to push forward with offshore oil exploration projects as an operator in the South China Sea. SK Innovation currently holds an 80 percent working interest in the block, and 20 percent is held by CNOOC (China National Offshore Oil Corp).
Source: Rigzone
Brazil regulator approves bidders for oil auction in March
February 21, 2018. Brazilian oil regulator ANP said it approved the participation of 14 companies in an oil round to be held on March 29. Among the companies authorized to bid for the round, that will auction offshore and onshore oil and gas exploration blocs, are BP Plc, Exxon Mobil Corp, Repsol SA, Petroleo Brasileiro SA, Royal Dutch Shell Plc and Total SA. If all the 70 blocs in auction are sold, the government would receive 4.8 billion reais ($1.5 billion). But ANP head Decio Oddone has said the government estimates a relevant number of the areas would not be sold. The government may raise around 1.1 billion in two auctions, he said, considering another round of so-called subsalt areas scheduled for June 7.
Source: Reuters
CGG, PCJ report oil discovery in onshore Jamaica
February 21, 2018. CGG GeoConsulting and the Petroleum Corporation of Jamaica (PCJ) have reported the discovery of two independent live onshore oil seeps from different parts of the Jamaican island. The oil seeps were found during fieldwork for a recently completed multi-client Robertson Study (Red Book) of the petroleum potential of on- and offshore Jamaica entitled ‘Petroleum Geological Evaluation of Jamaica’ made jointly by CGG GeoConsulting and PCJ. Subsequent detailed geochemical analyses confirmed the oil seeps originate from two separate Cretaceous source rocks. The discovery of these seeps indicates the presence of working petroleum systems on the island that are generating and expelling liquid hydrocarbons to the surface.
Source: Energy Business Review
INTERNATIONAL: GAS
Energean secures $1.25 bn in funding for Israeli gas fields
February 27, 2018. Greek energy firm Energean has secured $1.25 billion in funding for the development of two natural gas fields offshore Israel, the company said. The company signed commitment letters with Morgan Stanley, French investment bank Natixis and Israel’s Bank Hapoalim. Energean hopes to begin production at the Karish and Tanin fields, which contain an estimated 2.4 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, in 2021.
Source: Reuters
Peru resumes LNG exports with shipment to South Korea
February 27, 2018. Peru has exported its first shipment of liquefied natural gas (LNG) in three weeks after a pipeline rupture in the jungle disrupted production, the state energy agency Perupetro said. The ship Barcelona Knutsen departed Peru for South Korea with 170,999 cubic meters (6,038,772 cubic feet) of fuel from the Pampa Melchorita plant, which is operated by the consortium Peru LNG, Perupetro said. US-based Hunt Oil has a 40 percent stake in Peru LNG. Royal Dutch Shell Plc, Japan’s Marubeni Corp and other companies have smaller stakes in the consortium. Peru’s LNG exports had halted after landslides and heavy rains in southeastern Peru ruptured a natural gas pipeline operated by Transportadora de Gas de Peru SA. The pipeline transports natural gas from the Camisea fields, which are operated by Argentina’s Pluspetrol Camisea SA, to Pampa Melchorita, Peru’s sole natural gas liquefaction facility. Peru LNG normally exports five or six shipments of about 150,000 cubic meters each month.
Source: Reuters
LNG market needs $200 bn investment to meet demand: Shell
February 26, 2018. More than $200 billion of investment in liquefied natural gas (LNG) is needed to meet a boom in demand by 2030, Royal Dutch Shell, the world’s top LNG trader, said. The LNG market is set to continue its rapid expansion into 2020 as facilities approved for construction in the first half of the decade come on line, in a development expected easily to meet sharp growth in consumption of the super-chilled fuel. But a decline in spending in the sector since 2014 as a result of weaker energy prices will create a supply gap from the mid-2020s unless new investments emerge, Shell said. LNG plants are complex and expensive, requiring large processing units, known as trains, that cool natural gas to around minus 160 degrees Celsius (minus 260 Fahrenheit). The liquefied fuel is then shipped to demand centers and converted back into gas. While LNG demand is expected to grow from 293 million tonnes per year (mtpa) in 2017 to around 500 mtpa by 2030, supplies are seen slipping to 300 mtpa due to a lack of new projects and natural declines in existing production, Shell’s head of integrated gas and new energies, Maarten Wetselaar, said. The cost of developing the required capacity is roughly $1 billion per mtpa, Wetselaar said. That does not include investments in the development of the gas fields associated with LNG plants, he said. Shell is considering moving ahead on new projects such as LNG Canada and Lake Charles on the United States (US) Gulf Coast, Wetselaar said. The Anglo-Dutch company is expected this year to launch the Prelude floating LNG plant in Western Australia, one of the largest and most complex gas projects in history. LNG demand is set to grow twice as fast as gas power plants in China, South Korea and India switch from coal and governments move to reduce carbon emissions, Shell said.
Source: Reuters
Japanese firms in consortium to bring LNG to Australia’s east coast
February 26, 2018. A consortium including Japan’s JERA and Marubeni Corp is aiming to ship liquefied natural gas (LNG) to Australia’s east coast, looking to supply industrial gas users and possibly a new power plant, the group said. This is the second proposed LNG import terminal for Australia, the world’s no.2 LNG exporter, as the country grapples with a supply gap at a time when its gas producers have locked in long-term contracts to sell LNG to Japan, China and South Korea. A final investment decision is expected this year on the project to import up to around 2 million tonnes a year of LNG starting in 2020, James Baulderstone, who is leading the Australian Industrial Energy group, said. The LNG receiving terminal would be able to meet up to three-quarters of the gas needs of Australia’s most populous state, New South Wales, where manufacturers like BlueScope Steel and Orica have major operations. Baulderstone said the consortium would probably charter an existing LNG import vessel, at an estimated cost of around $30 million to $35 million a year, rather than building a new floating storage and regasification unit (FSRU). That is a fraction of the billions of dollars that would be needed to develop a new gas field and pipelines to supply the equivalent volume of gas, 100 petajoules a year. The proposed new LNG import terminal would be located at either Port Botany, Port Kembla and Newcastle, all of which are close to existing gas pipelines, helping to keep down costs.
Source: Reuters
East Timor, Australia agree on maritime border, ‘pathway’ to develop gas field
February 26, 2018. East Timor and Australia have reached an agreement for a treaty on their disputed maritime border and on a “pathway” to develop the giant Greater Sunrise offshore gas fields, the Permanent Court of Arbitration said. Under the agreement, the share of revenue from the offshore gas field will differ depending on downstream benefits that arise from “different development concepts”. The long-running dispute had led the owners of Greater Sunrise – Woodside Petroleum, ConocoPhillips, Royal Dutch Shell and Japan’s Osaka Gas – to shelve the project. The fields are estimated to hold 5.1 trillion cubic feet of gas and 226 million barrels of condensates, which analysts have previously estimated could be worth $40 billion. However, development could be at least a decade away, with Woodside looking at the latter half of the next decade. East Timor’s Oil Minister, Hernani Filomena Coelho da Silva, said that his country’s preference was for the gas to come to his country to help development.
Source: Reuters
Leaders launch start of Afghan section of TAPI gas pipeline
February 23, 2018. Regional leaders launched construction work on the Afghan section of an $8 billion natural gas pipeline that will link the energy-rich Central Asian nation of Turkmenistan through Afghanistan to Pakistan and India. Ex-Soviet Turkmenistan holds the world’s fourth-largest natural gas reserves but has been heavily dependent on gas exports to China after Russia cut back gas imports in the past few years. The project is expected to transport 33 billion cubic meters (bcm) of natural gas a year along an 1,800 kilometer (1,125 miles) route from Galkynysh, the world’s second-biggest gas field, to Fazilka near the border with Pakistan in northern India. While the pipeline will allow Turkmenistan to find new consumers in Asia and cut its dependence on Beijing, which buys about 35 billion cubic meters of gas annually. It is also being seen as a central plank in ambitious regional development goals. The TAPI (Turkmenistan–Afghanistan–Pakistan–India) project, supported by the United States and the Asian Development Bank, has been touted by Turkmenistan since the 1990s. But the start of work was delayed because of the problem of crossing Afghanistan. The pipeline will run for hundreds of kilometers (miles) through areas of southern Afghanistan largely controlled by Taliban insurgents fighting the Western-backed government in Kabul but the movement has signaled that it will not hinder the project. The Taliban issued a statement, pledging its cooperation with TAPI, which it said would be an important element in building up Afghanistan’s economic infrastructure. Afghanistan, which suffers from chronic energy shortages, is expected to take 5 billion cubic meters of gas itself, with the rest divided equally between Pakistan and India. In addition, Kabul will earn hundreds of millions of dollars in transit fees.
Source: Reuters
Cyprus accuses Turkey of blocking ship again in gas exploration standoff
February 23, 2018. Cyprus accused Turkey of threatening to use force against a drillship chartered by Italy’s Eni, in a standoff over hydrocarbons rights in the eastern Mediterranean. The Turkish navy on manoeuvres in the Mediterranean stopped the Saipem 12000 vessel on its way to drill for gas in the waters off Cyprus, triggering a diplomatic standoff which has underscored tensions in the region over competing claims for offshore resources. Cypriot President Nicos Anastasiades was expected to discuss the issue with European Union leaders who are meeting in Brussels. He said that Cyprus was determined to press ahead with its plans for oil and gas exploration. Eni and France’s Total discovered this month a promising natural gas field off Cyprus, which they said looked geologically similar to the mammoth Zohr field off Egypt. Cyprus was split in a Turkish invasion in 1974 after a brief Greek-inspired coup. Peace talks collapsed last year. Greek Cypriots, who are exploring for natural gas, run Cyprus’s internationally recognised government. Turkish Cypriots run a breakaway state in north Cyprus recognised only by Ankara.
Source: Reuters
Italian government issues early warning over gas supplies
February 23, 2018. Italy’s industry ministry issued an early warning over gas supplies in the country due to exceptionally bad weather and maintenance work on the network in Germany. The early waring was issued on a precautionary basis, the ministry said, following forecasts of severe weather conditions in the coming days and reduced import flows in relation to maintenance works the TENP pipeline in Germany. Snow storms are expected to hit northern Italy in the coming days as one of the worst cold spell in recent decades engulfs most of Europe.
Source: Reuters
Thailand pushes Erawan and Bongkot gas field auctions to April
February 22, 2018. Thailand expects auction terms for its petroleum gas fields to be ready in April, a month later than previously indicated, Energy Minister Siri Jirapongphan said. The auction terms will be submitted to the National Energy Policy Council in March and the auction will be announced to bidders in April, Siri said. Conditions for the winners include maintaining a combined output level in the two fields of at least 1.5 billion cubic feet per day at prices not higher than current levels, Siri said. The Erawan and Bongkot fields currently have combined output of 2.1 billion cubic feet a day, government data shows. Many of Thailand’s gas fields have been producing for decades and are in decline, and the tender winners will be expected to maintain baseline production levels. The government aims to determine the auction winners by November and December this year, Siri said.
Source: Reuters
INTERNATIONAL: COAL
China’s January coal imports from Australia surge as blizzard hits
February 24, 2018. China’s coal imports from key supplier Australia surged in January from a year ago, data from the General Administration of Customs showed, boosted by strong demand at utilities amid freezing weather. The world’s top coal consumer brought in 7.94 million tonnes of coal from Australia last month, data showed, up 9.4 percent from a year ago. That compares with 8.07 million tonnes in December. Indonesian coal supplies jumped almost 40 percent in January from a year ago to 5.04 million tonnes, one of the highest monthly totals for the country since 2014. Buyers of Indonesian coal had also been holding back orders of the fuel as new shipping rules for coal and crude palm oil issued by Jakarta are expected to restrict exports to Indonesian vessels. The regulation will take effect at the end of April. With several bouts of freezing weather sweeping across China in late January and early February, some coal-fired power plants warned of tight supplies of the fuel as their inventories fell below critical levels due to record daily consumption. Data showed that China brought in a total of 27.81 million tonnes of coal in January, the highest level in four years. Vessel-tracking and port data suggest China will import about 21.68 million tonnes of seaborne coal in February. China’s thermal coal prices on the Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange hit 679.8 yuan ($106.89) a tonne on January 29, up from around 390 yuan a year earlier. To ensure stable coal supplies, state- and local-level authorities have ordered miners to ramp up production and asked ports to speed up the process of receiving seaborne coal.
Source: Reuters
INTERNATIONAL: POWER
South Korea’s KEPCO selects ABB to improve power grid reliability
February 26, 2018. ABB has been awarded a contract by the South Korea’s electric utility Korea Electric Power Corp (KEPCO) to provide Series Compensation technology to help boost long distance transmission capability in the country. Under the contract, ABB will provide Thyristor Controlled Series Compensation (TCSC) technology, which is designed to allow existing Alternating Current (AC) lines to transmit more power. The ABB’s technology is said to provide cost-efficient and environmentally friendly solution to support the power flow control from the near-by generation plant while eliminating the need to build new power lines. ABB said that its solution would play a key role in supporting reliable power supply to Seoul area by addressing complex power quality issues in the grid. The TCSC solution is part of an ABB’s family of Flexible Alternating Current Transmission Systems (FACTS) technologies intended to help enhance power quality in the grid while improve the capacity and flexibility of power transmission systems. The South Korean government aims to reduce CO2 emissions by 30% by 2020 while meeting growing electricity demand. As part of this effort, the country is investing in smart grid infrastructure with support from KEPCO. The contract is part of KEPCO’s plan to optimize its transmission and distribution network to ensure stable electricity supply and build grid resilience.
Source: Energy Business Review
ATXI completes $130 mn Spoon River transmission project in Illinois
February 23, 2018. Ameren Transmission Company of Illinois (ATXI) has commissioned the $130 mn Spoon River transmission project, a 70 kilometre long, 345,000 volt transmission line built between Galesburg and Peoria in Illinois. The Spoon River Transmission Project will provide local and regional benefits, including improved energy-grid reliability, increased transmission capacity and greater access to lower-cost energy, including renewable sources such as wind. The $130 million project, which included construction of two new substations, was completed under budget and nine months ahead of schedule due to efficient project execution that included the use of helicopters to install the transmission line.
Source: Energy Business Review
Wartsila to provide additional generating capacity to Azores’s electricity grid
February 22, 2018. Wartsila will provide additional generating capacity to the local electricity grid in the Portuguese administered Azores Islands. A new 10 MW extension to the existing Belo Jardim power plant on the island of Terceira will be powered by a Wartsila 32 engine. The extension has been ordered by Energetus S.A, the Portugal based developer and installer of energy solutions, on behalf of the local utility, Electricidade dos Acores S.A. The order with Wartsila was booked in January. The plant is expected to be fully operational by May 2019. Energetus has earlier ordered Wartsila power generating solutions for a 54.5 MW plant on the island of Madeira, and for an extension to a power plant in Maia, Portugal.
Source: Energy Business Review
INTERNATIONAL: NON-FOSSIL FUELS/ CLIMATE CHANGE TRENDS
Global fossil fuel emissions underestimated by over 50 percent
February 27, 2018. Global levels of fossil fuels ethane and propane in the atmosphere have been underestimated by more than 50 percent, a study has found. These hydrocarbons are particularly harmful in large cities where, through chemical reactions with emissions from cars, they form ozone – a greenhouse gas which is a key component of smog and directly linked to increases in mortality. Ethane and propane escape into the air from leaks during natural gas extraction and distribution, including from fracking – the process of drilling down into the earth and fracturing rock to extract shale gas. The new study involving scientists at the University of York in the UK shows that global fossil fuel emissions of these hydrocarbons have been underestimated and are a factor of 2-3 times higher than previously thought. The researchers are now calling for further investigation into fossil fuel emissions of methane, a potent greenhouse gas which is emitted along with ethane and propane from natural gas sources.
Source: The Economic Times
European Council approves carbon market reform
February 27, 2018. Long-awaited reforms to the European Union (EU)’s carbon market received the final green light from the EU Council in a bid to shore up prices of the cap-and-trade system designed to cut greenhouse gas emissions from industry and the power sector. The changes to the EU’s Emissions Trading System (ETS), which broadly involve reducing the number of permits in circulation, were hammered out in November after more than two years of debate in Brussels between EU policymakers, political groups and EU nations. The European Council, which represents the bloc’s 28-member states, approved the reform. European carbon prices have risen almost 20 percent since the start of 2018 on expectations of lower supply under the reforms and also received a modest boost.
Source: Reuters
Farm groups urge Trump not to weaken US biofuel policy
February 27, 2018. US (United States) farm groups urged President Donald Trump in a letter not to weaken the nation’s biofuels policy requiring corn-based ethanol to be blended into gasoline, calling it a critical engine of rural American jobs. Trump is due to meet with senators and cabinet members to discuss potential tweaks to the law, called the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS), that would help oil refiners who have increasingly complained the program costs them a fortune. The policy was adopted during President George W. Bush’s administration to help farmers, cut petroleum imports and lower pollutant emissions.
Source: Reuters
Indonesia to challenge latest US biodiesel duty ruling at WTO
February 23, 2018. Indonesia plans to challenge the latest ruling by the United States (US) on anti-dumping and countervailing duties on Indonesian biodiesel at the World Trade Organization (WTO), the trade ministry said. The US Commerce Department imposed more import duties on biodiesel from Argentina and Indonesia, adding anti-dumping duties to already steep anti-subsidy duties on the fuels.
Source: Reuters
Rocky Mountain Power to build 1.3 GW new wind projects in Wyoming
February 21, 2018. Rocky Mountain Power, a business unit of US (United States) electric utility PacifiCorp, has selected four new wind projects in Wyoming with a combined capacity of over 1.3 GW as part of its wind power expansion plans. The wind projects, which are expected to be built with an investment of around $1.5 bn, are expected to significantly increase the amount of wind power served by Rocky Mountain Power to its customers by 2020.
Source: Energy Business Review
DATA INSIGHT
Coal Availability & Import Scenario of India
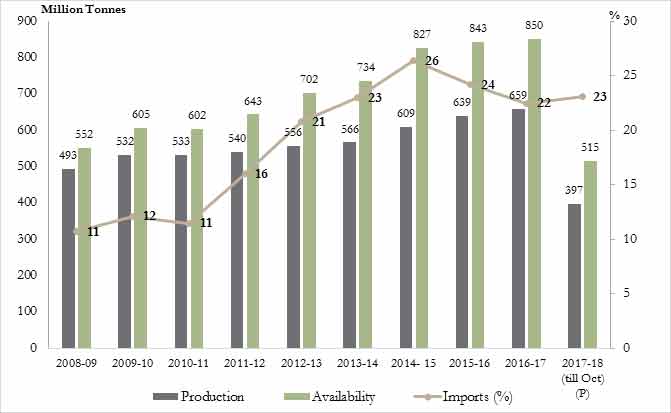
Direction of Coal Imports (for year 2016-17, till December)
Total Imports 144.87 Million Tonnes
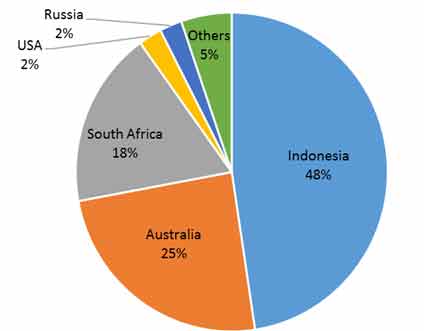
Source: MoC & Parliament Questions
Publisher: Baljit Kapoor
Editorial Adviser: Lydia Powell
Editor: Akhilesh Sati
Content Development: Vinod Kumar Tomar
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.









 PREV
PREV

