More Sunshine for Solar Power
Non-Fossil Fuels News Commentary: January – February 2017
India
Energy news was preoccupied with budget expectations and budget outcomes in February even though the budget was announced about a month before its usual date supposedly to break away from colonial traditions.
The Budget did not disappoint expectations from the solar sector as it let the sun shine on solar power generators. There was an announcement of another 20 GW of solar park development in phase II and a slew of duty reductions on components for fuel cell-based power generating and biogas systems, as well as wind energy equipment. The Budget announced solar power supply at about 7,000 railway stations and also proposed massive cuts in excise and customs duties on materials used in solar and wind plants. It also announced the second phase of solar park development for 20 GW capacity. Zero BCD on solar tempered glass for use in manufacture of solar cells/panels/modules from the present BCD of 5 percent was also proposed. Reduction of CVD on parts/raw materials for manufacture of solar tempered glass for use in solar photovoltaic cells/modules, solar power generating equipment or systems, flat plate solar collector, solar photovoltaic module and panel for water pumping and other applications, to 6 percent from existing 12.5 percent was also proposed. It also proposed to reduce the BCD, CVD and SAD of 24 percent on resin and catalyst for manufacture of cast components for Wind Operated Energy Generators to 5 percent.
Opening one more window for more sun shine, the MNRE was reported to be exploring a change in the tariff structure for electricity from solar energy. The proposal is to introduce a fixed-cost component to the tariff for electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar or wind so as to prevent discoms from backing off from procuring electricity generated by such projects, as they will have to pay the fixed tariff component even if they do not buy the electricity contracted for. Such a tariff mechanism already exists for electricity from conventional sources such as coal and gas which has two parts—a fixed cost, which is the investment incurred towards power generation equipment, and a variable cost or the cost of fuel. This is a step in the right direction as it will actually increase the tariff of renewable energy and bring it on par with conventional energy which include a fixed part for capacity and network maintenance. The MNRE was said to be working on a set of guidelines to provide compensation to solar power generators in case they are asked to back-down capacity by distribution companies. This would offer more sunshine for the solar sector. This was supposed to ensure that power distribution companies do not arbitrarily cut off solar and wind power or ask power generators to back-down capacities. This provision should also be extended to other generators to level the playing field. The impending imposition of GST and its impact on the bidding rate for solar power which has become the most watched number after GDP was discussed by many. According to CEEW the solar sector was expected to see tariffs rise by nearly 10 per cent if current tax exemptions were curtailed in the roll out of the GST. Multiple GST rates and their uncertain applicability to different equipment and services for solar projects was a growing concern from solar project developers and investors, the report said. It also observed that GST could also impact the second phase of solar park development for additional 20 GW capacity announced in the budget. CEEW also felt that GST could increase capital cost of a solar project by ` 4.5 million/MW if current tax exemptions were curtailed, setting back the sector in terms of cost competitiveness by about 18 months. Do these observations give away the dirty little secret of incentives that prop up the solar sector?

Moving to hydropower, the quiet contributor of non-fossil fuel based power, news on Pakistan’s resolution that asked India to immediately suspend the ongoing construction of the Kishanganga and Ratle hydro power projects in J&K was spotted in the international news. The two projects are being constructed on the Jhelum and Chenab rivers under the provisions of the IWT. The resolution also asked the World Bank to set up a Court of Arbitration to mediate the dispute over the IWT between the two countries. It said that under IWT, it is the responsibility of the World Bank to play its role without further delay. It is not clear why the IWT once thought to water tight is leaking into primary domains of conflict between India and Pakistan!
The power ministry was also reported to be considering renewable energy status to supplies from large hydropower projects to help keep power tariffs low under the proposed GST. The ministry, which has sought zero rating or deemed export status for solar power projects on the grounds that levy of GST will substantially increase tariffs, now wants the same to be extended to supplies for under-construction hydropower projects. These supplies are currently exempt from excise duty or enjoy concessional value-added tax of 0-5 percent and a central sales tax at 2 percent. Under GST all central and state taxes on goods and services are expected to be replaced by a single levy of 18 percent, pushing up the cost of these supplies, which in turn is expected to increase the cost of power. About 11 GW of hydro power capacity is expected to be added over the next five years and a GST rate of 18 percent would inflate capex by 10-12 percent.
On the nuclear side, the proposal from the DAE to construct two PFBR of 600 MW each at Kalpakkam, besides the present one of 500 MW capacity was reported. The 500 MW PFBR, which is to be functional by October, will be the first PFBR in the world for commercial use. It is not clear what is motivating India as it is essentially pursuing what the rest of the world has abandoned primarily on commercial and also on safety grounds. The DAE was also reported to have a proposal for building 12 nuclear reactors to ramp up power generation in the country. Of the 12 reactors 10 reactors will be indigenous PHWR while the other two will be Light Water Reactors of Kundakulam units 5 and 6 of 1,000 MW each. Staying with Kudankulam, the second 1,000 MW unit of the power plant was expected to start commercial operations this fiscal. The second unit of the project was made critical in July 2016 and connected to the grid in August.
Rest of the World
Going by news reports, Europe is continuing to lead the charge against high carbon energy, notwithstanding Trump. According to a new report released by the EU it is on track to reach its 20 percent renewable target by 2020, having covered 16 percent of its final energy consumption with renewables in 2014. However this does not mean that member states have reached their national goals. In 2014 all EU countries – except the Netherlands – showed a renewable energy share which was equal to or higher than their indicative pathway. In 2015, 25 Member States exceeded their indicative pathways, with some even surpassing their 2020 targets. By 2030, the EU has set a target of at least 27 per cent of renewables in energy consumption. Reaching this target would help reduce GHG emissions to meet the EU target of at least 40 per cent GHG reduction by 2030.
According to European wind association more than 12 GW of new wind capacity were added in the EU raising the installed wind capacity in Europe to 153.7 GW. Investment in new onshore and offshore wind farms reached a record €27.5 bn. According to the GWEC, global wind additions reached 54.6 GW in 2016, raising total capacity to nearly 487 GW. Ten country accounted for 88% of total installations, with 47.9 GW installed. As in previous years, China was the largest installer in 2016 with nearly 43% of global installations. The country installed 23.3 GW in 2016 and reached 168.7 GW. This is twice the installed capacity in the US. European utilities also announced that they will not reduce their investments in renewables if US President Donald Trump lowers US climate goals.
For its part, Sweden has agreed to pass a law in the coming months to force the government to reduce fossil fuel use through tougher targets revised every four year, in order to completely phase out GHG emissions by 2045. Sweden plans to cut its domestic GHG emissions by at least 85% by 2045, compared to 1990 levels. Remaining emissions would be offset by compensation actions, such as planting forests (carbon sinks) or investing in GHG emission cut measures abroad. The EU as a whole has already approved an 80-95% reduction target in GHG emissions by 2050. It is not clear if the greying of the EU is behind the greening of the EU.
Not to be undone by the EU China’s installed PV capacity was reported to have more than doubled last year, turning the country into the world’s biggest producer of solar energy by capacity according to its NEA. Installed PV capacity rose to 77.42 GW at the end of 2016, with the addition of 34.54 GW over the course of the year. China is expected to add more than 110 GW of capacity in the 2016-2020 period. Solar plants generated 66.2 billion kilowatt-hours of power last year, accounting for 1 percent of China’s total power generation. The country aims to boost the mix of non-fossil fuel generated power to 20 percent by 2030 from 11 percent. It is know that China is the only force holding up the secular decline of the nuclear sector. China’s plans took a controversial turn when it announced that it plans to build 20 floating nuclear power stations in the future, which will significantly beef up the power and water supplies on the South China Sea islands. China currently has 23 nuclear power generating units in operation and 27 under construction, about one-third of the world’s unfinished nuclear units. China will reportedly prioritise the development of a floating nuclear power platform in the coming five years, in an effort to provide stable power to offshore projects and promote ocean gas exploitation. The development of the facility is said to be a crucial part of the country’s five-year economic development plan, running through 2020.
The news from nuclear stalwarts Japan and France was less sensational. The plan to remove spent nuclear fuel from Tokyo Electric Power Co Holdings Inc’s Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant was reportedly postponed again due to delays in preparation. Work is now set to begin in fiscal 2018 at the earliest. Removal of the spent fuel from the No. 3 reactor was originally scheduled in the first half of fiscal 2015, and later revised to fiscal 2017 due to high levels of radioactivity around the facilities. The timeline has been changed again as it was taking longer than expected to decontaminate buildings and clean up debris, the news agency reported.
The French government was reported to have reached an agreement with state-controlled utility EDF on the conditions under which the company will shut down France’s oldest nuclear plant. EDF and the French government agreed in August on a €400 million compensation package for the closure of the Fessenheim nuclear plant. The government decree to halt operations at Fessenheim would be subject to the company obtaining necessary official authorization for its new generation EPR reactor in Flamanville.
NATIONAL: OIL
ONGC takes profit hit from royalty payments
February 21, 2017. Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) will take a Rs 16 billion ($239 million) hit to its quarterly earnings to account for previous royalty payments to two states, the oil exploration company’s finance head A K Srinivasan said. ONGC has already made a Rs 25 billion payment to the two states as royalty on crude oil produced from April 2014, but had not reflected this because it was under litigation, Srinivasan said. The Supreme Court has asked the federal government to compensate Gujarat and Assam for 150 billion rupees in lost revenues due to lower royalties paid by ONGC and Oil India Ltd (OIL). Indian law requires companies to pay 20 percent of the market value of oil produced as royalty to states where oil blocks are located. From April 2008 the oil ministry asked ONGC and OIL to pay royalty based on lower prices, as the two firms had given a hefty discount on crude sales to state refiners, in order to keep a lid on local fuel prices. However, last year the oil ministry asked the two firms to settle royalty dues from April 2014 based on the market value of oil produced. Despite this royalty adjustment ONGC is expected to post higher profits in the quarter to end-March due to higher prices on its crude sales.
Source: Reuters
India looks to expand energy ties with Myanmar
February 20, 2017. India plans to sell refined crude oil products to Myanmar as part of New Delhi’s efforts to deepen ties with its eastern neighbour, which is expected to see strong demand for fuels as it builds new roads, factories, utilities and airports. Oil Minister Dharmendra Pradhan began a five-day trip to Myanmar, scouting for opportunities in oil exploration, refining and products retailing. Prime Minister Narendra Modi wants to expand ties with the country’s eastern neighbours including Myanmar to develop its landlocked north-eastern states. Pradhan is expected to discuss laying fuel and gas pipelines linking India’s north-eastern states with Myanmar. Numaligarh refinery Ltd (NRL), a unit of Bharat Petroleum Corp Ltd, is looking at selling gasoil into northwest Myanmar. NRL plans to treble its refining capacity to 180,000 barrels per day in four to five years. Myanmar’s refined fuels consumption is estimated to rise at an average annual rate of 6 percent over the next 10 years to 2026, BMI Research, a unit of credit ratings agency Fitch Group, said.
Source: Reuters
DBT leads to Rs 500 bn savings for govt in 3 yrs
February 20, 2017. Savings due to Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) over the last three years have touched Rs 50,000 crore as on December 31, 2016, as per latest government figures. This amount is equivalent to the subsidy paid out under DBT in this financial year, implying nearly a year’s subsidy was saved. Presently, 84 schemes in 17 ministries are covered under the DBT, up from 34 schemes as on March 31, 2015. Nearly 33 crore people receive various subsidies directly in their bank accounts now through DBT. Though the DBT mechanism started in 2013 under the UPA on a pilot basis, it took off in a major way only under Modi government after the liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) subsidy scheme (Pahal) was commenced through the DBT mechanism in November 2014.
Source: The Economic Times
Indian refiner said to review $8 bn spend on tax shock
February 20, 2017. Indian Oil Corp (IOC), the nation’s top refiner, is reconsidering plans to invest $8 billion in the country’s east after a provincial government threatened to withdraw promised tax breaks. The government of Odisha state said in a letter to the company that it was no longer keen to provide a deferral of value added tax on the sale of petroleum products. The benefit was initially extended as an incentive to build the Paradip refinery in the state and ending it would hit profitability and impact future investments. The 11-year tax deferral was for products from the refinery sold in the state. IOC has plans to invest Rs 520 billion ($8 billion) in Paradip to expand the refinery, upgrade it to produce a superior quality of fuels and add downstream petrochemical units along with pipelines and storage facilities. The offer of the tax break on sales of petroleum products prompted Indian Oil to spend Rs 346 billion to build a 15 million metric ton-a-year refinery in Odisha. Work on the Paradip refinery began in 2004 and the plant is operating at 80 percent of capacity in the current financial year. Indian Oil is also an investor in the proposed Rs60 billion liquefied natural gas importing terminal at Dhamra in the state. The refiner has chalked out plans to spend Rs 1.84 trillion through 2022 to expand its refining, pipelines and distribution infrastructure. The refiner will add annual capacity of 24 million tons to its existing refineries over the next six years.
Source: Bloomberg
India awards 31 blocks for O&G exploration
February 16, 2017. India’s Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs have approved the award of operating licenses to 22 companies for exploration of 31 oil and gas (O&G) blocks, comprising 44 fields. The licenses approval for 28 onshore and 16 offshore fields were made as part of the discovered small and marginal fields (DSF) round of auction. The contract awards are expected to provide faster development of fields, helping improve the energy security of the country. Development of the small oil and gas fields are part of India’s efforts to reduce oil imports by 10% by 2022. Discovered long back by Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) and Oil India Ltd (OIL), the small oil and gas fields could not be monetized due to several reasons such as isolated locations, small size of reserves, high development costs, technological constraints, among others.
Source: Energy Business Review
NATIONAL: GAS
West Bengal decides to enter into JV with GAIL
February 21, 2017. The West Bengal government decided to enter into a joint venture (JV) with the GAIL (India) Ltd to supply natural gas to every household in greater Kolkata. Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee gave her approval to the JV at a meeting of the Cabinets standing committee on industry held at the state secretariat, state finance ministry said. GCGSC, which is a 100 percent state-owned company, will have an equity of 26 percent while GAIL will hold 74 percent stake for the Rs 3,000 crore project, the ministry said. The GAIL would invest for the project while the state government would provide various assets like the land and infrastructure support, the ministry said. The ministry said that urban areas would first have the supply and thereafter it which would be supplied all over the state including the small towns. The pricing of the gas was yet to be decided, the ministry said.
Source: India Today
Domestic natural gas price set to rise by 8 percent from April this year
February 16, 2017. India’s domestic natural gas price is set to rise by 8 percent to $2.7 per unit for the six months period beginning April 2017 from the current $2.5 per unit, in line with the trends in the global benchmark prices. The increase in gas price will push up prices of automobile fuel compressed natural gas (CNG), cooking fuel piped natural gas (PNG), prices of power produced from gas-based plants and bring relief for upstream companies including the Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) as well as gas distributers like Indraprastha Gas Ltd (IGL). The government had in September last year decreased domestic natural gas price to $2.50 per unit. India’s gas prices are revised every six months, based on a pricing formula notified in October 2014. The formula pegs the price to the weighted average of four global benchmarks including US based Henry Hub, Canada based Alberta gas, UK based NBP and Russian gas prices in the prior year and comes in effect after a lag of one quarter. The government in March 2016 in order to promote E&P activities in the gas sector introduced a new pricing formula for gas produced from ultra deepwater and high pressure-high temperature areas, however the pricing freedom given is subjected to a ceiling price revised every six months.
Source: The Economic Times
NATIONAL: COAL
India’s coal woes continue as power demand fails to pick-up: Bridge to India
February 21, 2017. India’s coal-fired power sector continues to suffer rising challenges posed by lack of demand, improving price competitiveness of renewable power and regulatory risk, research firm Bridge to India said in a report. In January 2017, India’s coal imports declined by 22 percent to 14 million tonnes because of lukewarm demand from power generating stations. Bridge to India said private investors planning long-term investments in coal mining or thermal power generation are likely to be put off by the combination of demand, off-take, regulatory and environmental risks. Coal India Ltd (CIL), which accounts for 80 percent of domestic coal production, has posted its worst ever financial results for H1-FY17 as revenues declined even as expenses rose. At the same time, plant load factor of thermal power stations continues to be near all-time lows of under 60 percent. Talking about power tariff, Bridge to India said politics continues to dictate power pricing in India.
Source: The Economic Times

Coal Secretary seeks state help to double output
February 18, 2017. As part of the attempts of central PSU Mahanadi Coalfields Ltd (MCL), to double its production by 2020, Union Coal Secretary Susheel Kumar discussed issues confronted by the public sector undertaking (PSU) with the state government and sought its cooperation to resolve them. The coal PSU, a subsidiary of the Coal India Ltd, produces nearly 125 million tonne per year. The state government assured to sort out issues related to acquisition of land and obtaining forest and environment clearances for the coal mining projects. The MCL authorities sought the state government’s help to remove encroachments on the coal-bearing areas to expedite coal exploration.
Source: The Economic Times
NCL gets green nod for Rs 7.4 bn mine expansion in UP
February 17, 2017. Northern Coalfields Ltd (NCL) has received green clearance for the Rs 741.62 crore coal mining expansion project in Sonebhadra district in Uttar Pradesh (UP). The subsidiary of Coal India Ltd wants to expand its Krishnashila open cast mine (OCP) for increasing production from 5 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) to 6.25 MTPA. The total cost of the project is estimated to be Rs 741.62 crore. Among the conditions specified, NCL has been asked to spend at least 2 percent of the average net profit during the three immediately preceding financial years, in pursuance of its Corporate Social Responsibility Policy. NCL is facing increasing demand of coal from industry and power sector. Augmentation of coal production will help NCL to bridge the demand-supply gap. In the proposal, the company said it has a mine lease area of about 851.78 hectare with coal reserves of 99.12 million tonnes. Approximately 72.94 million tonnes of mineable coal reserve are left to be mined. The company will not change its technology as well as backfilling and land reclamation plan. The company has linkage of coal with Hindalco Industries as well as Basket Linkage.
Source: The Economic Times
NTPC flags-off first coal rake from Pakri Barwadih mine
February 16, 2017. NTPC Ltd said it has flagged off the first rake of coal from its Pakri Barwadih coal mine situated in Jharkhand. The mine has an estimated mining capacity of 15 million tonnes per annum and has been allotted by the government to NTPC as basket mine to meet the fuel shortfall of its power stations. The company opened the block in March last year after it was re-allotted the mine in 2015. Five blocks of NTPC were cancelled by the Supreme Court in 2014 when the apex court terminated mining licences of 204 coal blocks across the country. The five blocks include Chatti-Bariatu, Chatti-Bariatu (South) and Kerandari in Jharkhand, Dulanga in Odisha and Talaipalli in Chhattisgarh. As on date, NTPC has total installed capacity of 48,028 MW with 19 coal-based, seven gas-based stations and one hydro-based station.
Source: The Economic Times
CIL’s e-auction prices for the solid fuel rises after 12 months
February 16, 2017. Coal India Ltd (CIL)’s average e-auction prices for the solid fuel have risen after about 12 months, reflecting a hardening global trend in the costs of the energy source. In the December quarter, average realisations from e-auction rose to Rs 1,546 per tonne, 17 percent higher than the preceding three months, reversing a series of declines that had begun in April 2015. Analysts expect prices to remain firm and aid CIL improve its financial performance because of output moderation by large regional exporter Indonesia and revival of demand from smokestack industries in China, which had initially triggered global declines by shutting some coal-fired power plants. Coal importer SPIML said international prices are expected to stay stable for the next few months: Imports from Indonesia into India and continued demand from China – key attributes in reversing price declines now – will likely continue. CIL, based in Kolkata, is one of the world’s few miners of the fossil fuel that returns at a rate higher than its weighted average cost of capital.
Source: The Economic Times
NATIONAL: POWER
NTPC to train discom officials to make IPDS more effective
February 20, 2017. NTPC’s Power Management Institute (PMI) will soon impart training to state distribution company (discom) staff across the country for capacity building under the Integrated Power Development Scheme (IPDS). The IPDS’ objective is 24×7 power supply for consumers and reduction of AT&C losses. The Budget 2017 has provided Rs 5,821.22 crore under IPDS for the next financial year against revised estimates of Rs 4,524.01 crore for the current finanacial year. The NTPC-PMI has inked a pact with the Power Finance Corp (PFC) for the purpose. PFC is the nodal agency for implementation of IPDS in the country.
Source: Business Standard
BJP, Congress slugfest over agricultural power tariff rollback in Rajasthan
February 19, 2017. Rajasthan Pradesh Congress Committee president Sachin Pilot termed the rollback of power tariff hike for agriculture connections as a victory of farmers and Congress while the BJP shot back saying the power tariff hike was the result of the previous Congress government’s undoing. Sachin Pilot said, the Congress would continue its fight and would take out a rally demanding the rollback of the tariff of domestic consumers as well. The government has failed to control the rampant power theft and put an unexpected additional burned on the people with power hike on all sections of the consumers. The BJP state president Ashok Parnami while lauding the government decision said it was the previous Congress decision guaranteeing power tariff hike while signing the MoU with the Power Regulatory authority forced the government to hike power tariff. The BJP government has been working on reviving power sector bleeding under heavy loss. He said the state government had taken over the loss of Rs 60,000 crore under Uday Bond.
Source: The Economic Times
Protests in Ajmer over power distribution privatization decision by state govt
February 19, 2017. Ajmer observed a bandh protesting state government’s decision to hand over the electric supply system in Ajmer to a private company. The Congress party had given the bandh call. The bandh was held to show protest that Ajmer is against the privatisation of electric supply sector.
Source: The Economic Times
Discoms seek community help to curb power theft in Jaipur
February 18, 2017. The perennially loss-making power distribution companies (Discoms) are seeking community help to tackle the rampant power theft in the rural areas. They have roped in sarpanchs of the panchayats with the promise that if theft is reduced drastically, then the power distribution companies would ensure round-the-clock power supply. The power department is banking on the Bithur model in Ajmer district where community initiative has helped to reduce transmission and distribution losses considerably. The villagers complained during a visit of Chief Minister Vasundhara Raje that they were getting power only for a few hours and it was found that the major reason for the power break down in the village was due to theft. She asked villagers to come forward and stop power theft due to which the whole village was suffering. The Bithur model is a community driven initiative against power theft in which a large number of women at Bithur became Urja Mitras. The initiative at Bithur village, which is affiliated to Bhimpura Power Feeder, led to the transmission & distribution (T&D) losses being cut to 21% from 47%. As a result, the villagers are now getting power supply for most of the time. This has encouraged the Discoms to fall back on community to address the issue. The sarpanch would lead from the front in managing power supply. Currently the T& D loss, a major part of it constitute theft, is considerably high at 27%.
Source: The Economic Times
UP to issue Rs 100 bn of bonds against discoms’ debt
February 17, 2017. One of the largest indebtors in the power distribution sector, Uttar Pradesh (UP) will issue bonds worth Rs 10,000 crore against the debt of its distribution companies (discoms) which it took over. This is the second issuance by the state under the provisions of the Ujwal Discoms Assurance Yojana (UDAY) agreement, which aims to restructure the financials of beleaguered power distribution companies. UP was the first state to issue bonds during the past financial year. Till July last year, it had issued bonds totalling Rs 24,000 crore in three tranches. India Ratings and Research (Ind-Ra) assigned UP Power Corp’s proposed bonds the rating of ‘Provisional IND AA(SO)’- outlook stable. The UP government, power ministry and Uttar Pradesh Power Corp Ltd (UPPCL) entered into a tripartite memorandum of understanding for availing the UDAY benefits, past year. Under the scheme, 50 percent of UPPCL’s debt of Rs 54,000 crore was taken over by the UP government by FY16 and the remaining 25 percent was taken over on July 4, 2016.
Source: Business Standard
REC inks 2 pacts with Jharkhand utilities for Rs 151.5 bn loan
February 17, 2017. Rural Electrification Corp (REC) said it has inked two pacts with Jharkhand utilities for providing financial assistance of Rs 15,150 crore. REC is a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) that provides financial assistance to power entities in the government as well as the private sector in the areas of generation, transmission and distribution.
Source: Business Standard
West Bengal govt committed to quality power to all
February 16, 2017. The West Bengal government said that it was committed to provide quality power to all consumers and with that end in view it would install 177 sub-stations across the state in the next two years to overcome voltage problems. State Power Minister Sobhandeb Chttopadhayay said his government had alreay drawn a roadmap to supply quality power when the government had almost completed power conenction across the state.
Source: Business Standard
BIA against power tariff hike
February 16, 2017. The Bihar Industries Association (BIA) is against hike in the electricity tariff as proposed by the power distribution companies to the Bihar Electricity Regulatory Commission (BERC). The BERC has announced public hearings at Muzaffarpur, Bhagalpur, Purnia, Gaya and Patna for seeking objections and suggestions from general public and consumers on the tariff hike proposals. The proposals have been made by the North Bihar Power Distribution Company and the South Bihar Power Distribution Company for the year 2017-18. The power companies can further reduce the cost through proper quality control and theft check. The transmission infrastructure is in dilapidated condition, which causes huge losses in transmission of electricity, BIA said. According to BIA, the cost incurred on the transmission losses is being passed on to the common man and industrial bodies.
Source: The Economic Times
Outlook for India’s power sector negative in FY18: India Ratings
February 16, 2017. India Ratings and Research (Ind-Ra) said it has maintained a stable negative outlook on power sector for the next financial year despite an improvement in coal availability, restructuring of distribution companies’ debt and operationalisation of stuck projects. India Ratings said while credit profiles of large-sized power companies appear to have stabilised, the sector’s return on capital employed remains unattractive and small private companies are the worst hit. It said there is a possibility of sector consolidation, which could be triggered by the new bankruptcy code. India added nearly 115 GW of coal-based capacity over since FY11. However, demand growth did not keep pace with such capacity addition. This has put pressure on the PLFs of coal-based thermal power plants. In the past, coal and distribution company (discom) financial health were the two key constraints to the overall plant load factor (PLF). However, demand, solar capacity addition and discom financial health will be the major factors putting pressure on PLF in future. Earlier, the private sector kept a part of the capacity untied due to high short-term prices. The PLF of the private sector’s coal-based power plants fell to 56.3 percent in FY17 from 83.9 percent in FY10. According to Central Electricity Authority estimates, 50 GW of capacity has a high probability of getting commissioned over FY18-FY22.
Source: The Economic Times
India, Nepal agree to build new cross-border power lines
February 15, 2017. In view of the various power projects being developed in Nepal, India and the Himalayan nation have agreed to lay down new cross-border transmission lines. In this regard, laying of new Butwal (Nepal)-Gorakhpur (India) and Lumki (Nepal)-Bareilly (India) transmission lines and setting up of new 400kV sub-stations at Dhalkebar, Butwal and Hetauda — all in Nepal — were discussed during the fourth meeting of the Indo-Nepal Joint Working Group and Joint India-Nepal Steering Committee (JSC) on Power Cooperation. During the meeting, the Indian side conveyed that the new guidelines issued by India on cross-border trade of electricity is fair and liberal and covers all elements of Power Trade Agreement. In the meeting, Nepal side conveyed its deep appreciation for the efforts by India to supply enhanced quantities of electricity to Nepal that made several parts of the country, including Kathmandu, free of load-shedding this winter. The current import of 380 MW of power from India has been possible on account of the installation of additional transformer at Muzaffarpur by the Indian side, as also by technical improvements at Tanakpur at Nepal’s request. With the commissioning of two new lines — Raxaul-Parwanipur and Kataiya-Kusaha, the installed capacity for export of power to Nepal will increase by another 100 MW to 120 MW by the end of February 2017. Further, with the completion of 220 kV substation at Dhalkebar, the installed capacity will increase to almost 700 MW by the middle of 2017. The Indian side agreed to extend technical assistance for improvement of existing infrastructure, so that the era of load-shedding can end in Nepal for good.
Source: Business Standard

NATIONAL: NON-FOSSIL FUELS/ CLIMATE CHANGE TRENDS
India needs to say no to nuclear power: Greenpeace
February 21, 2017. India needs to “re-think” its energy policies and say no to nuclear power, Greenpeace India said after the NGO released a report highlighting high radiation levels in Fukushima in Japan. As Fukushima nuclear disaster nears its sixth anniversary, it continues to be a grim reminder of the destruction and loss lives that nuclear power can cause, it said. Red Alert, a Greenpeace India report had said nuclear power is neither safe nor economical and India is grossly ill-prepared to handle a nuclear disaster. The NGO said it should also be noted that India is currently in a situation of ‘surplus power’ witnessing massive installed overcapacity in the electricity sector. With the solar power tariffs going down to record low levels, India’s energy needs for the next ten years can be fulfilled by cleaner and safer sources of energy in the form of solar and wind, it said. Greenpeace India stands by the victims of Fukushima who are being “forced” to return to the accident site for economic reasons, the NGO said.
Source: The Indian Express

J&K CM for harnessing of solar, wind power in a big way
February 21, 2017. Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) Chief Minister (CM) Mehbooba Mufti asked the Science and Technology Department to undertake projects for harnessing of solar energy in a big way to supplement the energy needs of the state. Chairing a review meeting of J&K Energy Development Agency (JAKEDA) and Science and Technology Innovation Council, the CM said J&K has a fair potential for developing solar and wind energy which if harnessed adequately would rid the state of its energy deficiency. On the occasion, the meeting was apprised of the enhanced mandate of JAKEDA for taking up of solar power plants from 2 MW to 10 MW. It was also told that 25 sites have been identified in the state for setting up solar power plants with generation capacity of around 41 MW of power. The meeting was conveyed that under the Grid Connected Rooftop Power Plants Scheme, the Department has fixed a target of setting up plants up to 450 MW capacity by 2022. Also a wind energy plant of 6 MW capacity is being set up at Bidda in Reasi district at a cost of Rs 45 crore for which the land is being acquired.
Source: The Economic Times
Solar power tariff in Tamil Nadu drops 40 percent to Rs 4.4 per unit in a year
February 19, 2017. Solar power generation tariff was fixed at Rs 4.40 per unit by Tangedco. With this, the tariff came down from Rs 7.10 to Rs 4.40 within a year. The Tamil Nadu Generation and Distribution Cooperation (Tangedco) opened the bids for 300MW of solar power to be set up during 2017-18 and found a bid for 100 MW at Rs 4.40 per unit and the upset tariff fixed by the discom was Rs 4.50 per unit. The Tamil Nadu Electricity Regulatory Commission permitted Tangedco to set up solar projects to the extent of only 500 MW for the coming year. Out of this Tangedco received bids for 300 MW. In November last year, Tangedco received 20 bids for only 116 MW and with the latest tenders, the distribution company has a total of 416 MW out of 500 MW.
Source: The Economic Times
Kerala’s renewable energy organization ANERT to campaign for Solar connect project
February 19, 2017. Agency for Non-Conventional Energy and Rural Technology (ANERT) is set to include more institutions, individuals and companies under the grid-connect solar power project to reduce dependence on hydroelectric power. The plan is to utilise solar energy to its maximum to meet the electricity needs during day time. Under the solar connect project, the excess solar power generated during day time will be transferred to the Kerala State Electricity Board Ltd (KSEB) with the help of grid system. The energy requirements of the building during night time will be met by borrowing electricity from the KSEB. Under the solar connect scheme, solar power generated will be transmitted to the grid and no storage facility is required for storing the power. This reduces the cost for installing the solar plant.
Source: The Economic Times
India may meet its energy needs from resources on the moon by 2030
February 19, 2017. India may be able to meet all its energy requirements from resources on the moon by 2030, Sivathanu Pillai, a distinguished professor at the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), said. Sivathanu Pillai said that India’s all energy requirements can be met through Helium-3 mined from the moon. By 2030, this process target will be met, Pillai said while delivering the valedictory address at the three-day ORF-Kalpana Chawla Space Policy Dialogue, organised by Observer Research Foundation. According to an ORF release, Pillai said other countries are also working on the project and there is enough helium on the moon, which can meet the energy requirements of the world. He said that India possesses one of the largest constellations of communication and remote sensing satellites covering Asia Pacific.
Source: The Economic Times
Five Uttarakhand hydro power plants to be repaired under World Bank project
February 19, 2017. Two dams and three barrages in Uttarakhand are likely to be rehabilitated under the project of World Bank with an estimated cost of Rs 200 crore. Uttarakhand Jal Vidyut Nigam Ltd (UJVNL) said in Roorkee that the rehabilitation work of these five hydrogenation units will be completed in three years. The conference organized by UJVNL, in association with Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee (IIT-R), saw participation of nearly 400 hydro power experts, including 50 foreign participants from countries like Japan, France and Germany. According to UJVNL, two dams — Ichhari dam over Tonk river in Dehradun and Manaeri (stage one) dam over Bhagirathi river in Uttarkashi — will be repaired under the project. Besides the dams, Asan barrage in Doon valley, Dakpather barrage in Dehradun and Pashulok barrage in Rishikesh are being covered under the dam rehabilitation and improvement project of World Bank. The project is reportedly covering 250 dams in seven states in the first phase and Rs 2,100 crore has been sanctioned by World Bank for the purpose.
Source: The Economic Times
India’s largest WTE plant to be launched at Narela-Bawana in March
February 18, 2017. Having missed multiple deadlines, the country’s first integrated municipal solid waste-to-energy (WTE) plant at Narela-Bawana is set for a March launch. Spread over 100 acres, the Rs 458 crore plant is the country’s biggest WTE plant and will cater to Civil Lines and the Rohini zone. North Corp conceptualised the green project way back in 2012 and it was originally scheduled for inauguration in 2014. The WTE plant, which has two boilers, is capable of incinerating over 2,000 tonnes of waste per day to generate 24 MW energy, almost double the capacity of the existing two in the capital. India’s largest waste-to-energy plant to be launched at Narela-Bawana in March. Developed by Ramky Group, a waste management company, through an agreement with the North Corp, the operational technology has been sourced from Chinese and American companies. The plant will meet all environmental standards set by the Delhi Pollution Control Committee. The National Green Tribunal and the ministry of environment have given their go-ahead for the plant. The company’s 1,000-strong sanitation workforce will collect garbage from door to door and transport it to the site where it will be segregated. The electricity and the compost will be sold by the operating agency. Land for the project has been provided by the corporation. The project was delayed due to a dispute between the North Corp and Ramky Group over alleged violations of agreement. Work was resumed after NGT stepped in in December 2016.
Source: The Economic Times
Solar power plant at Thalakulathur to be commissioned next month
February 17, 2017. Kerala Transport Minister A K Saseendran said that the solar power plant at Thalakulathur will be commissioned in the second week of March. Saseendran said that the trial run of the solar power plant constructed by the Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) will be commenced on February 22 onwards. Saseendran said project envisaged under Renewable Purchase Obligation project set up on a 3.76 acres of land. Saseendran said that the government is planning to expand the existing project by constructing additional 350 kilowatt solar power plant on the site in case gets required land. Saseendran said the road situated adjacent to the project site will be renovated using Rs 25 lakh from the MLA fund.
Source: The Times of India
India played key role in climate action plan: Railway Minister
February 17, 2017. Railway Minister Suresh Prabhu described climate change as a major global issue and pointed out that India played a key role in initiating climate action plan as part of solutions. Recently, the Indian railways has taken several measures to mitigate its operational carbon footprint such as a massive shift towards solar energy, water conservation and increasing bio-toilet installations. The Science Express will be open for public viewing at Delhi Cantonment Railway Station on February 18-19 and will embark on its journey of over 19,000 km to cover 68 locations across India till September 8, 2017. According to the railway ministry, the special train will run for 205 days, and is expected to attract over 30 lakh visitors.
Source: Business Standard
Snapdeal to set up 1 MW rooftop project at warehouses
February 15, 2017. E-commerce platform Snapdeal is all set to embrace renewable energy with the company setting up solar rooftop projects of total 1 MW at its warehouses across various locations. The project is being implemented by Amplus Energy Solutions, which will set up the rooftop plats for an investment of around Rs 5 crore for Snapdeal’s logistics arm Vulcan Express. Gurgaon-based Snapdeal plans to reduce its carbon dioxide emissions by 34,500 metric tonne or reduced consumption of 2,55,000 barrels of crude oil which will be equivalent to planting 43,000 trees in India with this association. The e-commerce company currently has nearly 3 million sq ft of warehousing with 69 fulfilment centres across 25 cities in India and mega logistics hubs across key locations, including Delhi/NCR, Hyderabad, Lucknow and Kolkata. Industry experts believe the Indian rooftop market is currently growing at over 100 percent annually. The government has set a target to increase energy sourced from grid connected solar rooftop systems to 40 GW by 2022.
Source: The Economic Times
INTERNATIONAL: OIL
US crude prices rise as investors bet big on oil strength
February 21, 2017. The United States (US) crude futures rose for a second day, with data showing hedge funds are betting big across oil markets following the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) production cuts agreed last year. Investors hold more crude futures and options than at any time on record, after members of the OPEC committed last year to cut production. US crude oil and gasoline inventories soared to record highs as refineries cut output and gasoline demand softened, the Energy Information Administration said.
Source: Reuters
Iraq, Iran consider building pipeline to export Kirkuk crude
February 20, 2017. Iraq and Iran signed a memorandum of understanding to study the construction of a pipeline to export crude oil from the northern Iraqi fields of Kirkuk via Iran, the Iraqi oil ministry said. The agreement, signed in Baghdad by the Oil Ministers of the two countries, also calls for a commission to solve a conflict about joint oilfields and the possible transportation of Iraqi crude to Iran’s Abadan refinery, it said. The pipeline would help Iraq diversify the export routes of crude produced in Kirkuk and reduce its reliance on transit through the Kurdish Region Government’s territory. Iraqi Oil Minister Jabar al-Luaibi said that he agreed with visiting Iranian counterpart Bijan Zanganeh to cooperate on the policies of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). The two neighbours are OPEC’s second- and third-largest producers after Saudi Arabia. Iraq produces and exports most of its crude from the southern region.
Source: Reuters
Russia’s Rosneft starts drilling first exploration well in Iraq
February 20, 2017. Russian oil company Rosneft said it had started drilling a first exploration well at Block 12 in Iraq, where it is organising exploration and development of the block. Rosneft said it planned to complete drilling in July 2017.
Source: Rigzone
Iraq’s oil reserves increase to 153 bn barrels: Oil Minister
February 19, 2017. Iraq’s oil reserves have increased to 153 billion barrels, from a previous estimate of 143 billion barrels, Oil Minister Jabar al-Luaibi said. Iraq will ask the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) to adopt the new figure as the official estimate for its reserves, he said. The increased estimate is the result of appraisals and exploration carried out at seven oil fields in central and southern Iraq, he said. Iraq is developing its oil reserves with the help of foreign companies, to make up for three and a half decades of conflict and international sanctions, starting with the 1980-1988 war against Iran. Iraq’s new proven reserves estimate brings it closer to Iran’s 158 billion barrels. It is OPEC’s second-largest producer, after Saudi Arabia.
Source: Reuters
Gasoline glut in New York has traders sending cargoes abroad
February 18, 2017. Traders are lining up to export gasoline and diesel from New York Harbor, an area that normally relies on fuel imports from Europe and eastern Canada, shipping data show. While at least 6 cargoes that were headed to New York from Europe in January and early February were diverted to the Caribbean or the United States (US) Gulf Coast, that wasn’t enough to stem the oversupply building up in terminals along the Eastern Seaboard. Record-high inventories in the region are now pushing prices low enough to turn the typical trade flow on its head. At least two million barrels of clean products like gasoline and diesel are planned to be exported from New York Harbor and Philadelphia in coming days. Total US gasoline stocks also touched a record 259 million barrels, even as American refiners produce less fuel during the height of refinery maintenance season. US crude unit outages are expected to average about 1 million barrels a day this month, and peaked last week at 1.29 million, data show.
Source: Bloomberg
Iran finds 2 bn barrels shale oil reserves in western province
February 18, 2017. Iran has found shale oil reserves of 2 billion barrels of light crude in its western Lorestan province, the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) said. NIOC said exploration was also being carried out for shale gas reserves in the area, and the studies were expected to be completed by October, 2017. Iran’s proven oil reserves of about 160 billion barrels, almost 10 percent of the world’s total, rank it fourth among petroleum-rich countries.
Source: Reuters
Gasoline costs to fall slightly, prices set daily: Mexico
February 17, 2017. Mexico’s finance ministry said that national gasoline prices would fall 2 Mexican cents per liter, but prices would be set daily beginning next week as the country moves toward a free market in gasoline. The ministry said that maximum prices would be published daily, with price holding until the next update. Prices will be set going forward on the web page of the Energy Regulatory Commission. Mexico raised gasoline prices at the start of the year, and the 14 percent hike in regular gas prices sparked protests and looting around the country. The hike helped drive the annual inflation rate in January to its highest level in more than four years. The government is expected to adjust the amount of tax it charges on gasoline in a bid to moderate price fluctuations this year. The government said a rebound in oil prices above estimates used in the 2017 budget and a stronger exchange rate “allow for more gradual movements” in gasoline prices “in a fiscally responsible way.”
Source: Reuters
Marathon Oil beats estimates, doubles 2017 capital budget
February 15, 2017. Marathon Oil Corp, a US shale exploration company, doubled its projected capital spending for the full year, as crude prices stabilize following a two-year rout. The company, which reported a smaller-than-expected wider fourth-quarter loss, expects to spend more as it ramps up activity in Oklahoma and the Bakken Shale formation. Oil producers are betting big on a continued rise in crude prices by buying up acreage and raising capital spending. Marathon said it plans to spend about $2.2 billion this year, or roughly double the $1.1 billion it spent in 2016. Industry peers Exxon Mobil, Chevron Corp and Hess Corp also boosted their capital budgets for the year.
Source: Reuters
Alberta orphan oil well tally jumps as Lexin licenses suspended
February 15, 2017. The Alberta Energy Regulator (AER) suspended licenses on all oil and gas well facilities and pipelines belonging to Lexin Resources Ltd, nearly doubling the number of orphaned wells in Canada’s main crude-producing province. Calgary-based Lexin also owes more than C$1 million to Alberta’s orphan fund and more than C$70 million in security for its obligations to clean up its oil and gas facilities at the end of their producing life. Alberta’s Orphan Well Association (OWA) is responsible for cleaning up wells that have no owners financially able to deal with abandonment and decommissioning costs. It is overseen by the AER and funded by levies from the oil and gas industry. The enforcement action by the regulator means the 1,380 wells belonging to Lexin are now in the care and custody of the OWA, taking the total numbers of ownerless wells in Alberta to 2,970.
Source: Reuters
INTERNATIONAL: GAS
Global LNG demand set to rise to 2030
February 20, 2017. Global demand for liquefied natural gas (LNG), which reached 265 million tonnes (MT) in 2016, is set to grow to 2030, according to Royal Dutch Shell plc. China and India, which are expected to continue driving a rise in demand, were two of the fastest growing buyers, increasing their imports by a combined 11.9 MT of LNG in 2016, Shell said. This boosted China’s LNG imports in 2016 to 27 MT and India’s to 20 MT. Egypt, Jordan and Pakistan were among the fastest growing LNG importers in the world in 2016. Due to local shortages in gas supplies, they imported 13.9 MT of LNG in total, Shell said.
Source: Rigzone
China expects 24 percent increase in 2017 gas production to 170 BCM
February 20, 2017. The National Energy Administration (NEA) of China expects domestic production to soar by nearly 1/4, from 136.8 billion cubic meters (BCM) in 2016 to 170 BCM in 2017, in a context of lower coal consumption and declining crude oil production. In 2017, China plans to add 3.5 BCM of new shale gas production capacity and to start three new gas storage facilities with a total storage capacity of 300 mcm. The NEA expects crude oil production to remain steady at 200 million tonnes (MT) in 2017, while coal production should stabilise at 3.65 Giga tonnes in 2017 despite the committed closure of more than 500 coal mines with a combined coal production capacity of 50 MT.
Source: Enerdata
UAE’s Dana Gas revises 2016 results down to net loss of $88 mn
February 20, 2017. United Arab Emirates (UAE)-based Dana Gas revised down its unaudited preliminary results for 2016 to a net loss of $88 million from the net profit of $33 million which it had previously reported. Dana said the tribunal had also found that Pearl Petroleum Co, in which Dana Gas has a 35 percent stake, was entitled to interest on overdue receivables from the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) at the London interbank offered rate plus 2 percent. Previously, Dana had calculated its own share of overdue receivables under different assumptions.
Source: Reuters
Petronas considers $1 bn stake sale in offshore gas project
February 20, 2017. Malaysian state-owned oil and gas firm Petroliam Nasional Bhd (Petronas) is aiming to sell a large minority stake in a prized upstream local gas project for up to $1 billion as it seeks to raise cash and cut development costs. Petronas is looking to sell a stake of as much as 49 percent in the SK316 offshore gas block in Malaysia’s Sarawak state.
Source: Reuters
Japan’s heavyweight LNG buyers wrestle more flexible deals from suppliers
February 17, 2017. Japan’s liquefied natural gas (LNG) buyers are upending the traditional practices of the market, using their leverage as the world’s biggest buyers of the fuel to wrestle concessions for more flexible terms. Japan’s electric utilities have won provisions that will allow them to divert contracted LNG cargoes if they restart their nuclear reactors, most of which have been shut since the 2011 Fukushima disaster. Japan has traditionally used so-called take-or-pay contracts for LNG purchases that oblige them to pay for a fixed volume of imports, and they are restricted from reselling cargoes if demand drops. Now, LNG buyers are being offered the restart provisions to entice them to sign up for new contracts, said an executive at one of Japan’s gas importers.
Source: Reuters
California natural gas storage upgrades to reduce withdrawals: SoCalGas
February 15, 2017. Southern California Gas Co (SoCalGas) told state regulators the amount of natural gas it will be able to pull from its three smaller storage facilities would decline as it upgrades wells at those fields. SoCalgas is upgrading the wells at all of its storage facilities following a massive leak at Aliso Canyon, its biggest field, between October 2015 and February 2016. The utility plans only to use wells that have been converted so the flow of gas in or out is through an inner tube surrounded by an outer casing. That will limit the amount of fuel that can be injected into or pulled out of the storage facilities. In the past, SoCalGas, like many utilities, injected and pulled gas through both the inner tubing, if there was one, and outer casing. The regulators proposed to reduce the amount of gas in Aliso Canyon to a maximum of 29 billion cubic feet (BCF). Aliso Canyon can hold up to 83 BCF. In 2016, the state required SoCalGas to keep 15 BCF in Aliso Canyon to help prevent gas shortages that could cause power outages but would not allow injections into the facility until regulators determined it was safe.
Source: Reuters
INTERNATIONAL: COAL
China steel mills caught on the hop by North Korea coal ban
February 20, 2017. China’s steel mills and traders were scrambling to find alternative supplies of coking coal for steel making after Beijing slapped a surprise ban on coal imports from its isolated northern neighbour. Chinese prices of steel, coking coal and coke all rallied, as traders and analysts said mills will likely be forced to buy more expensive domestic material or seek alternatives further afield from Russia or Australia, driving up costs. While North Korea accounts for only a small portion of China’s total coal imports, it is the main foreign supplier of high-quality thermal coal, called anthracite, which is used to make coke, a key ingredient in steelmaking. Business with North Korea had become increasingly difficult under years of sanctions and the once-bustling trade handling coal from the north had shrunk to just a few private merchants. China bought 22.48 million tonnes of anthracite from North Korea in 2016, 85 percent of its total imports.
Source: Reuters
INTERNATIONAL: POWER
Minister blames pipeline vandals for drop in power generation
February 19, 2017. Minister for Power, Works and Housing, Babatunde Fashola, has blamed Nigeria’s recent drop in power generation, on pipeline vandals. Fashola made this known during an inspection of a road project in Benin City, Edo State. The minister stressed that acts of vandalism on the gas pipelines at the Ihovbor Power Plant in Edo state was majorly responsible for the current drop in power generation.
Source: Pulse Nigeria
INTERNATIONAL: NON-FOSSIL FUELS/ CLIMATE CHANGE TRENDS
Singapore carbon tax would hit refiners, help renewables
February 21, 2017. Singapore’s proposed plan to tax greenhouse gas emissions would probably hit oil refiners hard, ramping up costs in an industry that has been central to the city-state’s rapid development over the last half-century. The announcement that a carbon tax on direct emitters is to be introduced from 2019 shows that Singapore, Asia’s main oil trading hub, could be moving towards a longer-term future dominated by cleaner technology and resources. Countries around the world have been under increasing pressure to crack down on carbon emissions, with Singapore part of the historic Paris climate accord that went into force late last year. In parts of Europe and countries such as Australia, the introduction of carbon taxes or carbon trading schemes has often driven a decline in established refining industries and a parallel surge in investment in clean energy technology. The government said the carbon tax would probably cover 30 to 40 “large direct emitters” including power stations, petrochemical facilities and semiconductor makers. But it is Singapore’s three refineries, run by ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch Shell and Singapore Refining Company, that would probably need to brace for the hardest blow. The tax proposal comes as those refineries, with a combined fuel generation capacity of around 1.38 million barrels per day (bpd), grapple with rising competition from China, India and the Middle East.
Source: Reuters
Russia, Iran begin building 1.4 GW thermal power plant
February 21, 2017. Russia and Iran have begun the construction of a 1.4 GW thermal power plant in the city of Bandar Abbas in southern Iran. Russian company Technopromexport and an Iranian holding company signed an agreement on the construction of a thermal power plant in Iran with €1.2 billion ($1.27 billion) funding of by Russia. The Russians will improve the efficiency at the Ramin power plant in Khuzestan Province to 50-55 percent from the current 36 percent.
Source: Trade Arabia
Ukraine boosts nuclear power generation amid coal shortage
February 21, 2017. Ukrainian nuclear power plants have increased their energy generation due to the shortage of anthracite coal, which is needed for running thermal power stations. The daily production of electricity at four Ukrainian nuclear power plants has reached a 13-year-high, the state-run nuclear energy operator Energoatom said. Separately, Energy and Coal Minister Igor Nasalyk said that the share of nuclear power in the country’s energy mix has increased from about 50 percent to 62 percent.
Source: Famagusta Gazette
Sri Lanka may stop hydro power generation by end April
February 20, 2017. Sri Lanka will have to stop hydro power generation by the end of April if the prevailing dry weather condition continues, the power minister said. Power Minister Ranjith Siyambalapitiya said that priority has to be given to save water for drinking and not for the electricity generation. Government has already decided to use Castlereigh and Mawussakale reservoirs only to supply drinking water which further increases a looming power crisis. The minister pledged an uninterrupted power supply using more costly methods of electricity generation. The power minister while requesting the public to use electricity sparingly added that it is a victory for Sri Lanka if the country is able to save at least 50 MW of power. Siyambalapitiya proposed to reduce the time period of lighting the street lamps by one hour to save more electricity.
Source: Lanka Business Online
Clean energy fund could underwrite new coal plants: Australia
February 18, 2017. Australia is considering altering legislation to enable funds slated for clean energy developments to be used to bankroll construction of new low emission, coal-fired power plants. The suggestion by Energy Minister Josh Frydenberg comes after a major power outage during a heat wave in South Australia state worsened a row with the national government over energy security and the state’s heavy reliance on wind and solar power. Frydenberg said current laws governing the Clean Energy Finance Corp (CEFC) prevented it from investing in the high-energy, low emission (HELE) coal plants. The government suggestion to tap taxpayer funds to build the HELE plants also comes after industry participants indicated the private sector was not interested in investing in the plants. Australia is one of the largest carbon emitters on a per capita basis due to its reliance on coal-fired power plants. Power generators account for roughly one-third of Australia’s carbon emissions. The national government wants 23.5 percent of Australia’s energy mix to come from renewables by 2020, but nearly all states have set much more ambitious renewable goals to cut carbon dioxide emissions from their electricity sector – clouding the outlook for many generators.
Source: Reuters
California demand for wind power energizes transmission firms
February 15, 2017. A firm controlled by Philip Anschutz, the billionaire entertainment and pro sports magnate, will soon build the largest wind farm in the United States to serve utilities in California, where officials have set ambitious green power goals. The $5 billion project will be constructed 700 miles away in Wyoming, a state better known for coal mines and oil fields. In all, about 5,700 miles of transmission lines are in development with the goal of delivering renewable energy to California from other states, according to the Western Interstate Energy Board. Such investments are an outgrowth of an emerging paradox of California’s well-known political bent toward aggressive environmentalism. Green power advocates and state officials want more wind power – but California conservationists increasingly oppose more wind farms as an environmental blight on the state’s pristine desert landscape. The California Wind Energy Association estimates that only 2 GW of additional wind power can be developed. California will need about 15 GW to meet its goal of deriving half of its power from renewable sources by 2030 – and far more if the state succeeds in a separate effort to promote electric vehicle adoption, according to state estimates.
Source: Reuters
Chile regulator eyes refinery sanction over environmental failures
February 15, 2017. Chile’s environmental regulator, the SMA, said that it was considering sanctions of state-run energy producer ENAP after finding infractions relating to emissions and noise at its Aconcagua oil refinery. The SMA said it had found 17 infractions, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide over the allowed limit, and unacceptable noise levels during both day and night. The company said that it would present an action plan within the timeframe required by the regulator. Planned improvements included a $60 million project to reduce particle emissions, expected by 2022, and the replacement or covering of noisy valves, it said. Chile’s environmental regulators have cracked down harder on resources companies in recent years, following a wave of local activism, and many companies have been increasing their efforts to operate more harmoniously with local communities.
Source: Reuters
DATA INSIGHT
Imports of Crude Oil & Petroleum Products: Value & Volume
| Particulars |
2015-16 |
2016-17 (till January) |
| Volume (in Billion Tonnes) |
| Petroleum Products |
29.46 |
30.15 |
| Crude Oil |
202.85 |
179.27 |
| Total (Petroleum) Imports |
232.31 |
209.41 |
| Value (in US$ Billion) |
| Petroleum Products |
9.95 |
8.41 |
| Crude Oil |
63.97 |
57.23 |
| Total (Petroleum) Imports |
73.92 |
65.64 |
Distribution of Petroleum Imports (Value)
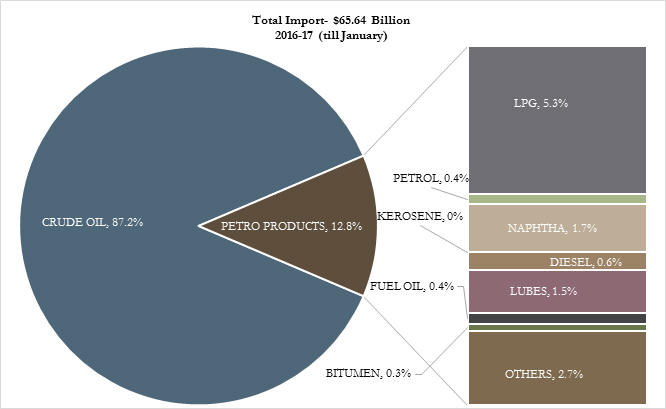
Source: Petroleum Planning and Analysis Cell
Publisher: Baljit Kapoor
Editorial advisor: Lydia Powell
Editor: Akhilesh Sati
Content development: Vinod Kumar Tomar
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.









 PREV
PREV

