NEW TARIFF POLICY TO ADDRESS DISCOM LOSSES
Monthly Power News Commentary: August - September 2019
India
The government is in the process of rolling out a new tariff policy and UDAY 2.0 to address the issue of losses of discoms, which is the key difficulty in ensuring round the clock electricity supply for all. According to the PRAAPTI portal, the total outstanding of the discoms to gencos as of July this year stood at ₹734.25 bn, including the overdue amount of ₹552.76 bn. The dues to discoms become overdue after 60 days of non-payment of the bill, allowing gencos charge penal interest on that. The central government has already made it mandatory for discoms to open letters of credit for getting supply from gencos, excluding state government power plants from 1 August 2019. The new tariff policy has already gone to the Cabinet for vetting and approval while the power ministry is working on the UDAY 2.0 scheme which would be launched this fiscal only. Under the new tariff policy, the discoms would have to pay a surcharge for delayed payment, which would be equal to the commercial rate of interest. Under the new tariff policy, a provision for standards of service which would provide timeline for various services like time period for replacing a burnt transformer etc. The tariff policy provides that the CEA would set standards of service and there would be a penalty for not meeting those standards. UDAY 2.0 provides that the funds from the Centre would only be released if the discom takes steps to reduce losses. The Centre in November 2015 had launched the UDAY to bring about operational and financial turnaround of debt-laden power distribution companies.
The power ministry has put conditions to check possible misuse of the rescue package for stressed coal-fired power stations as well as ensure fair play by both generation and distribution companies on the issue of making payments on time. The government had in March approved a slew of measures, recommended by a high-level committee, to de-stress power plants with aggregate capacity of 40,000 MW. According to the package, coal linkages of power plants that cancel PPAs because of payment default by discoms were to be valid for two years. This was done to allow generation companies adequate time to look for alternative PPAs. Power stations cancelling PPAs for payment default by discoms will not be allowed to sell electricity bilaterally but only through the government’s DEEP portal or power exchanges at market-determined price for maximum two years. It was also decided that even in case of payment default by discoms, generation units will be able to cancel PPAs only in accordance with the provisions of the agreement. To create a market for the stressed power plants, procurement of bulk power by a nodal agency against pre-declared linkages was approved with the provision to allow Central/state generating companies to act as aggregators.
NTPC Ltd commissioned the first 660 MW unit of a 1,980 MW power plant in Nabinagar, Bihar. Nabinagar Power Generating Company is a wholly-owned subsidiary of NTPC. NTPC currently operates 53 power stations in total out of which 22 are coal-based, seven are of combined gas-liquid fuel cycle, two hydro as well as one wind project. Apart from this, there are 11 solar projects also operational under NTPC. It further owns nine coal and one gas station in joint ventures taking the capacity to 55,786 MW. NTPC is aiming to achieve a total installed capacity of 130 GW by the year 2032.
Haryana government announced to waive surcharge on electricity bills of tubewells. Besides, it also announced to give relief ranging from 9 percent to 45 percent to plot holders of HSVP under the Enhancement Recalculation Scheme, as per an official statement. After three settlement schemes for loanee farmers of cooperative banks, the state government has now decided to provide relief to tubewell consumers having electricity connection and plot holders of HSVP. 610,000 farmers in the state have taken electricity connection for the tubewells. Out of this, about 244,000 connections have become defaulters and an amount of ₹1.47 bn is outstanding towards them. If such farmers want to pay their electricity bills, then they have to pay the surcharge and the maximum surcharge amount has reached 20-25 percent. The surcharge amount would be waived if such farmers make lump sum payment of their bills up to 30 November. Connections of farmers, which have been discontinued for less than two years for turning defaulters, would be restored.
Reliance Power said it has signed a partnership agreement with Japan’s energy major, JERA, for jointly setting up 750 MW gas-based power project at Meghnaghat in Bangladesh. Reliance Power will hold 51 percent stake while JERA will hold 49 percent stake in the joint venture company. The project agreements for Phase-1 were signed with the authorities in Bangladesh. Scheduled to be set-up within 36 months of signing the agreements, this project will be the largest foreign direct investment in Bangladesh’s power sector. The agreement includes a power purchase agreement and land lease agreement with Bangladesh Power Development Board, gas supply agreement with Titas Gas, a subsidiary of Petrobangla, and implementation agreement with the power ministry. Reliance Power had signed an MoU in June 2015, for setting up a 3,000 MW gas-based combined cycle power project in phases in Bangladesh.
The power demand in Delhi this summer peaked at night with "cooling load" due to the use of AC, coolers and fans contributing to maximum consumption of electricity. Data from Delhi’s SLDC shows that on 90 days between May and August, the city’s power demand peaked during night. Delhi’s peak power demand has increased by over 250 percent since 2002, when it was 2,879 MW. It clocked an all-time high of 7,409 MW on 2 July this year, according to the data. Air conditioning can account for up to 30-50 percent of annual energy cost of a company or households. During summers, Delhi’s power demand peaked during night on 89 days - 19 in May, 18 in June, 24 in July and 28 days in August, the data shows. In fact, even on 2 July, when Delhi’s demand clocked an all-time high of 7,409 MW, power demand in South and West Delhi first made an all-time high record on 3,159 MW in the afternoon only to again breach it during the night (3,189 MW). The power sector in Delhi has seen a steady decline in regulatory assets to ₹83.77 bn over the last five years, helping the AAP government keep tariffs under check. The transformation of the Delhi’s power sector is best captured by the fact that tariff rates have continuously reduced in the last five years and are now the cheapest in the country, with round the clock power supply in all parts of Delhi. Since 2008-09, the combined RAs of the three discoms in Delhi- BYPL, BRPL and TPDDL shot up drastically from ₹9.37 bn to ₹114.06 bn in 2014-15, Delhi government’s power department said. The RAs have registered a steady decline over the last five years from ₹114.06 bn in 2014-15 to ₹83.77 bn in 2018-19, showing a decline of ₹30.29 bn in that period. The Delhi government has fully subsidised monthly consumption of up to 200 units of electricity and extended 50 percent subsidy to consumers in the range of 201-400 units. The financial health of discoms is majorly affected by the cost of power purchase and the factors that affect it. Several initiatives by the Delhi government and its SLDC have brought this under control.
The UP power department has started installing dual meters for residents of housing societies, a move that could drastically bring down electricity bills. The move follows a long pending demand from residents and an order last year by the UPERC to install dual meters and provide direct connections to each flat. As part of the plan, the newly installed meters will have two sections. The first part of the meter will display the units consumed by a flat owner directly from Pachimanchal Vidyut Vitaran Nigam Ltd, while the second one will calculate the charges for power backup provided by the builder. A consumer can pay the electricity bill to the power department and fee for backup to the builder. In a severe blow to UPPCL, Power System Operation Corp has blocked the company from purchasing any electricity from power exchanges due to alleged lapses. UPPCL has faced the action for deliberately keeping state power generating companies, including independent power producers, out of the ambit of the Union power ministry’s order regarding implementation of a payment security mechanism-based scheduling of power at intra-state level. Faced with this piquant scenario, the cash-strapped UPPCL has asked its discoms to launch a drive to disconnect electric supply of consumers who have more than ₹10,000 dues and have not paid any bill since 1 April. UPPCL authorities are trying to persuade Bajaj Energy to withdraw its complaint and help lift the ban on it buying power from the exchanges by assuring it that a certain amount of payment would be made to them every day. The UPERC has approved a hike of 8 to 12 percent in power tariffs. The Industrial Sector category will have to pay more in the range of 5-10 percent. The electricity tariffs have also been hiked in urban and rural areas.
Odisha government has decided to introduce pre-paid smart electricity meters in the state in order to stop power theft and meter tampering. The consumers will get a pre-paid card to re-charge their electricity meter as they do in mobile phone service after completion of their paid amount. The main purpose of installing such meters is to put a check on meter tampering and power theft. Smart meters will be launched on a pilot basis in Sambalpur and Rourkela and the government will decide on extending this facility to the rest of the state after getting feedback from the two towns. States such as Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, New Delhi and Puducherry have already implemented such meters.
IndiGrid, an infrastructure investment trust is looking to buy power transmission assets worth around ₹80 bn in 10 states. This, the trust plans to buy in the next 2 years which, would include framework agreement assets. IndiGrid is backed by Sterlite Power Grid Ventures and was established in 2016 to own inter-state power transmission assets in India. The IndiGrid InvIT currently manages a portfolio of six electricity transmission assets with a total network of power transmission lines that more than 3,361 circuit kilometres across nine Indian states. With an electricity demand surge expected in the coming decade, India's transmission system requires expansion. From Q1 of FY 18 till date the trust has returned ₹7.85 bn or ₹24.56 per unit to investors. In Q1 of this fiscal, IndiGrid distributed ₹1.75 bn as dividends.
The Centre has decided to launch IT-enabled IPDS in 53 small towns of J&K to improve electricity supply to the people. These towns, including Uri, Gulmarg, Pahalgam, Pampore and Chrar-i-Sharief, have a population of close to 400,000 with about 88,000 electricity consumer families. The J&K Power Development department will be executing the project after having implemented such a system in bigger towns of the state. The initiative will help the authorities calculate the correct transmission losses and ensure development of system for automated daily calculation of reliability indices. The Centre’s IPDS for urban areas involves strengthening of subtransmission and distribution network in urban areas, provisioning of solar panels on government buildings and the metering of feeders, distribution transformers and consumers.
The Northern India Power Engineers Federation has opposed the union government’s initiatives to 'privatise' the power distribution across the country. The federal council of the federation in its meeting held criticised the mandatory LC policy mechanism for discoms issued by the union power ministry to facilitate the payment of private power producers without similar benefit to state generating companies. All India Power Engineers Federation said the mandatory system of LC opening would cause an upheaval in the power sector as they will face cash crunch even to pay the salaries to its employees in some of the states. In case of power supply stoppage by a private generator, discoms will have to pay fixed charges and they would not be able to purchase power in the open market and the consumers will be the worst sufferers. The federation supported the move of Andhra Pradesh for re-negotiating power purchase agreements made at exorbitant rates. The federation observed that since the government has altered its terms of payments why the state governments cannot renegotiate the power purchase agreements for consumer benefits.
The water supply and sanitation department tops the list of power bill defaulters in the district, owing ₹85 mn to the PSPCL. The PSPCL has put up a list of 110 defaulters on its office notice board as a name-and-shame exercise. The total dues amount to ₹105.7 mn. The Mohali unit of vigilance department has not paid ₹1.7 mn in electricity bills for two to three months, while police stations owe ₹1.4 million and primary, middle and high schools of Manauli, Sohana, Kambala, Bhagomajra and Raipur Kalan ₹700,000. The issue of non-recovery of outstanding bills has been flagged in the annual audit report. Slamming the department for non-recovery of outstanding amount, the audit department has said that being a commercial organization, PSPCL cannot afford to allow accumulation of dues from the customers. Necessary steps should be taken to ensure arrears do not become bad debts or time barred, the audit department said.
Rest of the World
Poland secured EU approval to launch a €417 mn ($465 mn) scheme to compensate energy-intensive companies hurt by higher electricity prices. The European Commission said the project, which will run until the end of next year, complies with EU state aid rules, which seek to ensure that EU governments do not grant unfair support to companies. When it announced the plan in June, the Polish government said that around 300 companies would be entitled to receive compensation. The EU has criticized Poland for its heavy use of polluting coal for electricity. However, the Polish government has said the scheme would encourage companies to stay in Poland and not move production elsewhere. Wholesale power prices in Poland soared last year as carbon emission costs and coal prices surged because the country generates most of its electricity from coal. Companies eligible for the compensation scheme must submit appropriate documents to the energy regulator by end of March every year.
South Africa’s state power firm Eskom could sell its coal-fired power stations, possibly through a series of auctions, according to a policy paper published by the finance ministry. Eskom supplies more than 90 percent of the power in Africa’s most advanced economy but is dependent on government bailouts. It is deep in crisis as its electricity sales are on the decline and its debt-service costs have soared. The government of Siouth Africa promised this year to split Eskom into different units for generation, distribution and transmission, as part of steps to make it more efficient. Eskom would sell the power station itself, all its power station-specific obligations, together with a PPA at a predefined power station-specific tariff, the policy paper said.
Royal Dutch Shell has made its first foray into Australia’s highly competitive power sector with a A$617 mn ($419 mn) takeover offer for ERM Power Ltd, the country’s no.2 energy retailer to businesses and industry. The deal would instantly give Shell a power supplier with almost a quarter share of the commercial and industrial retail market in Australia, second only to Origin Energy in that space. Shell, already one of Australia’s biggest gas producers, wants to use its global scale in oil and gas to build a power business, as the world rapidly shifts toward cleaner energy. The power business will also give Shell another product to sell to its long established big fuel customers, like miners.
Nasdaq’s commodities exchange plans to launch its day-ahead auction market for electricity in Germany, France and Nordics around April 2020. Currently Nord Pool is alone in the Nordics in offering day-ahead electricity trading, but will be joined by EPEX SPOT at the end of the year.
Tanzania is targeting to generate 10 GW of power by 2025, which will be sufficient for industrialization. The country has made significant strides towards implementation of various SADC energy policies and targets, including the protocol on energy. The increased investment in electrical energy infrastructure in the Southern African Power Pool region was needed to enable increased electricity access and economic growth. Tanzania was also implementing two major projects of power transmission which were vital in the SADC energy networks, namely the 400 kV Zambia-Tanzania-Kenya interconnector as well as the line linking Iringa to Zambia. 60 percent of the villages had been connected to reliable and affordable electricity through the Rural Energy Agency with a target of connecting all households in the country by 2025.
Finland has signed contracts to construct the initial two sections of a 310 km (192.6 miles) power line that will primarily help transport electricity from its north to its south, Fingrid said. The planned €100 mn ($110.82 mn) line, called Forest Line, will cross through Finland’s vast forested centre, replacing ageing grids and enabling transport of power from wind farms in the country’s north. Finland has a power deficit and imports more than a quarter of the electricity it needs from neighbours Sweden and Russia, so maximising the use of its own resources is key to the country’s energy-hungry industries. The 400 kV transmission link will consists of six sections and a contract was awarded to Finnish infrastructure firm Destia Oy to construct two of them. The work to build the Forest Line will take place between 2019 and 2023, Fingrid said.
China’s July power consumption rose 2.7 percent y-o-y, according to the NDRC. China’s January-July power consumption up 4.6 percent y-o-y to 4.1 tn kWh the NDRC said.
Russia, Iran and Azerbaijan have signed an agreement on a joint feasibility study to connect power systems of the three Caspian littoral states. The feasibility study is expected to encompass the technical and economic aspects of the conditions for connecting the power systems and explore the possibilities for electric power transmission. The idea of linking to each other’s grids has been in the works for years. Iran’s capacity to export electricity to neighbouring countries is almost 2,000 MW with the bulk going to Afghanistan, Pakistan and Iraq. Fixing and upgrading Iraq’s power system requires investments of at least $30 bn. Iraq continues to suffer electricity shortages, 14 years after the US led invasion that toppled Saddam Hussein.
Spanish power generation in August rose 1.7 percent year on year to 21.3 TWh with gas-fired output hitting a 10-year high. Output in mainland Spain from combined cycle gas turbine plants, the main contributor to the country’s power mix, almost trebled to 7.1 TWh, its highest since September 2009. It also came despite a 2.9 percent contraction in total mainland power demand to 21.4 TWh.
| UDAY: Ujwal Discom Assurance Yojana, discoms: distribution companies, gencos: generating companies, CEA: Central Electricity Authority, MW: megawatt, GW: gigawatt, mn: million, bn: billion, tn: trillion, PPAs: power purchase agreements, HSVP: Haryana Shehri Vikas Pradhikaran, MoU: Memorandum of Understanding, SLDC: State Load Dispatch Centre, AAP: Aam Aadmi Party, RAs: regulatory assets, BYPL: BSES Yamuna Power Ltd, BRPL: BSES Rajdhani Power Ltd, TPDDL: Tata Power Delhi Distribution Ltd, UP: Uttar Pradesh, UPERC: UP Electricity Regulatory Commission, UPPCL: UP Power Corp Ltd, IndiGrid: India Grid Trust, InvIT: infrastructure investment trust, Q1: first quarter, IPDS: Integrated Power Development Scheme, J&K: Jammu and Kashmir, LC: letter of credit, PSPCL: Punjab State Power Corp Ltd, EU: European Union, SADC: Southern Africa Development Community, kWh: kilowatt hour, TWh: terawatt hour, kV: kilovolt, km: kilometre, y-o-y: year-on-year, NDRC: National Development and Reform Commission, US: United States |
NATIONAL: OIL
India signs pact expressing interest in taking stake in Far East Russian oilfields
17 September. India signed a non-binding cooperation agreement with Russia that reiterated interest of Indian firms in taking stake in oilfields in Far East region of the former Soviet Republic. Oil Minister Dharmendra Pradhan discussed investment opportunities when he met Russian oil major Rosneft CEO (Chief Executive Officer) Igor Sechin. During the talks, the two sides reviewed existing stake of Indian firms in Russian oilfields such as Sakhalin-1, Taas-Yuryakh and Vankor fields. Both the Eastern Cluster and Vostok project refer to the cluster of oilfields near the Vankor project in Arctic/Far East Russia. Rosneft said the Vostok project will enable development of the unique resource potential of the Arctic Cluster. By 2030, the cluster oil production might come to 100 million tonnes (mt). India already imports a small quantity of oil from Russia, but is looking to raise it through a new sea navigation channel between Vladivostok and Chennai. During the meeting with Sechin, Pradhan renewed pitch for a consortium of Indian companies led by ONGC Videsh Ltd (OVL) taking about 49 percent stake in Russia’s Vankor cluster oilfields. Sechin indicated Rosfnet’s readiness to intensify cooperation, aimed at strengthening of energy security in India and in supplying of high-quality feedstock and crude oil to India.
Source: Business Standard
Government nominates ONGC to operate Panna-Mukta oilfields
16 September. The government has nominated Oil and Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) to operate the Panna-Mukta oilfields after the contract with Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) and Shell runs out in December. RIL and Shell each own a 30 percent participating interest in Panna, Mukta and Tapti (PMT) fields, while ONGC holds the balance 40 percent. Tapti stopped production three years ago while the other two fields have been sharply declining, prompting RIL and Shell to decide on exiting the fields at the end of the 25-year lease in December. The government has, therefore, directed ONGC to operate Panna and Mukta fields after the two private companies exit on 21 December. ONGC is preparing to take over facilities of the two fields and put in place teams that will operate the fields. Once it takes over, ONGC will reassess the fields and figure out their investment needs. The output from these fields will attract royalty and cess as are applicable to production from any nomination field. Panna and Mukta produced 0.84 mn barrels of crude oil and 11.2 bn cubic feet of natural gas in the April-June quarter, as per RIL’s earnings report. Some of Tapti’s facilities have already been handed over to ONGC. The PMT fields, located close to Bombay High fields, were discovered by ONGC but the government, under its privatisation drive, handed over its operation to a consortium of RIL and Enron in 1994. Enron’s stake is now owned by Shell. RIL and Shell are engaged in an arbitration with the government over the state’s share of revenue from the PMT fields. ONGC is not party to the arbitration, but will have to honour the arbitration award. Last year, the oil ministry ordered RIL, Shell and ONGC to together pay $3.8 bn as the increased share of the government’s earnings from the PMT fields, following an arbitration award in government’s favour.
Source: The Economic Times
India’s strategic petroleum reserve levels at 55 percent capacity
16 September. India’s strategic petroleum reserves stand at 55 percent of available underground storage capacity of 5.33 million tonnes (mt). India has three strategic reserves in the southern cities of Vizag, Mangalore and Padur. Saudi Arabia has assured Indian refiners of continued supply, the Indian government said after an attack on Saudi Arabia’s crude oil facilities
Source: Reuters
Petrol, diesel prices to rise if crude price stays high: HPCL Chairman
16 September. Hindustan Petroleum Corp Ltd (HPCL) has said that price of petrol and diesel at retail outlets might go up if the price of crude stays at current levels. Price of product at fuel outlets might be impacted if crude price continues to go up by 10 percent, HPCL Chairman M K Surana said. Indian fuel marketing companies fix the price of petrol and diesel at retail outlets based on an average of last 15 days of benchmark price of petrol and diesel in the Middle East. Surana, however said, that a continued high crude price is not sustainable.
Source: Reuters
Air India’s monthly fuel bill might rise by ₹500 mn after Aramco attack
16 September. Air India’s monthly fuel bill might rise by at least ₹500 mn if the crude oil prices continue to surge in the wake of drone attacks on oil facilities in Saudi Arabia. The national carrier’s fuel bill every month is around ₹5 bn. The bill could go up by at least ₹500 mn if the oil prices jump 10 percent from $60 per barrel level on a sustained basis. Drone attacks targeted Abqaiq, the site of the largest oil processing plant run by the Saudi state oil company, Aramco, and the Khurais oilfield in Saudi Arabia.
Source: Business Standard
India’s diesel demand in August falls to a 10 month low
< style="color: #ffffff">QuIck Comment
< style="color: #ffffff">Fall in diesel demand growth is a sign of a stagnant economy!
< style="color: #ffffff">Bad! |
12 September. A broad decline in automobile sales coupled with excess rainfall and floods in some parts of the country may have finally caught up with diesel demand in India, which fell to its lowest level in 10 months to 6,116 thousand metric tonne (tmt) in August, data published by the oil ministry’s statistical arm Petroleum Planning and Analysis Cell (PPAC) showed. Demand for the fuel in August 2019 declined 1.13 percent to 6,116 tmt. While India’s overall petroleum consumption during the month increased 2.78 percent to 17,044 tmt, the consumption recorded in the month was the lowest in the last eight months, data showed. The fall in automobile sales seems to have not impacted the country’s demand for petrol, which registered a growth for two years in a row. Petrol demand in August rose 9 percent to 2,574 tmt. The demand for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) increased 13 percent to 2,396 tmt in the month, primarily due to an aggressive roll-out by Oil Marketing Companies to achieve the target of rolling out 80 mn LPG connections under Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY). Demand for Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) declined marginally to 681 tmt in August as compared to 686 tmt recorded in the corresponding month last year.
Source: The Economic Times
India’s oil demand to rise at fastest pace in world: OPEC
11 September. India’s oil demand will rise by the fastest pace globally this year and the next even as its economic expansion has slowed down, OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) said. OPEC said India's oil demand is projected to rise by 3.21 percent to 4.88 mn barrels per day (bpd) in 2019 from 4.73 mn bpd in the previous year. In 2020, it will further rise by 3.36 percent to 5.05 mn bpd. This outpaces China’s oil demand growth of 2.73 percent in 2019 and 2.37 percent in 2020. China, however, is the world's second-biggest oil consumer at 13.06 mn bpd in 2019, behind only the US (United States) whose consumption is projected at 20.94 mn bpd. World oil demand in 2019 is expected to grow by 1.02 mn bpd, which is 0.08 mn bpd lower than the previous projection, OPEC said.
Source: Business Standard
NATIONAL: GAS
UAE can play major role in India’s transition to gas-based economy: Pradhan
13 September. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) can play a major role in India’s ambitious transition from a hydrocarbon economy to a gas-based economy as the two countries are "enjoying an excellent relationship, Oil Minister Dharmendra Pradhan said. The current share of gas in India’s energy mix is 6.2 percent, in comparison to the global average of 24 percent. The Indian government aims to increase it to 15 percent by 2030. He said that pre-construction activities would start soon on the project site of $44 bn Ratnagiri Refinery in the western Indian state of Maharashtra, with the participation of the UAE. As a supplier of crude oil and petroleum products to India, the UAE will now have a major role in India’s transition to become the top energy consumer in the world, he said.
Source: The Economic Times
GAIL un-bundling crucial for natural gas trading hub to work: H-Energy CEO
< style="color: #ffffff">QuIck Comment
< style="color: #ffffff">Un-bundling of gas monopolies will facilitate gas trading!
< style="color: #ffffff">Good! |
13 September. The un-bundling of state-owned natural gas utility GAIL (India) Ltd must happen for the country’s plan to set up a gas trading hub to achieve its desired purpose, H-Energy Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Darshan Hiranandani said. Hiranandani said H-Energy plans to spend around ₹40 bn over the next 3-4 years in order to set-up pipeline infrastructure and two liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals on the Eastern coast. According to Hiranandani, the 4 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) LNG terminal in Jaigarh, Maharashtra is ready and only a small stretch of 60 kilometre (km) natural gas pipeline connecting the terminal to Dabhol-Bangalore natural gas pipeline is pending, which is expected to be completed by December 2019. On the Eastern side, H-LNG is setting up two terminals -- a 3 mtpa terminal in Kukrahati in West Bengal and another 3 mtpa terminal in Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh. The company expects both the terminals to be completed by mid-2022. Hiranandani said the company is exploring various avenues of collaboration with Russia gas giant Novatek including setting up a joint gas marketing company, sourcing LNG from Novatek and investment opportunities in LNG terminals in Russia. Hiranandani said LNG retail infrastructure is growing at a very slow pace in the country which is discouraging transporters to adopt the fuel. Hiranandani said the company has received approval from Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organization (PESO) for setting up an LNG retail outlet at Panvel in Maharashtra and the firm is keen on expanding its presence in the space.
Source: The Economic Times
RIL to start gas production from R-Cluster in 2nd half of FY21
12 September. Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) has stated that it will start natural gas production from R-Cluster gas field in the flagging KG-D6 block in the Bay of Bengal from the second half of the 2020-21 fiscal. RIL and its partner BP Plc of UK (United Kingdom) had in June 2017 announced an investment of ₹400 bn in the three sets of discoveries to reverse the flagging production in KG-D6 block. These finds were expected to bring a total 30-35 mn cubic metres (1 bn cubic feet) of gas a day onstream, phased over 2020-22. R-Cluster will be first to come on stream. RIL has so far made 19 gas discoveries in the KG-D6 block. Of these, D-1 and D-3 -- the largest among the lot -- were brought into production from April 2009 and MA - the only oilfield in the block, was put to production in September 2008. The government had in 2012 approved a $1.529 bn plan to produce 10.36 million metric standard cubic meter per day (mmscmd) of gas from four satellite fields of block KG-D6 by 2016-17. The four fields have 617 bn cubic feet of reserves and can produce gas for eight years. However, the companies did not begin the investment citing uncertainty over gas pricing. After the government allowed a higher gas price for yet-to-be-developed gas finds in difficult areas like the deep sea, RIL and BP decided to take up their development. RIL-BP have kept the $3.18 bn investment plan for D-34 or R-Series gas field in the same block, which was approved in August 2013. About 12.9 mmscmd of gas for 13 years can be produced from D-34 discovery, which is estimated to hold recoverable reserves of 1.4 tn cubic feet.
Source: The Economic Times
NATIONAL: COAL
APTEL allows Adani Power arm to charge higher coal cost from Rajasthan discoms
17 September. Adani Power said APTEL (Appellate Tribunal for Electricity) has allowed its subsidiary Adani Power Rajasthan to charge a higher cost of coal regarding a 1,200 MW power supply agreement with distribution companies (discoms) of Rajasthan. The tribunal has allowed the compensation due to the shortage of domestic coal, the company said. APTEL has allowed compensation for domestic coal shortfall arising from change in law pertaining to the New Coal Distribution Policy, 2007 (NCDP), and the Scheme for Harnessing and Allocating Koyala (Coal) Transparently in India policy of the Government of India (SHAKTI Policy).
Source: Business Standard
Government inks allotment pact with WBPDCL for a coal block
16 September. The coal ministry inked an agreement with West Bengal Power Development Corporation Ltd (WBPDCL) for allotment of Deocha Pachami Dewanganj-Harinsingha coal block. The project is expected to address the immediate and future coal and power requirements of the region. In accordance with the provisions of Coal Block Allocation Rules, 2017, made under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulations) Act, 1957, the WBPDCL has been allocated the coal block located in West Bengal containing an area of 12.28 square kilometre with estimated reserves of 2102 million tonnes (mt) for power generation.
Source: Business Standard
Odisha reiterates demand for revision of coal royalty
14 September. With the Odisha government losing huge revenues due to non-revision of royalty on coal, Chief Secretary Asit Tripathy once again urged the Centre to revise the royalty on coal, which is due since April 2015. The meeting was attended by Union Coal Secretary Sumanta Chaudhuri. Responding to state’s demand, the Union coal secretary said increase on coal royalty may lead to hike in the prices of power. While royalty on coal at present is 14 percent, the state government has been demanding to revise to 20 percent. Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik has demanded it in March in a letter to the then Union Coal Minister Piyush Goyal. Royalty on coal was last revised in April 2012. Though the Centre should revise the rate in every three years, the rate remained unchanged for the past six years. In 2018-19, the state government has earned ₹19.48 bn as royalty from coal. Odisha produces about one-fifth of the total coal production in the country. The Centre had constituted a sub-group to study coal royalty revision which has submitted its report in February 2018.
Source: The Economic Times
Government committee recommends privatisation of coal sector
13 September. A high level committee, comprising cabinet secretary, Department of Economic Affairs secretary, revenue secretary, coal secretary and Niti Aayog vice-chairman, has recommended some sweeping policy changes to reform the coal sector. Government said that a high-level panel has recommended reforms to privatise the coal sector. One of the biggest recommendations is to move away from any allocation of captive coal mines. A one-year roadmap has been recommended to shift all concessions to commercial mining. All new auctions or allotments of coal mines has been recommended for commercial purpose only. The committee recommend removal of private sector’s disadvantageous position by doing away with the direct coal allotment to PSUs (Public Sector Undertakings). Other recommendations included privatising Coal India Ltd (CIL)’s washeries to reduce India’s 80 percent import dependency on coking coal for steel, in addition to incentivise the private sector by auctioning coking coal linkages for 20 years. CIL should auction 222 non-operational, loss making mines on production sharing basis, the committee recommended.
Source: The Economic Times
Adani Power’s Tiroda plant gets MERC nod for higher coal price
11 September. Adani Power said power regulator MERC (Maharashtra Electricity Regulatory Commission) has allowed pass through of higher coal prices for its Tiroda plant. The coal mine allocated to Tiroda plant was de-allocated and the company had to make arrangement for fuel supplies at higher cost. Adani Power arm Adani Power Maharashtra Ltd (APML) runs Tiroda plant. As per the referred order from the MERC, the de-allocation of the Lohara coal block by the coal ministry would qualify as Change in Law, and APML is entitled to compensation for alternative coal used to meet the shortfall from the commencement of power supply under the power purchase agreement (PPA).
Source: Business Standard
NATIONAL: POWER
Unsteady NTPC supply may increase power bill for some
17 September. A section of power consumers faces the likelihood of higher utility bills as some of NTPC Ltd’s pithead plants that have among the lowest generating costs are running way below capacity, forcing distribution companies to make up the shortfall through costlier purchases from alternative sources. NTPC said power output at pitheads in Korba and Talcher, among others, was affected by frequent law and order issues, which disrupted mining operations and led to coal shortage. Pithead plants, including the 2,600 MW Korba Super Thermal Power Station, the 2,980 MW Sipat Thermal Power Station, and 3,000 MW Talcher-Kaniha Power Station, are unable to run at full load. Stocks at Talcher-Kaniha Power Station are not enough for even a day and two of its six generating units are shut, while the rest are running at partial load. The plant had capacity utilization of 88.91 percent in April, which has dipped to 45.62 percent in August. Under Security Constrained Economic Dispatch, implemented over a year ago, pithead plants are to generate at near 100 percent capacity and it was estimated that the scheme would lead to savings of ₹10.95 bn a year.
Source: The Economic Times
CIL offers ₹503.2 mn for power line restoration in Odisha
14 September. Coal India Ltd (CIL), which has a large presence in Odisha through one of its subsidiaries, Mahanadi Coalfields Ltd, has provided ₹503.2 mn to Odisha State Disaster Management Authority, for restoration of power lines in Bhubaneswar, Cuttack and Puri. The fund will be used to restore three 220 kilovolt (kV) and two 132 kV damaged power transmission lines and for restructuring of transmission lines damaged by Cyclone Fani at these three locations.
Source: The Economic Times
UPCL to install prepaid power meters in government buildings
13 September. Following the Manipur model, the Uttarakhand Power Corp Ltd (UPCL) has decided to install prepaid power meters in state-owned buildings and establishments in a phased manner from next month. The UPCL has purchased over 7000 prepaid meters to launch the ambitious project which aims to cut down the losses of the distribution company (discom). State government departments owe over ₹2.5 bn to the UPCL.
Source: The Economic Times
Adani Power arm REGL to supply 295 MW to Tamil Nadu, Telangana under power ministry’s scheme
13 September. Adani Power said its arm Raigarh Energy Generation Ltd (REGL) will supply a total of 295 MW to Tamil Nadu and Telangana over the next three years under a pilot scheme. REGL would supply 185 MW to Tamil Nadu and 110 MW to Telangana from its 600 MW power plant in Raigarh, Chhattisgarh, under the power ministry’s Pilot Scheme-II. The scheme is to facilitate the procurement of power for three years from coal-based power plants that are already commissioned and do not have power purchase agreements (PPAs).
Source: Business Standard
UP discom launches drive to recover power dues in Ghaziabad, disconnects over 2k connections
12 September. UP (Uttar Pradesh) discom (distribution company) the Pashimanchal Vidhyut Vitran Nigam Ltd has launched a special drive to recover power bill arrears from consumers. Chief engineer R K Rana said in the five zones of the electricity department, 3,400 consumers who have defaulted in payment of bills for the last two months were identified. The department has disconnected electricity connections of around 2,100 consumers whose unpaid dues was more than ₹10,000. Of the ₹60 mn in arrear, ₹22.5 mn have been recovered, he said. He said a drive will be launched against domestic and commercial consumers who are somehow using electricity more than sanctioned load.
Source: Business Standard
Bihar collects only 30 percent of the cost of electricity supply
< style="color: #ffffff">QuIck Comment
< style="color: #ffffff">Under-recovery of cost of service for electricity is a political economy problem that cannot be fixed by administrative measures!
< style="color: #ffffff">Ugly! |
12 September. Power distribution companies in Bihar collect as revenue only around 30 percent of the cost of supplying electricity, a study conducted by researchers from the London School of Economics & Political Science (LSE), University of Chicago and Yale University has found. The research team — led by Robin Burgess from LSE, Michael Greenstone and Anant Sudarshan from the University of Chicago and Nicholas Ryan from Yale -- working in collaboration with the state government found less than half of all the consumers across income levels paid electricity bills. The study found that the mean revenue rate in Bihar is 30 percent. So, across a state of 100 mn people, the electric utilities can only manage to recover revenues equivalent to one-third of the cost of power, it said. The study found that in Bihar the poor spend three times more on cell phones than they do on electricity -- 1.7 percent versus 0.6 percent of total expenditure.
Source: The Economic Times
NATIONAL: NON-FOSSIL FUELS/ CLIMATE CHANGE TRENDS
Bharathi Cement sets up 10 MW solar unit in Kadapa
16 September. Bharathi Cement has commissioned a 10 MW ground-mounted solar power plant in its manufacturing facility located at Kadapa in Andhra Pradesh. This plant, executed by Hyderabad-based Fourth Partner Energy, in a record 60 days, is expected to generate 16 mn units of electricity annually and help reduce Bharathi’s overall energy costs by reducing its reliance on Thermal power.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
TPREL commissions 150 MW solar capacity in Rajasthan
16 September. Tata Power announced that its 100 percent subsidiary Tata Power Renewable Energy Ltd (TPREL) commissioned 150 MW solar capacity in Village Chhayan, Tehsil Pokharan, State Rajasthan. With this, the overall operating renewable capacity of TPREL now stands at 2,628 MW in India.
Source: Business Standard
Vikram Solar commissions eastern India’s largest rooftop solar project in West Bengal
16 September. Clean energy solution provider Vikram Solar said it has commissioned eastern India’s largest single-shed rooftop solar project for Keventer Agro at Nilganj, West Bengal. The 2.15 MW project was awarded to Vikram Solar by Keventer Agro Ltd, the company said. The shed top solar plant has been built to increase the capacity of Keventer’s food processing plant as well as to leave a green footprint by using non-conventional energy at the Barasat plant, the company said. The project is expected to have 2.835 mn unit energy yield and will offset 2,647 metric tonne CO2 (carbon dioxide) annually.
Source: Business Standard
BJP’s Ladakh MP puts conditions before mega solar power project
15 September. Jamyang Tsering Namgyal, the BJP (Bharatiya Janata Party) MP representing Ladakh Lok Sabha constituency, has welcomed the ₹500 bn mega solar power project in the region, but made it clear that it can go ahead if jobs are reserved for the locals and can work on a land lease model. The need is to tread on a "middle path" between the development and the local interests, such that both the Ladakhis as well as rest of India benefit, he said. He said Ladakh always possessed huge potential to develop solar energy and credited the Narendra Modi government for trying to tap the potential.
Source: Business Standard
Surat’s renewable energy capacity increases by 30 percent in 18 months
11 September. Renewable energy production capacity has seen an increase of 30 percent in Surat in the past 18 months. Of the 250 mn units of electricity that the city produces, share of wind and solar energy is 90 percent. Surat happens to be the only city in the country whose captive power generation meets 33 percent of demand of consumers, with wind and solar power plants playing a significant role in this. Surat Municipal Corp (SMC)’s annual energy demand is 250 gigawatt hour (GWh). At present, SMC produces 78.4 GWh of wind energy. This saves SMC ₹472 mn per annum on electricity bills, it helps reduce emission of 64,000 tonne per annum of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Source: The Economic Times
NLC India exceeds 1 GW installed renewable energy capacity
11 September. Public sector NLC India Ltd, formerly Neyveli Lignite Corp Ltd, said it has surpassed the 1 GW installed renewable energy capacity at its facility. The Tamil Nadu-based 'Navratna' company under the coal ministry had a present mining capacity of 30.6 million tonnes (mt) of lignite per annum. The present power generation capacity, including that of its joint venture with Tamil Nadu Generation and Distribution Corp Ltd, is 5,192 MW.
Source: Business Standard
INTERNATIONAL: OIL
US shale oil output to rise to record 8.8 mn bpd in October: EIA
16 September. US (United States) oil output from seven major shale formations is expected to rise by 74,000 barrels per day (bpd) in October to a record high 8.843 mn bpd, the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) said. The largest change is expected in the Permian Basin of Texas and New Mexico, where output is seen climbing around 71,000 bpd to a record high 4.485 mn bpd in October. Even though the number of rigs drilling new wells in both the Permian and Bakken has declined since the start of the year, output has increased in both basins because the productivity of those rigs - the amount of oil new wells produce per rig - has increased to record levels.
Source: Reuters
CNPC signs 3-year diesel supply contract with Australia’s Arrow Energy
16 September. China National Petroleum Corp (CNPC) will supply diesel to its Australian joint venture, Arrow Energy, for three years, the company said. The supply contract will help CNPC to expand refined oil product sales in Australia, it said. Arrow Energy, a coal seam gas producer, was jointly acquired by CNPC and Royal Dutch Shell in 2010
Source: Reuters
South Korea will consider release of oil reserves if Saudi situation worsens: Energy ministry
16 September. South Korea said that it would consider releasing oil from its strategic oil reserves if circumstances around crude oil imports worsen in the wake of attack on Saudi Arabia’s oil facilities. South Korea’s energy ministry said it anticipated no short-term impact on securing crude oil supplies from Saudi Arabia. But if the situation drags on it might disrupt crude oil supplies, the ministry said. US (United States) President Donald Trump also authorized the use of the US emergency oil stockpile to ensure stable supplies after the attack, which shut 5 percent of world production. South Korea, the world’s fifth-largest crude oil importer, currently has about 96 mn barrels of crude oil and refined products as strategic stockpiles. Of the total 96 mn barrels, the country holds 82 mn barrels of crude oil and the rest is refined products such as gasoline, diesel and naphtha. The stockpiles cover about South Korea’s 90 days of oil requirement.
Source: Reuters
France’s Total tenders to sell 1.3 mn barrels of tainted oil
13 September. France’s Total has issued a tender to sell 1.3 mn barrels of contaminated Russian Urals crude oil for loading from Rotterdam port, traders said. Russia loaded some 11 mn barrels of Urals crude oil with organic chloride content that exceeded allowed levels from Ust-Luga port during an oil contamination crisis. Organic chloride is a chemical compound used to boost oil extraction by cleaning wells and accelerating the flow of crude. It must be removed before oil is sent to costumers because it can destroy refining equipment. Contaminated Urals is very difficult to sell as the only way to make it acceptable for a refinery is to mix it with clean oil in a proportion of one to ten, or even more depending on the organic chloride content in the crude, traders said. Total, as a big buyer of Urals oil, suffered a major impact on its business as it received contaminated Russian crude both via the Druzhba pipeline to its Leuna refinery in Germany and via seaborne cargoes loading from Ust-Luga.
Source: Reuters
Petrol prices in Pakistan at all-time high
13 September. A fact-checking organisation has found truth in Pakistan Peoples Party Chairman Bilawal Bhutto Zardari's statement that petrol prices in the country have reached an all-time high. Opposition leader Bilawal Bhutto had criticised Imran Khan’s government for the high petrol prices. An independent think tank, the Pakistan Institute of Legislative Development and Transparency (PILDAT), has found the statement to be true. It found that the Pakistan government, on 31 July, hiked the prices of petroleum products. After this, the price of petrol (altron premium) touched (Pakistani) ₹117.83 per litre. Data from Pakistan State Oil, the organisation said that from 1 January 2006 to 1 August 2019, petrol prices had never touched ₹117.83.
Source: The Economic Times
Ukraine imports first US LPG cargo
12 September. Ukraine imported its first cargo of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) from the United States (US), according to traders and Refinitiv Eikon data, as Kiev seeks to cut its dependence on energy supplies from Moscow. The tanker Ladybower with about 6,000 tonnes of LPG arrived at the Black Sea port of Odessa, the data showed. Russia has been one of the main LPG suppliers to Ukraine, but Kiev wants to diversify its sources of the fuel due to political tensions with Moscow. According to a Ukrainian industrial body, the share of direct Russian LPG supplies to Ukraine fell last year to 36.8 percent from 48 percent in 2017. Starting from 1 August, Ukraine introduced tariffs on imports of Russian LPG and diesel.
Source: Reuters
Global oil demand to peak in 3 yrs: DNV GL
11 September. Global oil demand will peak in three years, plateau until around 2030 and then decline sharply, energy adviser DNV GL said in one of the most aggressive forecasts yet for peak oil. Most oil companies expect demand to peak between the late 2020s and the 2040s. The International Energy Agency (IEA), which advises Western economies on energy policy, does not expect a peak before 2040, with rising petrochemicals and aviation demand more than offsetting declining oil demand for road transportation.
Source: Reuters
Indigenous protests in Peru halt output at Frontera oil block
11 September. Indigenous communities took control of a small airport and an oil pumping station in Peru to demand the government clean up pollution, halting production at an oil block operated by Frontera Energy Corp’s, Aurelio Chino, the head of local indigenous federation Fediquep, said. Protesters in the Amazonian region of Loreto want government officials to fulfill state commitments to cleaning up oil pollution and building health clinics, Chino said. Villagers seized the Andoas airport in the region of Loreto and an oil pumping station operated by Petroperu, halting operations at both installations as well as at Frontera’s Block 192, Chino said. Frontera, based in Canada, produced about 8,300 barrels of oil per day in August, according to the Peruvian Society of Hydrocarbons.
Source: Reuters
INTERNATIONAL: GAS
Iran signs $440 mn deal with local firm to develop Gulf gas field
14 September. Iran signed a $440 mn contract with local company Petropars to develop the Belal gas field in the Gulf. Under the deal signed with a subsidiary of the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC), Petropars is to produce 500 mn cubic feet per day of gas.
Source: Reuters
Cameron LNG declares force majeure at Louisiana export terminal
13 September. Cameron LNG, a liquefied natural gas (LNG) facility in Louisiana operated be Sempra Energy has declared force majeure due to technical problems at the export terminal but the impact on volumes was not immediately clear, LNG traders said. The export terminal is one of three new facilities to have come onstream this year, boosting US (United States) LNG production and prompting a wave of imports into Europe which has depressed gas prices there. Traders said they were notified by Cameron LNG of the force majeure. Cameron LNG has sent out eight cargoes since May, reaching a level of three cargoes a month in August, Refinitiv shipping data showed. The last cargo left on 7 September. Cameron LNG’s first plant, or train, has a capacity of 5 million tonnes per annum (mtpa), with another two trains of 5 mtpa each due to start up in the first and second quarters of 2020. The US exported 22 mtpa last year, as Train 5 of Sabine Pass and Train 1 of Corpus Christi, operated by Cheniere Energy and the Cove Point terminal of Dominion Energy began operations.
Source: Reuters
German energy regulator orders Opal pipeline to curb gas flows
13 September. Germany has ordered the Gazprom and Wintershall DEA controlled Opal gas pipeline to stop selling a significant amount of capacity to ship gas from the subsea Nord Stream 1 pipeline to onshore European grids, its energy regulator, the Bundesnetzagentur, said. The European Court of Justice overruled a previous European Union decision that allowed the operator of Opal, Opal Gastransport, and Gazprom to sell and ship more supply, after Poland contested the arrangement. Gazprom is building the Nord Stream 2 pipeline parallel to the first as it tries to bypass Ukraine, still its main gas transit route to Europe despite rows about prices, while Belarus and Poland serve as routes on the Yamal pipeline. Gazprom supplies around a third of Europe’s gas needs, but exports via Ukraine were partly suspended on several occasions due to disputes over price. Some European countries including Poland have begun importing liquefied natural gas (LNG) to diversify purchasing away from Russia.
Source: Reuters
Western Gas seeks partner for Equus LNG project off Western Australia
11 September. Privately owned Western Gas said it has appointed Goldman Sachs to advise on finding a partner for its Equus LNG (liquefied natural gas) project off Western Australia, as it aims to start producing from the $3.5 bn project in 2024. Western Gas wants to develop the field using a 2 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) floating LNG facility, rather than feeding into larger existing facilities as contemplated by the field’s previous owner, Hess Corp. The project will be competing against large new developments led by Woodside Petroleum, also off Western Australia, designed to feed the North West Shelf LNG plant and an expansion of Woodside’s Pluto LNG plant. To achieve its target of first production from Equus in 2024, Western Gas will need to make a final investment decision on the project in 2020.
Source: The Economic Times
INTERNATIONAL: COAL
Australia’s New Hope flags coal market volatility
17 September. Australian coal producer New Hope Corp Ltd said coal markets would likely remain volatile in the near term though demand is strong for high-quality thermal coal across Asia, as it posted a 41 percent rise in annual net profit. New Hope in the past year signed a $600 mn debt facility to fund its Bengalla purchase and to develop the Acland mine and Burton project, based on expectations of demand for its higher-quality thermal coal.
Source: Reuters
INTERNATIONAL: POWER
China’s power generation accelerates in August
16 September. China’s power generation climbed 1.7 percent year on year in August, a faster growth than the 0.6 percent rate recorded in July, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) data showed. Power generation hit 668.2 bn kWh (kilowatt hour), data showed. A breakdown showed a milder decline in coal-fired electricity, which edged down 0.1 percent year on year in August.
Source: Xinhua
Siemens, Orascom sign deal to rebuild Iraq power plant
14 September. Siemens and Orascom Construction signed an agreement with the Iraqi government to rebuild two power plants in the north of the country that will have a combined capacity of 1.6 GW. Iraq signed five-year “roadmap” agreements with GE and Siemens AG last October under which the country plans to spend about $14 bn on new plants, repairs, power lines and, eventually, equipment to capture for use natural gas that is now being flared off.
Source: Reuters
Japan’s first electricity futures may spark market shake-up
13 September. The Tokyo Commodities Exchange will start trading Japan’s first electricity futures after delays, a move that may boost competition in Japan’s roughly $130 bn power sector after liberalization. The futures are due to start trading, three and a half years after the government pushed through the biggest shakeup in the country’s electricity sector following the 2011 Fukushima disaster. Liberalization of the electricity market comes more than 10 years after similar moves in Europe and US markets, Tokyo Commodities Exchange said. Sweltering summer temperatures last year drove prices on the Japan Electric Power Exchange to just above 100 yen ($0.93) per kWh (kilowatt hour) in July, the highest on record, as new entrants scrambled to meet the demand for air conditioning.
Source: Reuters
Kenya plans to double power generation by 2022 as economy grows
12 September. Kenya plans to almost double its power generation capacity by 2021-22 as East Africa’s largest economy expands, partly driven by manufacturing. Generation capacity will probably reach 5,221 MW from about 2,700 MW currently, State Department of Planning Principal Secretary Torome Saitoti said.
Source: Bloomberg
Indonesia’s PLN, TNI join forces to safeguard electricity transmission lines following massive blackouts
11 September. Indonesia’s PLN has enlisted the help of the Indonesian Military (TNI) to safeguard its Java-Bali 500 kilovolt (kV) overhead transmission lines, in an effort to ensure that serious incidents, such as the hours-long mass blackout in Greater Jakarta and West Java last month, would not happen again. The cooperation agreement with the military covers the safeguarding of several PLN transmission lines within its designated right-of-way network, including the Java-Bali 500 kV transmission line. A disruption on the line in early August left millions of households in Greater Jakarta, West Java and some parts of Central Java in the dark as the worst blackouts since 1997 paralyzed the cities.
Source: Jakarta Post
INTERNATIONAL: NON-FOSSIL FUELS/ CLIMATE CHANGE TRENDS
Turkey’s daily wind power generation sets record
17 September. Turkey’s wind electricity generation hit a daily record with 19 percent of the total power being generated from wind, according to data from the Electricity Transmission Corp (TEİAŞ). The country produced 132.90 gigawatt hour (GWh) of electricity from wind farms, according to data provided by TEİAŞ. In this particular time period, wind power became the third largest energy source after imported coal, which generated 157.87 GWh of electricity.
Source: Daily Sabah
US President backs plan that would boost biofuel quotas 10 percent in 2020
16 September. US (United States) President Donald Trump has tentatively approved a plan to increase the amount of biofuels that oil refiners are required to blend each year to compensate for exemptions handed out to small refiners by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Under the plan, the US EPA will calculate a three-year rolling average of total biofuels gallons exempted from the mandates under its Small Refinery Exemption program and add that figure to its annual biofuel blending quotas each year. For 2020, that figure would be 1.35 bn gallons. As a result, if the Trump administration followed through on the plan, next year’s total blending mandate would come out to about 22.4 bn gallons, from just over 20 bn in the EPA’s current proposal. The EPA has until the end of November to finalize its 2020 biofuel volumes mandates.
Source: Reuters
Russia’s first sea-borne nuclear power plant arrives to its base
14 September. Russia’s first-floating nuclear power plant has arrived to its permanent base near an isolated Russian town across the Bering Strait from Alaska, Russian state nuclear energy company Rosatom said. Rosatom said it aims to make the floating station operational by the year-end. It would become the world’s northernmost nuclear power station.
Source: Reuters
EU considers energy taxes to counter climate change
13 September. The European Union (EU) is considering new energy taxes, including on the aviation sector, to meet its climate targets, with Germany calling for “drastic steps” to reduce carbon emissions. German Finance Minister Olaf Scholz said drastic steps were needed to counter climate change and urged an international approach on the matter.
Source: Reuters
Japan should stop using nuclear power: New Environment Minister
12 September. Japan’s New Environment Minister Shinjiro Koizumi wants the country to close down nuclear reactors to avoid a repeat of the Fukushima catastrophe in 2011. Three reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi station run by Tokyo Electric Power melted down after being hit by a massive earthquake and tsunami in March 2011, spewing radiation that forced 160,000 people to flee, many never to return. Most of Japan’s nuclear reactors, which before Fukushima supplied about 30 percent of the country’s electricity, are going through a re-licensing process under new safety standards imposed after the disaster highlighted regulatory and operational failings.
Source: Reuters
France’s Neoen to build massive renewable power station in Australia
11 September. France’s Neoen SA announced plans for a massive renewable power station in South Australia including wind, solar and storage facilities. The Goyder South Renewable Power Station will have a battery storage capacity of 900 MW.
Source: Reuters
DATA INSIGHT
Export Prices of Petrol & Diesel to Different Countries
Diesel:
| Country |
Price* (₹/kilolitre) |
| Malaysia |
34942.07 |
| UAE |
32016.38 |
| Singapore |
34075.36 |
| Mauritius |
35688.45 |
| Togo |
35948.61 |
| Mozambique |
32144.37 |
| Bangladesh |
33343.59 |
*During April-June 2019
Export Price of Petrol by IOC to Nepal/Bhutan
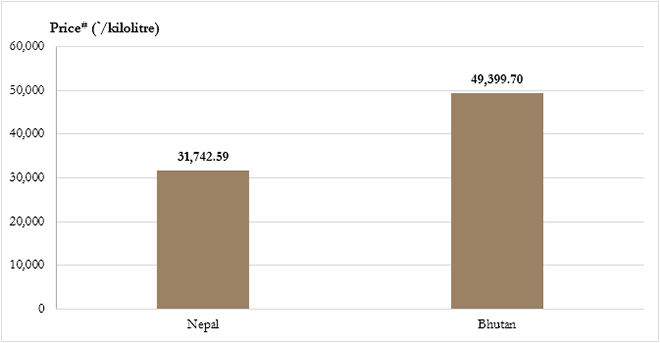 #Prices effective from 1 July 2019
#Prices effective from 1 July 2019
Source: Lok Sabha Questions for Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas
This is a weekly publication of the Observer Research Foundation (ORF). It covers current national and international information on energy categorised systematically to add value. The year 2019 is the sixteenth continuous year of publication of the newsletter. The newsletter is registered with the Registrar of News Paper for India under No. DELENG / 2004 / 13485.
Disclaimer: Information in this newsletter is for educational purposes only and has been compiled, adapted and edited from reliable sources. ORF does not accept any liability for errors therein. News material belongs to respective owners and is provided here for wider dissemination only. Opinions are those of the authors (ORF Energy Team).
Publisher: Baljit Kapoor
Editorial Adviser: Lydia Powell
Editor: Akhilesh Sati
Content Development: Vinod Kumar
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.




 #Prices effective from 1 July 2019
#Prices effective from 1 July 2019 PREV
PREV

